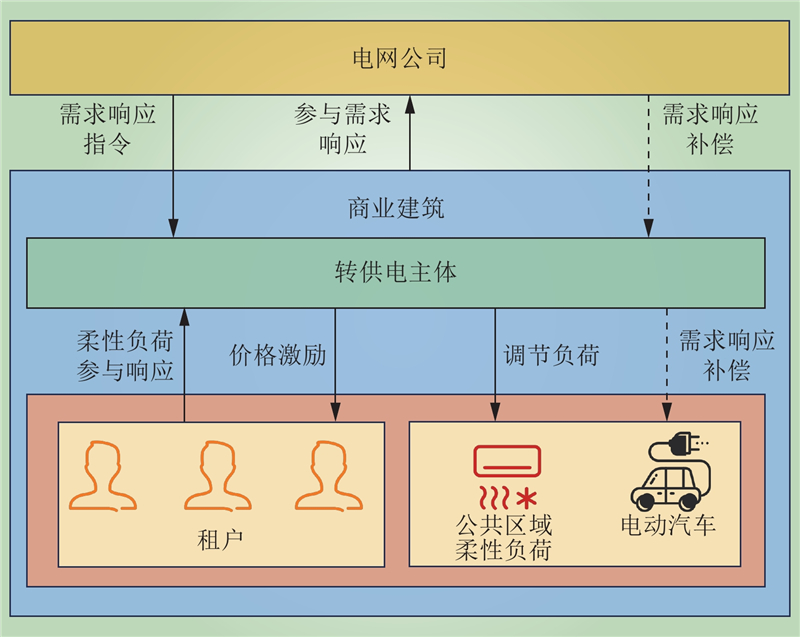
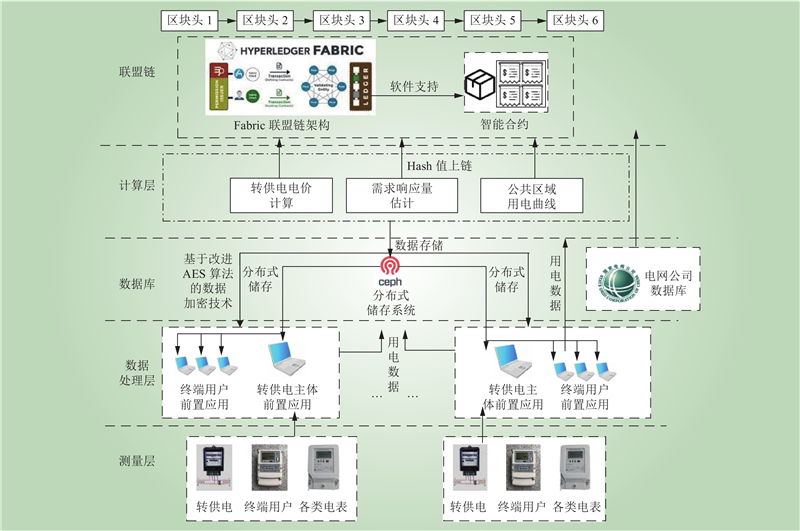
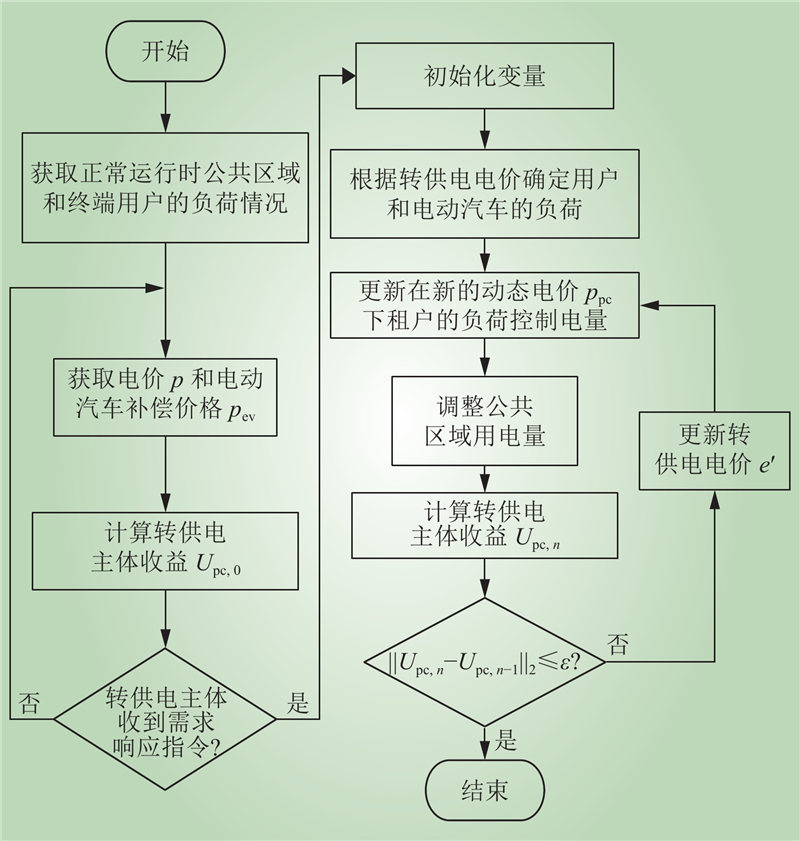
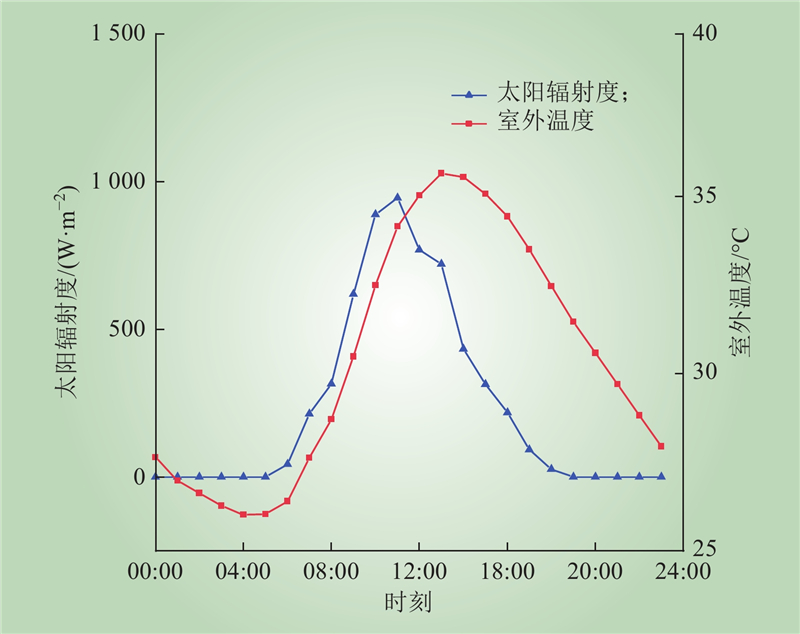
| 1 |
CHEN X Y. Green and low-carbon energy-use[J]. The Innovation Energy, 2024, 1 (1): 100003.
|
| 2 |
国家发展改革委. 国家发展改革委办公厅关于清理规范电网和转供电环节收费有关事项的通知. (发改价格〔2018〕787号)[A]. 2018.
|
| 3 |
袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42 (4): 481- 494.
|
|
YUAN Yong, WANG Feiyue. Blockchain: the state of the art and future trends[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (4): 481- 494.
|
| 4 |
周蠡, 熊川羽, 柯方超, 等. 基于区块链和禀赋效应的主动配电网经济运行方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 58- 68.
|
|
ZHOU Li, XIONG Chuanyu, KE Fangchao, et al. Economic operation method of active distribution network based on blockchain and endowment effect[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 58- 68.
|
| 5 |
POP C, CIOARA T, ANTAL M, et al. Blockchain based decentralized management of demand response programs in smart energy grids[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18 (2): 162.
|
| 6 |
WEN S , XIONG W , TAN J , et al. Blockchain enhanced price incentive demand response for building user energy network in sustainable society[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021(2): 102748.
|
| 7 |
MENGELKAMP E, NOTHEISEN B, BEER C, et al. A blockchain-based smart grid: towards sustainable local energy markets[J]. Computer Science-Research and Development, 2018, 33 (1): 207- 214.
|
| 8 |
KOLAHAN A, MAADI S R, TEYMOURI Z, et al. Blockchain-based solution for energy demand-side management of residential buildings[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 75: 103316.
|
| 9 |
孙毅, 刘昌利, 刘迪, 等. 计及滚动评价的居民群需求响应策略[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (2): 34- 45.
|
|
SUN Yi, LIU Changli, LIU Di, et al. Residents demand response strategy considering rolling evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (2): 34- 45.
|
| 10 |
ZHANG X Y, BIAGIONI D, CAI M M, et al. An edge-cloud integrated solution for buildings demand response using reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (1): 420- 431.
|
| 11 |
JINDAL A, AUJLA G S, KUMAR N, et al. GUARDIAN: blockchain-based secure demand response management in smart grid system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2020, 13 (4): 613- 624.
|
| 12 |
李昭昱, 艾芊. 分时电价下居民用户用电需求响应估计方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (10): 121- 127.
|
|
LI Zhaoyu, AI Qian. Demand response estimation method of electricity consumption for residential customer under time of use price[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (10): 121- 127.
|
| 13 |
胡可心, 李康平, 刘春阳, 等. 动态分时电价下居民用户需求响应基线负荷预测方法[J/OL]. 电测与仪表, 2023: 1–11. (2023-01-17).https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20230116.1821.002.html.
|
|
HU Kexin, LI Kangping, LIU Chunyang, et al. A baseline load forecasting method for residential demand response under dynamic time-of-use electricity price[J/OL]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2023: 1–11. (2023-01-17).https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20230116.1821.002.html.
|
| 14 |
WANG F, ZHOU L D, REN H, et al. Multi-objective optimization model of source-load-storage synergetic dispatch for a building energy management system based on TOU price demand response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2018, 54 (2): 1017- 1028.
|
| 15 |
姜昊, 王玉峰. 基于在线学习的面向居民用户激励型需求响应[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2023, 42 (6): 23- 33.
|
|
JIANG Hao, WANG Yufeng. Incentive demand response for residential users based on online learning[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2023, 42 (6): 23- 33.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG Y R, GLOCK C H, CHEN Z X. Estimating the participation value of electricity demand-response programmes for a two-stage production system[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2022, 60 (21): 6508- 6528.
|
| 17 |
CHEN X, NIE Y T, LI N. Online residential demand response via contextual multi-armed bandits[J]. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2021, 5 (2): 433- 438.
|
| 18 |
KRIŽAN F, KUNC J, BILKOVÁ K, et al. Transformation and sustainable development of shopping centers: case of Czech and Slovak Cities[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 14 (1): 62.
|
| 19 |
颜拥, 陈星莺, 文福拴, 等. 从能源互联网到能源区块链: 基本概念与研究框架[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (2): 1- 14.
|
|
YAN Yong, CHEN Xingying, WEN Fushuan, et al. From energy internet to energy blockchain: basic concept and research framework[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (2): 1- 14.
|
| 20 |
阎红灿, 陈子昂, 刘盈. 面向区块链应用的密码算法研究[J]. 华北理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45 (2): 76- 83.
|
|
YAN Hongcan, CHEN Ziang, LIU Ying. Research on cryptographic algorithms for blockchain applications[J]. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 45 (2): 76- 83.
|
| 21 |
DI SILVESTRE M L, GALLO P, SANSEVERINO E R, et al. Aggregation and remuneration in demand response with a blockchain-based framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56 (4): 4248- 4257.
|
| 22 |
IFTEKHAR A, CUI X, TAO Q, ZHENG C. Hyperledger fabric access control system for internet of things layer in blockchain-based applications[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23 (8): 1054.
|
| 23 |
MENGELKAMP E, NOTHEISEN B, BEER C, et al. A blockchain-based smart grid: towards sustainable local energy markets[J]. Computer Science-Research and Development, 2018, 33 (1-2): 207- 214.
|
| 24 |
CHEN X Y, BU L, CHEN C, et al. An operational optimization method of regional multi-energy system considering thermal quasi-dynamic characteristics[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2021, PP (99): 1- 13.
|
| 25 |
DU P W, LU N. Appliance commitment for household load scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2011, 2 (2): 411- 419.
|