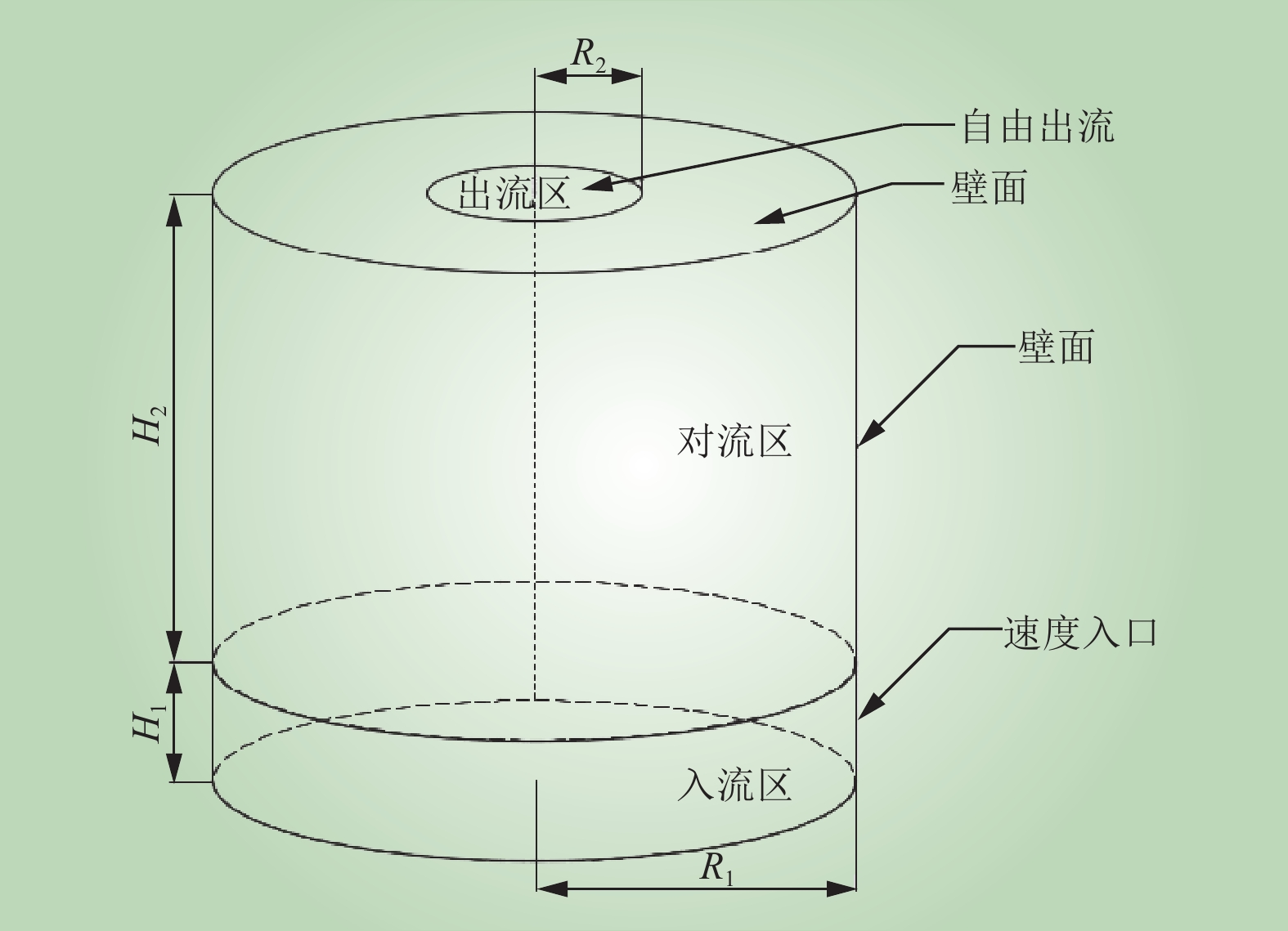
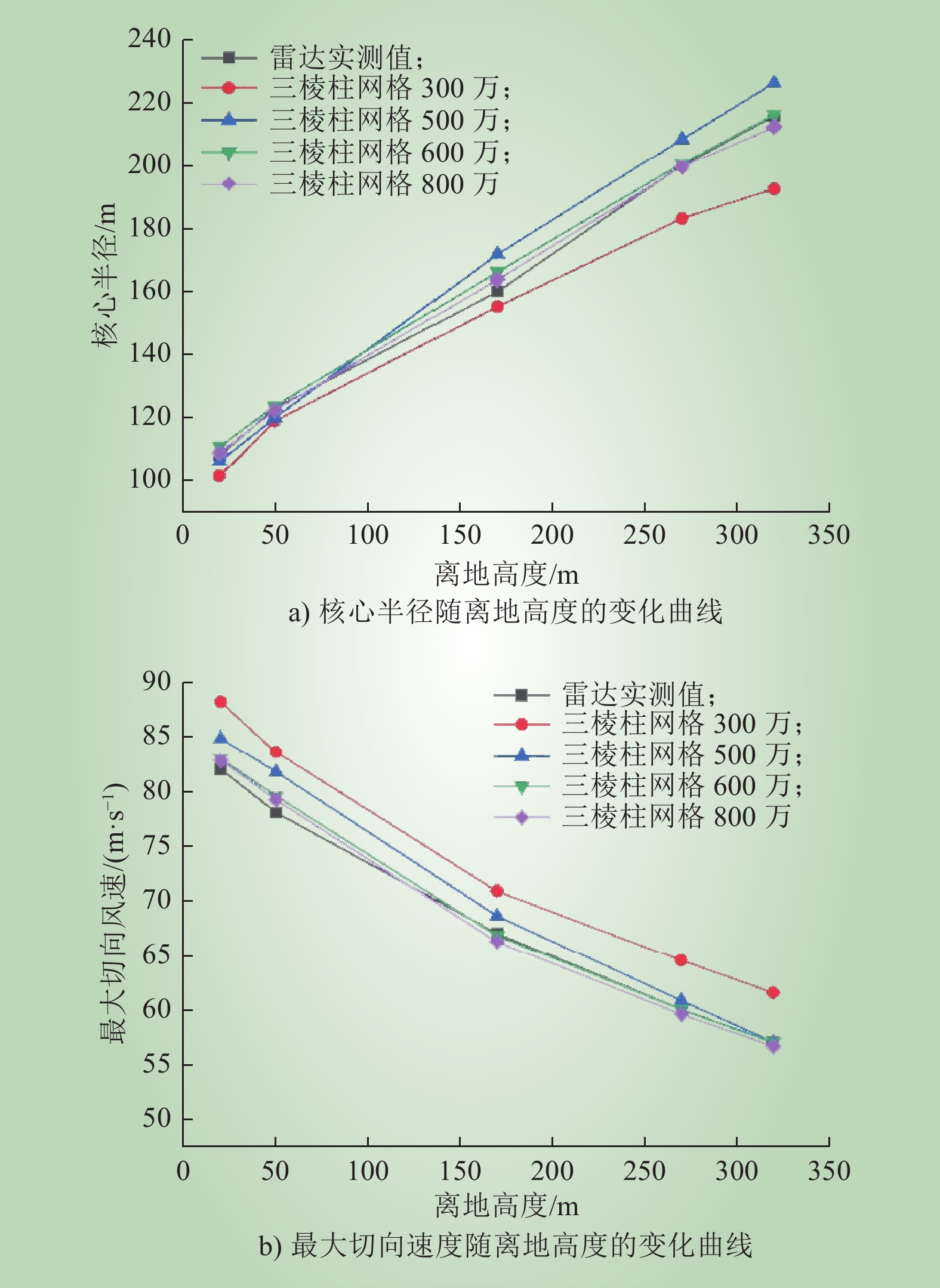
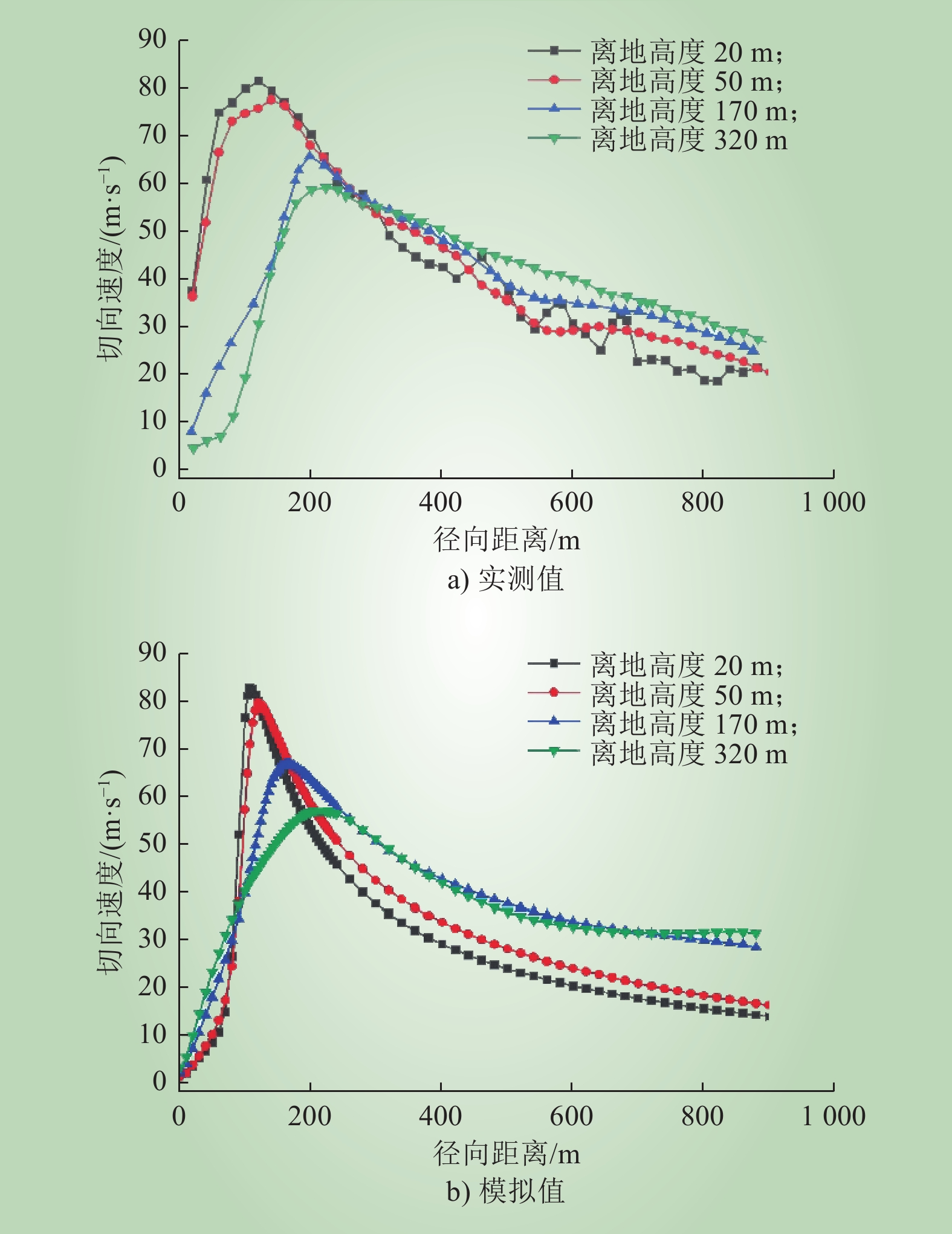
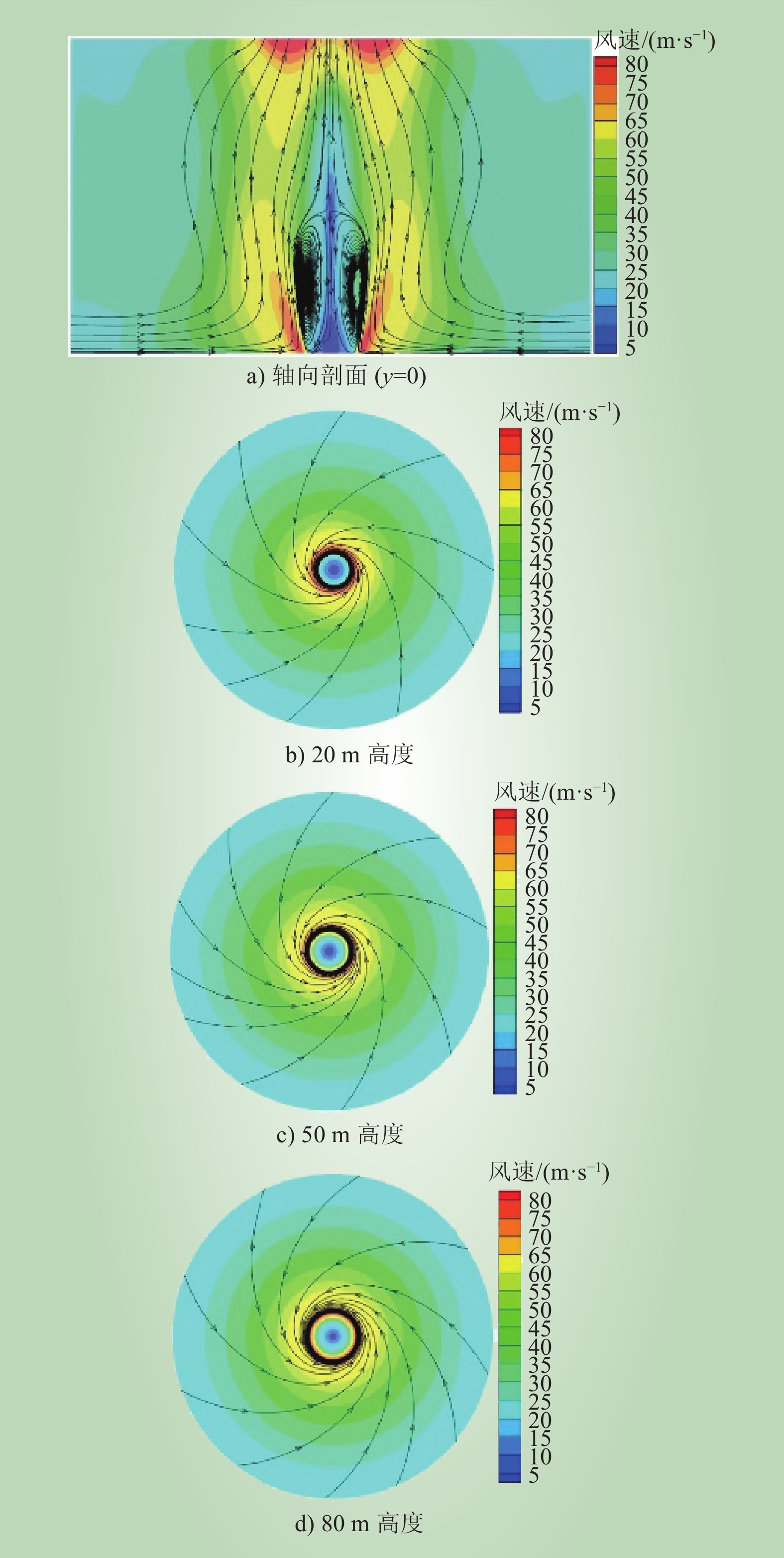
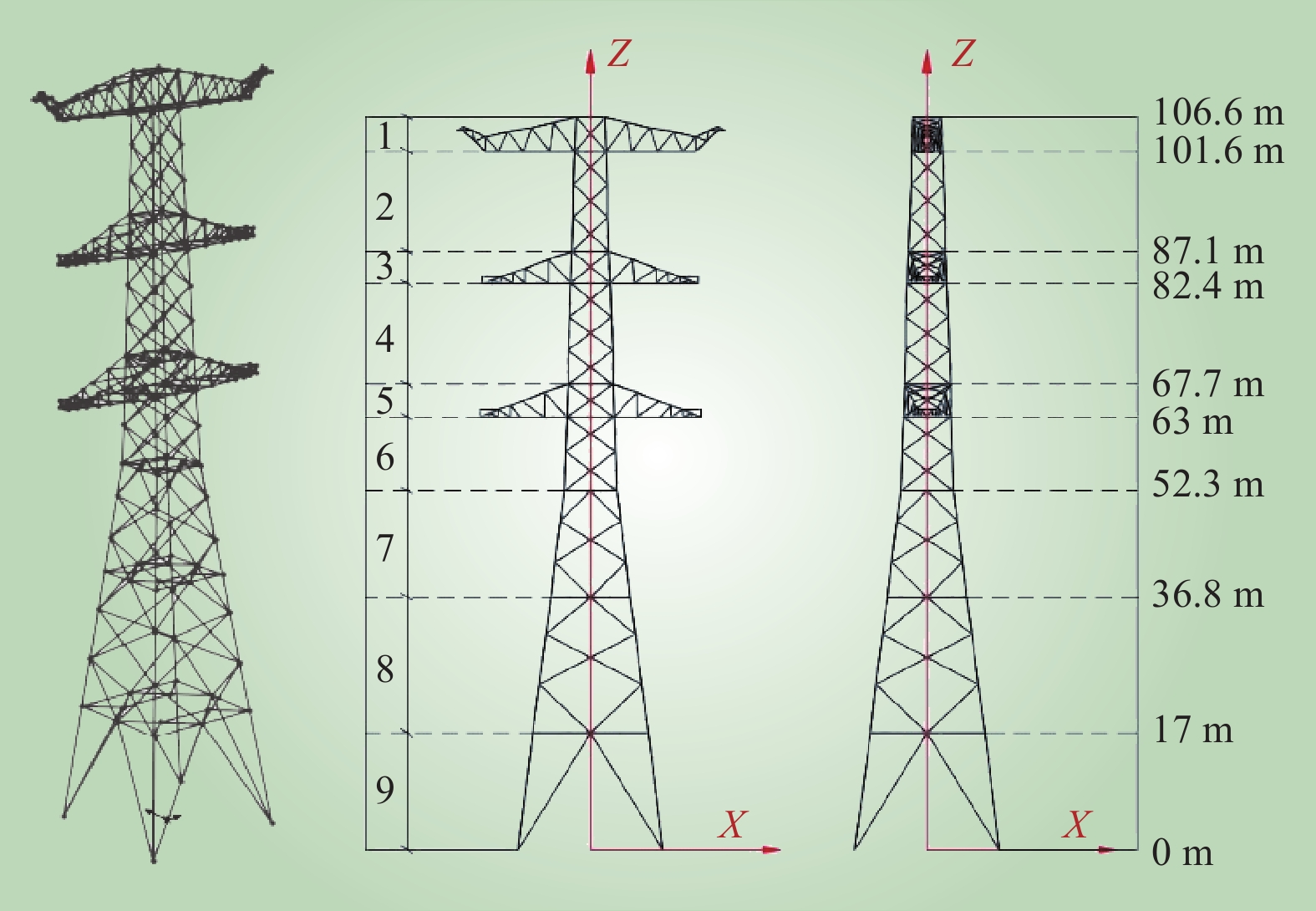
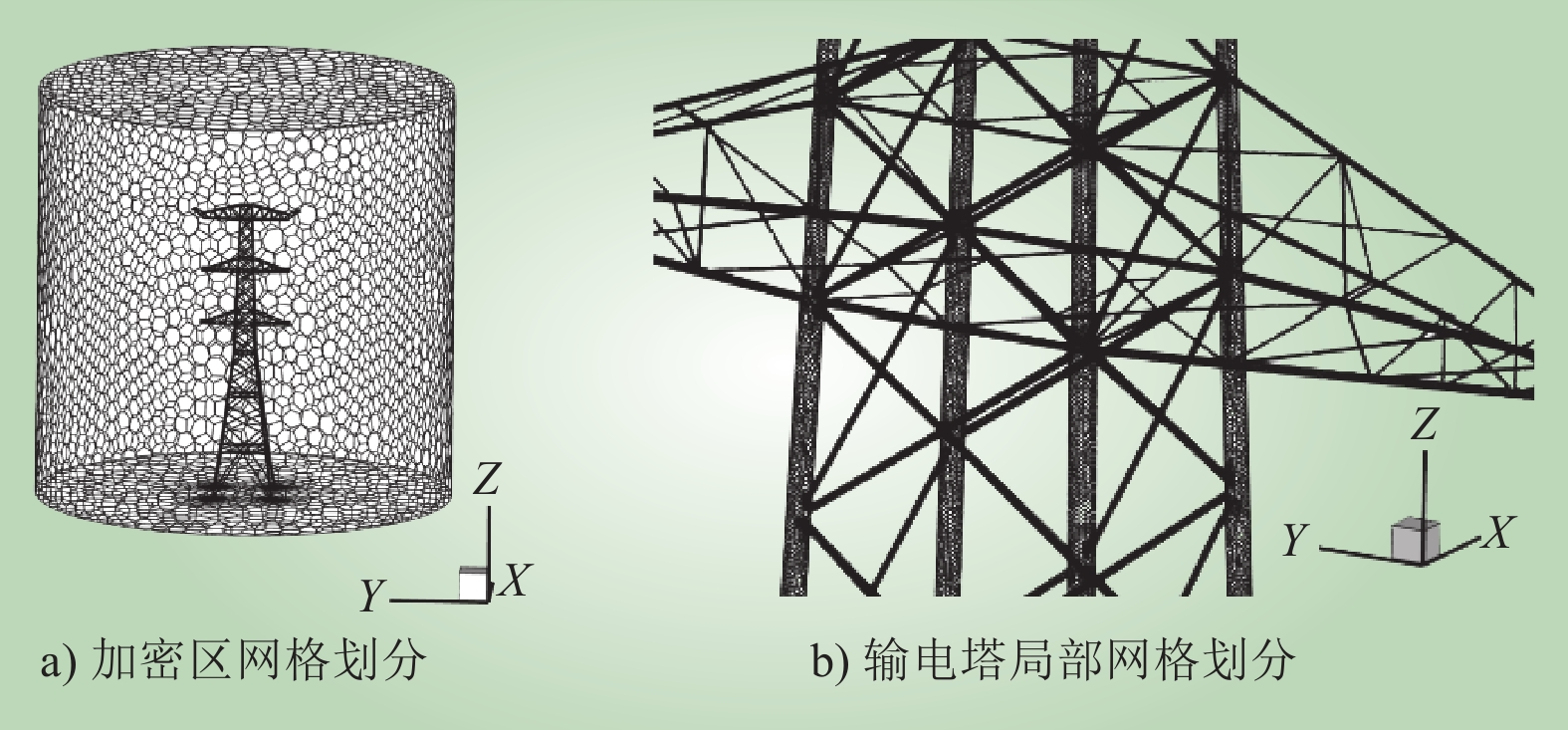
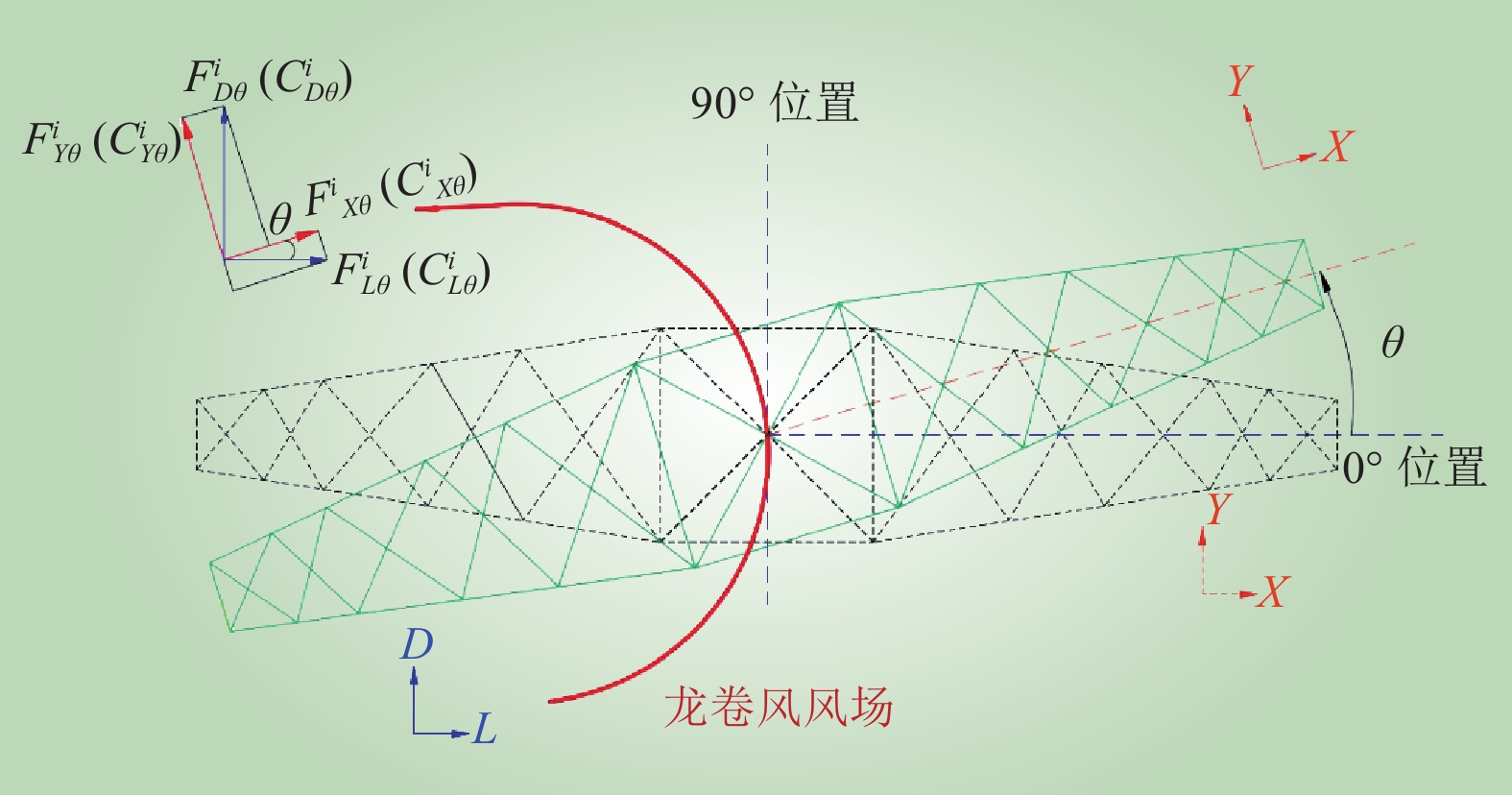
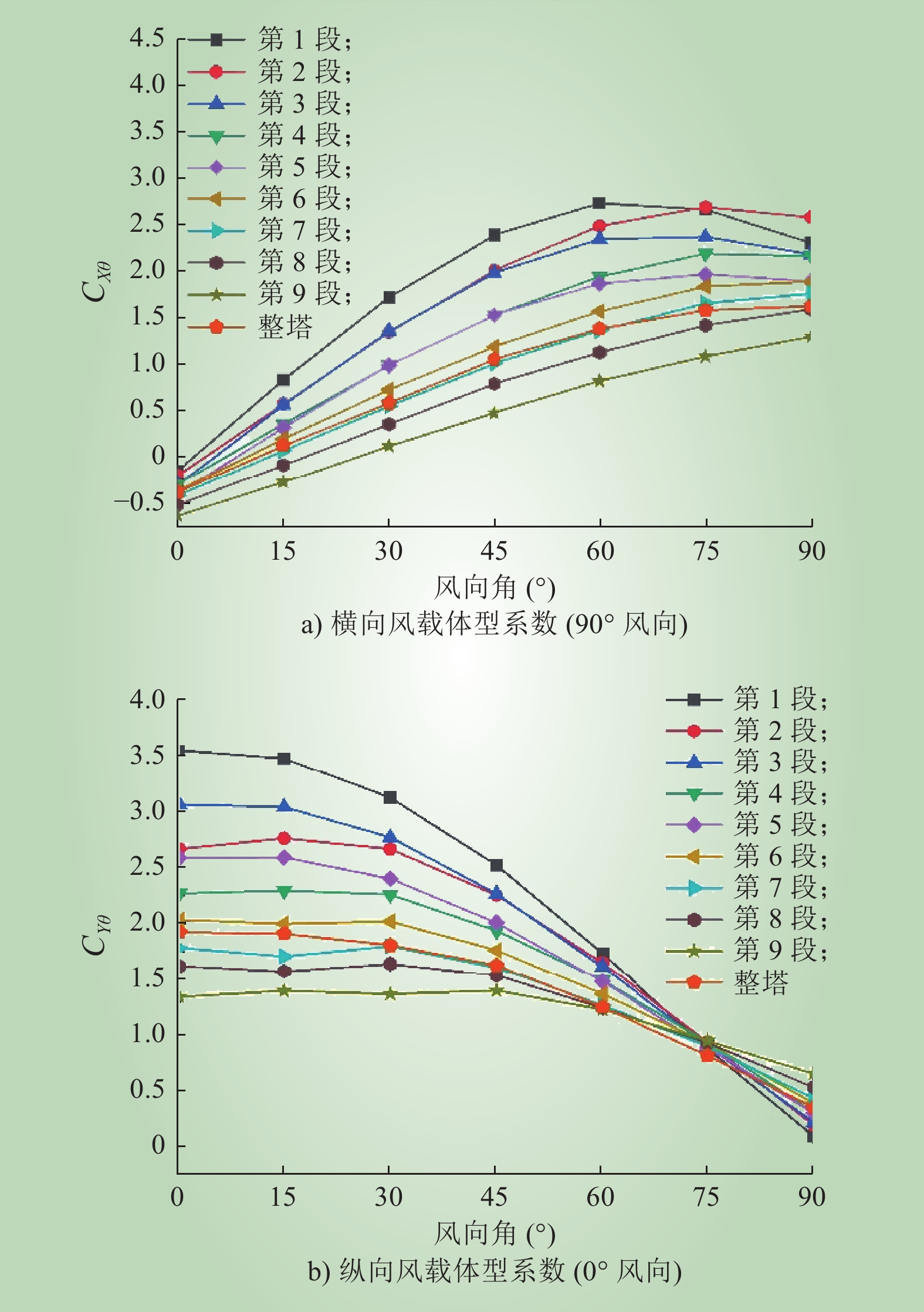
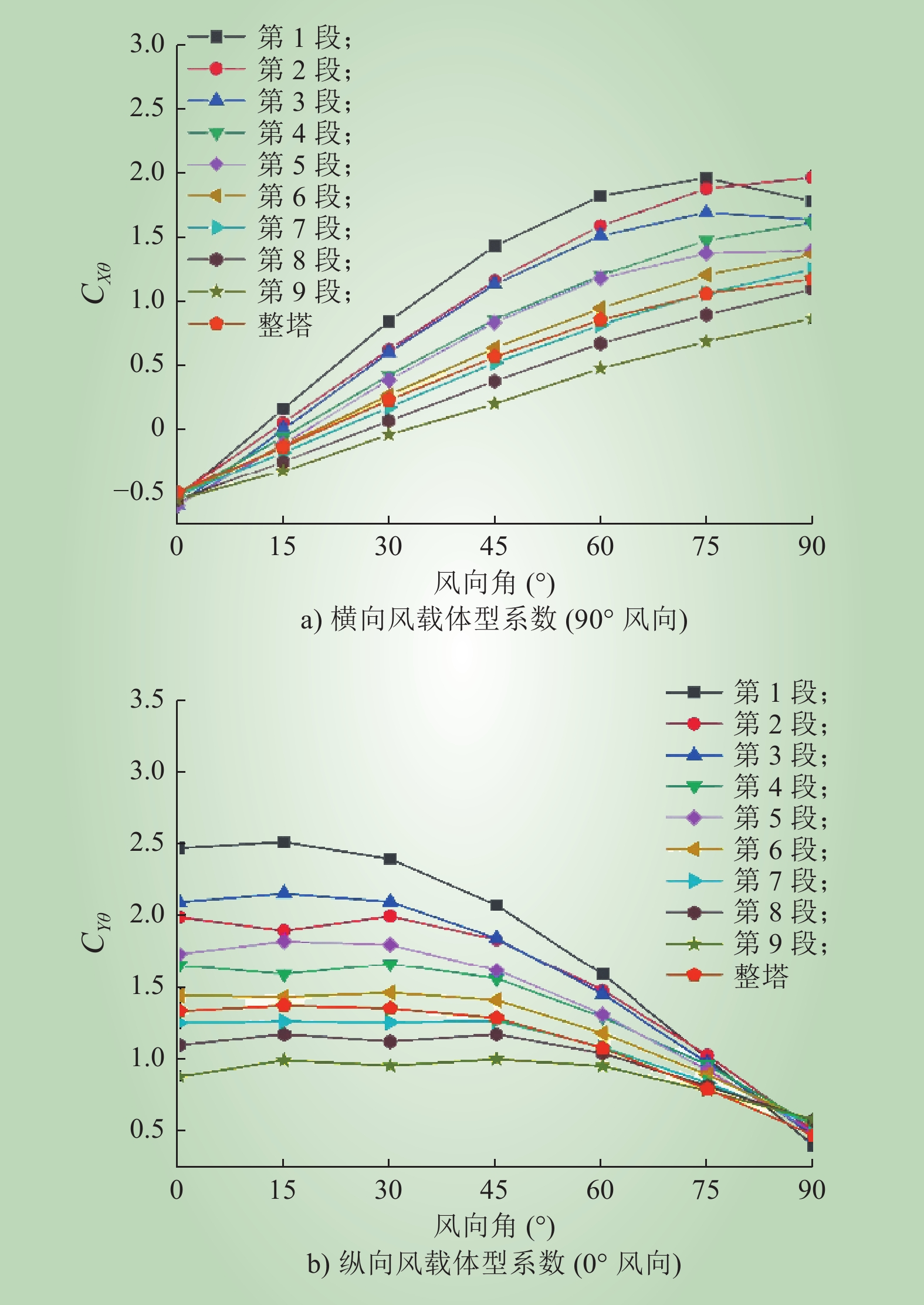
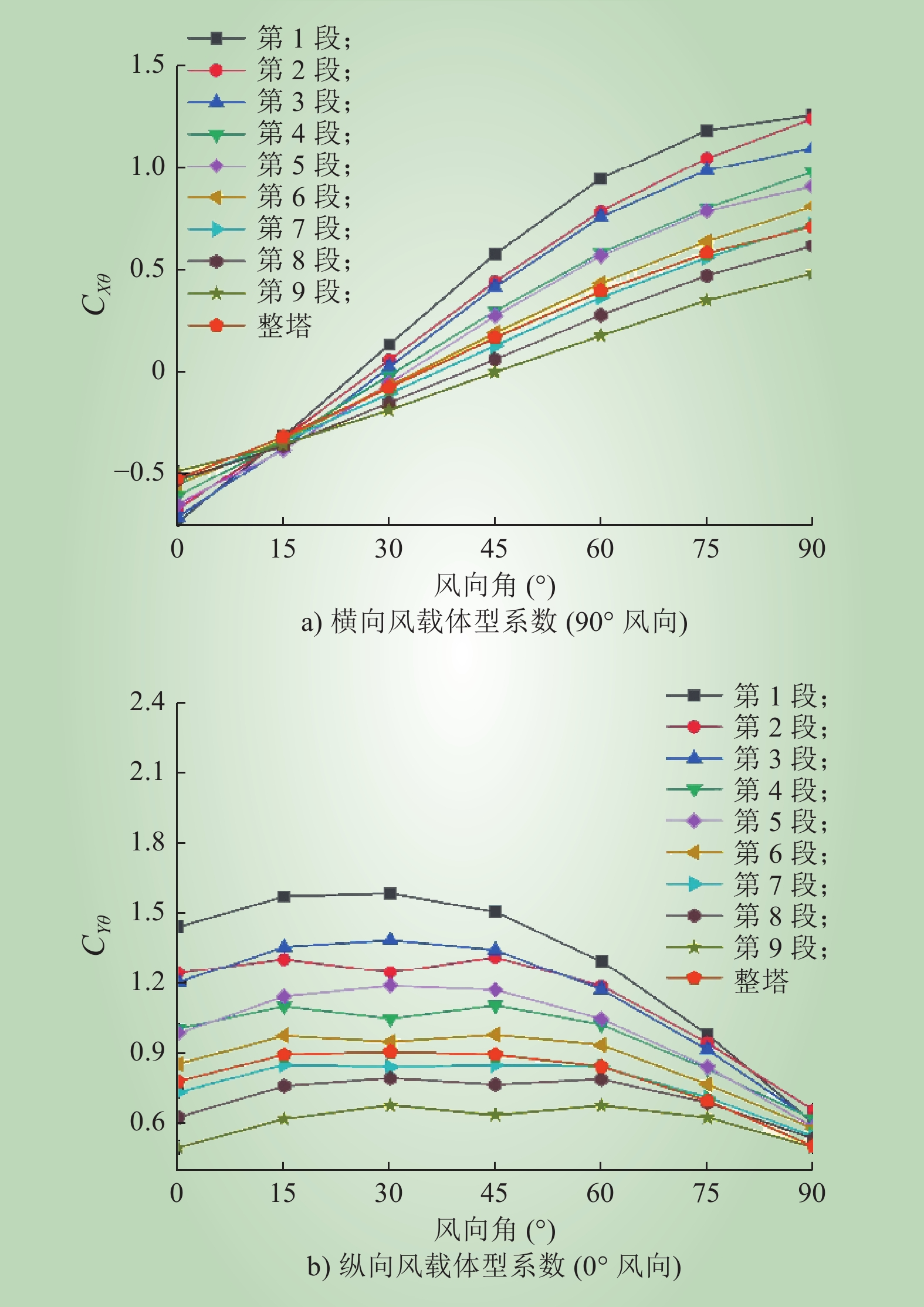
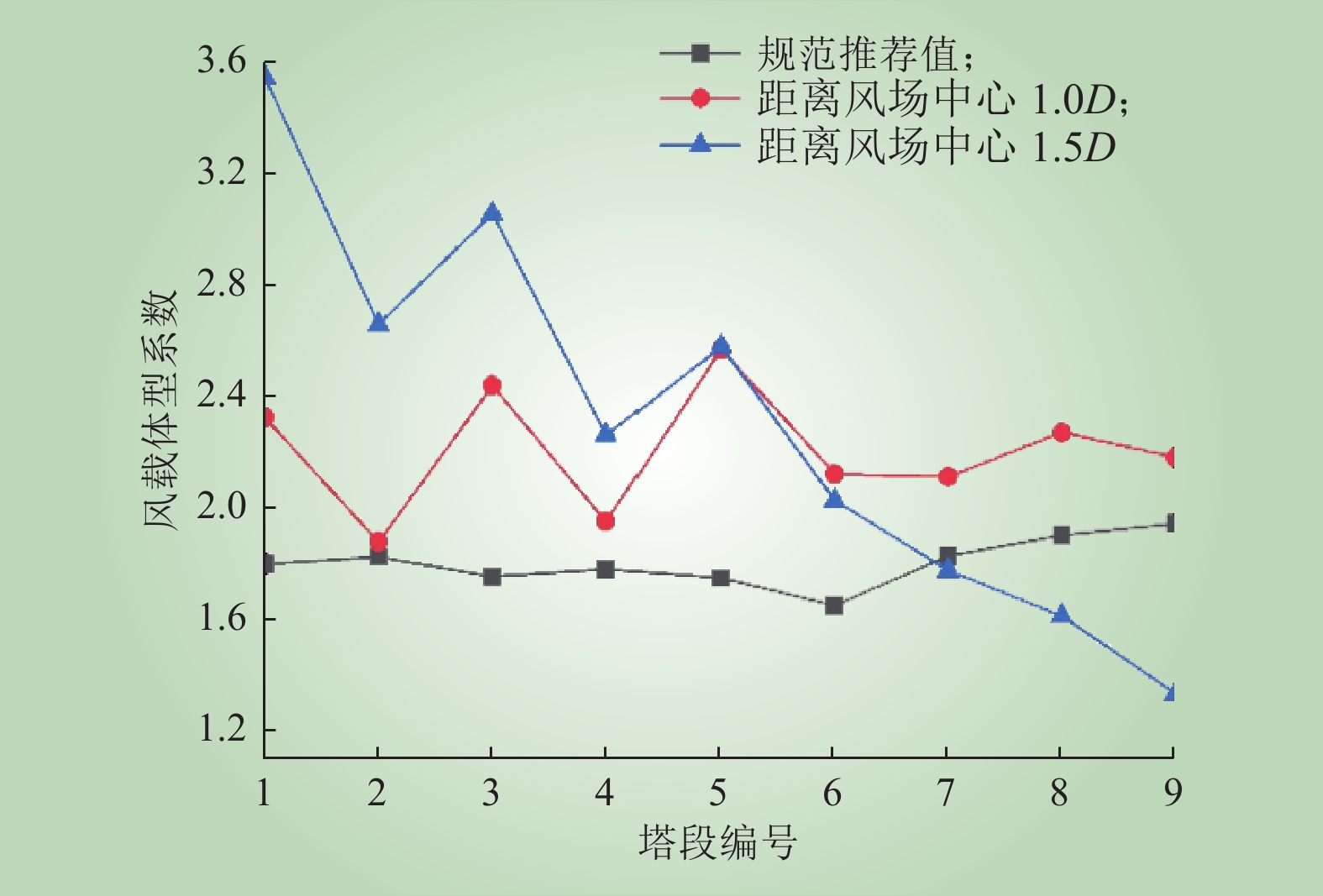
| 1 |
李政麒, 蔡晔, 曹一家, 等. 美国得州“2·15”停电事故分析及对中国新型电力系统供电充裕度的启示[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (5): 17- 24.
|
|
LI Zhengqi, CAI Ye, CAO Yijia, et al. Analysis of "2·15" blackout in Texas and its enlightenment to China's new power system supply adequacy[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (5): 17- 24.
|
| 2 |
方健, 王红斌, 刘育权, 等. 配电网灾后动态抢修滚动优化决策方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2021, 15 (5): 122- 128.
|
|
FANG Jian, WANG Hongbin, LIU Yuquan, et al. Rolling optimization decision strategy of dynamic repairing in power distribution network after disasters[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2021, 15 (5): 122- 128.
|
| 3 |
何嘉兴, 张行, 王红斌, 等. 极端灾害下考虑应急转供的配网停电过程仿真方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48 (4): 104- 111.
|
|
HE Jiaxing, ZHANG Hang, WANG Hongbin, et al. Simulation method of distribution network outages porcess considering emergency transfer under exetreme disaster[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48 (4): 104- 111.
|
| 4 |
胡源, 薛松, 张寒, 等. 近30年全球大停电事故发生的深层次原因分析及启示[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (10): 204- 210.
|
|
HU Yuan, XUE Song, ZHANG Han, et al. Cause analysis and enlightenment of global blackouts in the past 30 years[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (10): 204- 210.
|
| 5 |
HAMADA A, EL DAMATTY A A, HANGAN H, et al. Finite element modelling of transmission line structures under tornado wind loading[J]. Wind and Structures an International Journal, 2010, 13 (5): 451- 469.
|
| 6 |
李改琴, 许庆娥, 吴丽敏, 等. 一次龙卷风天气的特征分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40 (5): 628- 636.
|
|
LI Gaiqin, XU Qing'e, WU Limin, et al. Characteristics analysis of tornado weather[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2014, 40 (5): 628- 636.
|
| 7 |
黄大鹏, 赵珊珊, 高歌, 等. 近30 a中国龙卷风灾害特征研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2016, 35 (2): 97- 101.
|
|
HUANG Dapeng, ZHAO Shanshan, GAO Ge, et al. Disaster characteristics of tornadoes over China during the past 30 years[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2016, 35 (2): 97- 101.
|
| 8 |
单葆国, 刘青, 张莉莉, 等. 新形势下“十四五”后三年中国电力需求形势研判[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 1- 11.
|
|
SHAN Baoguo, LIU Qing, ZHANG Lili, et al. Analysis of China's power demand situation in the last three years of the "14 th five-year plan" under the new situation[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 1- 11.
|
| 9 |
姚远, 赵文彬, 卢武, 等. 多风速段下低风阻导线抗风能力实验分析及导线截面结构参数优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (21): 97- 106.
|
|
YAO Yuan, ZHAO Wenbin, LU Wu, et al. Wind resistance test and optimal design of cross-sectional structure of a drag-reduced conductor at multiple wind speed levels[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (21): 97- 106.
|
| 10 |
白俊峰, 鞠彦忠, 曾聪. 龙卷风作用下空间桁架的受力分析[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2011, 31 (S1): 46- 51.
|
|
BAI Junfeng, JU Yanzhong, ZENG Cong. Force analysis of space truss subjected to tornado loads[J]. Journal of Northeast Dianli University, 2011, 31 (S1): 46- 51.
|
| 11 |
赖嘉贤. 龙卷风作用下输电铁塔稳定性分析[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2018.
|
|
LAI Jiaxian. Stability analysis of transmission tower under tornado[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2018.
|
| 12 |
庞小龙. 龙卷风作用下高压输电塔-线体系倒塌破坏机理研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2020.
|
|
PANG Xiaolong. Study on collapse failure mechanism of high voltage transmission tower-line system under tornado[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2020.
|
| 13 |
国家能源局. 架空输电线路荷载规范: DL/T 5551—2018[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2018.
|
|
National Energy Bureau of the People's Republic of China. Load code for the design of overhead transmission line: DL/T 5551—2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2018.
|
| 14 |
SAVORY E, PARKE G A R, ZEINODDINI M, et al. Modelling of tornado and microburst-induced wind loading and failure of a lattice transmission tower[J]. Engineering Structures, 2001, 23 (4): 365- 375.
|
| 15 |
ASCE 74-2009. Guidelines for electrical transmission line structural loading[S]. America: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2009.
|
| 16 |
HAMADA A, EI DAMATTY A A. Behaviour of guyed transmission line structures under tornado wind loading[J]. Computers & Structures, 2011, 89 (11/12): 986- 1003.
|
| 17 |
EI DAMATTY A A, HAMADA A. F2 tornado velocity profiles critical for transmission line structures[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 106, 436- 449.
|
| 18 |
HAMADA A, EI DAMATTY A A. Behaviour of transmission line conductors under tornado wind[J]. Wind and Structures, 2016, 22 (3): 369- 391.
|
| 19 |
ALTALMAS A, EI DAMATTY A A. Finite element modelling of self-supported transmission lines under tornado loading[J]. Wind and Structures, 2014, 18 (5): 473- 495.
|
| 20 |
王勇, 吕令毅. 龙卷风作用下输电塔结构的单向流固耦合分析[J]. 特种结构, 2017, 34 (2): 13- 19.
|
|
WANG Yong, LV Lingyi. One-way fluid-structure interaction analysis of transmission tower under tornado loading[J]. Special Structures, 2017, 34 (2): 13- 19.
|
| 21 |
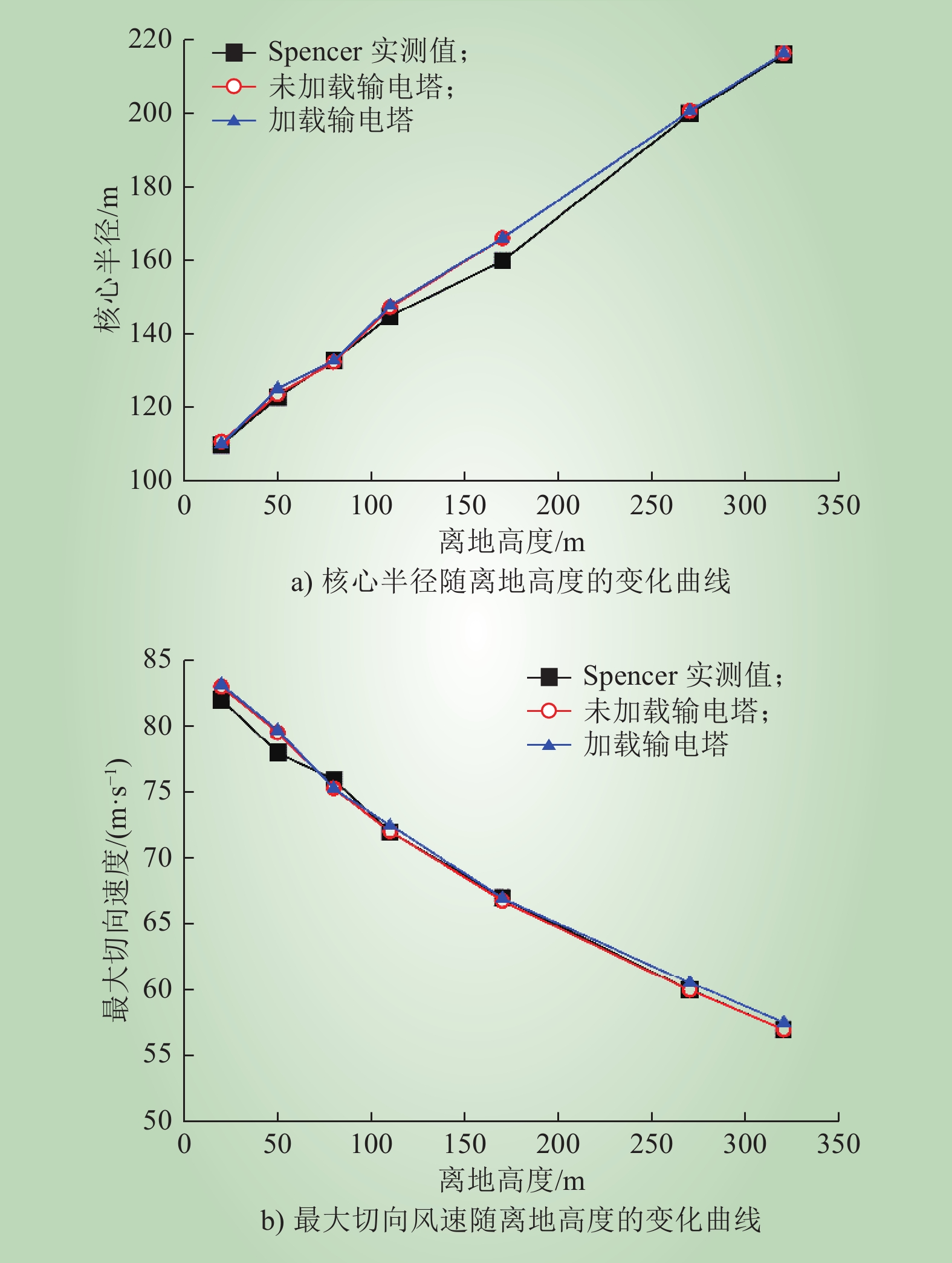
ALEXANDER C R, WURMAN J. The 30 may 1998 spencer, South Dokota, storm. part Ⅰ: the structural evolution and environment of the tornadoes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2005, 133 (1): 72- 97.
|
| 22 |
WURMAN J, ALEXANDER C R. The 30 may 1998 spencer, South Dokota, storm. part Ⅱ: comparison of observed damage and radar-derived winds in the tornadoes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2005, 133 (1): 97- 119.
|
| 23 |
MOCHIDA A, TABATA Y, IWATA T, et al. Examining tree canopy models for CFD prediction of wind environment at pedestrian level[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96 (10/11): 1667- 1677.
|
| 24 |
张洪华. OpenFOAM中稳态大气边界层风洞的开发研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.
|
|
ZHANG Honghua. Development and research of steady-state atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel in OpenFOAM[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
|
| 25 |
马杰. 移动龙卷风对低矮建筑物风荷载特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
|
|
MA Jie. Study on wind load characteristics of moving tornado on low buildings[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
|
| 26 |
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑工程风洞试验方法标准: JGJ/T 338—2014[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015.
|
|
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for wind tunnel test of buildings and structures: JGJ/T 338—2014[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015.
|
| 27 |
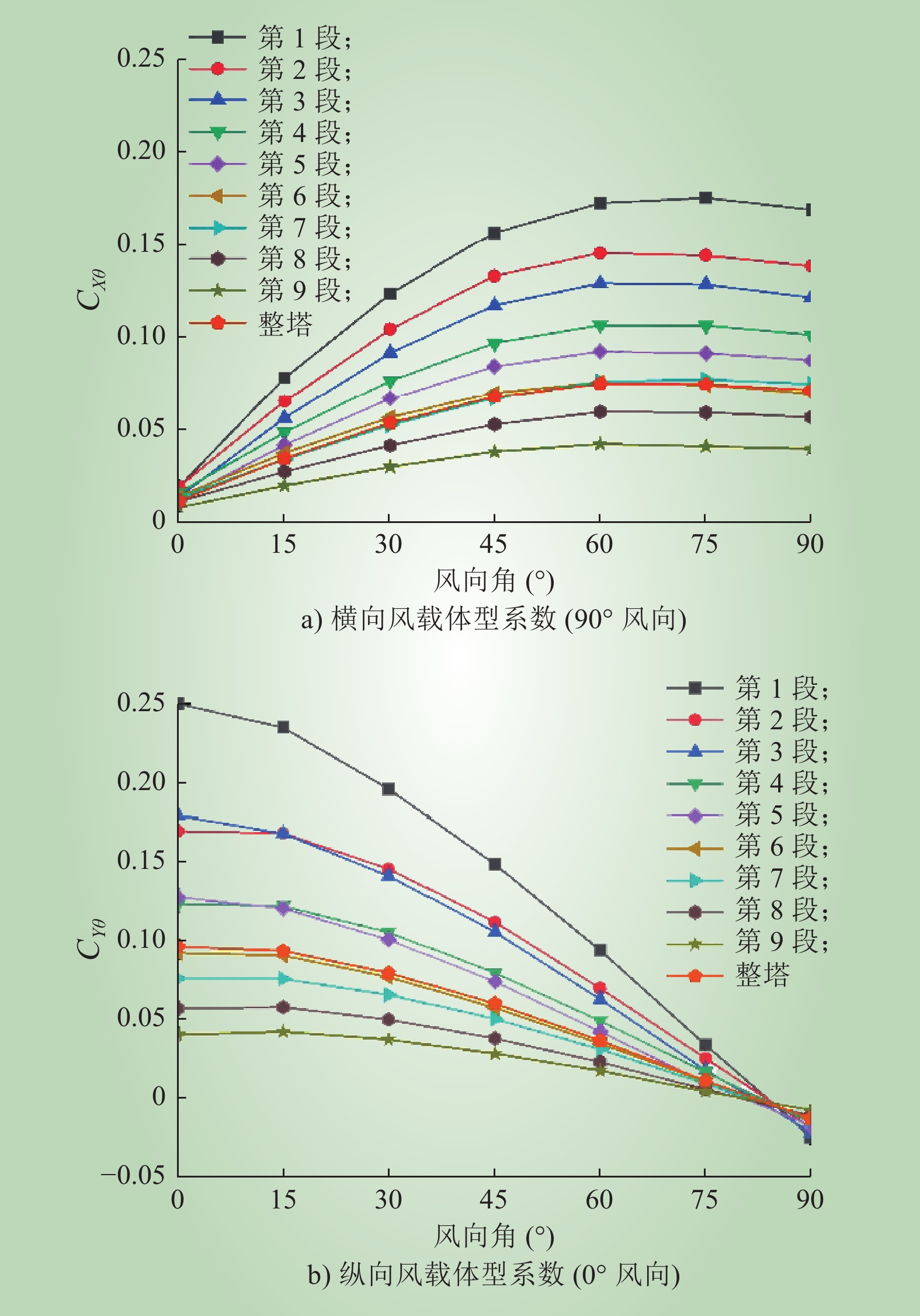
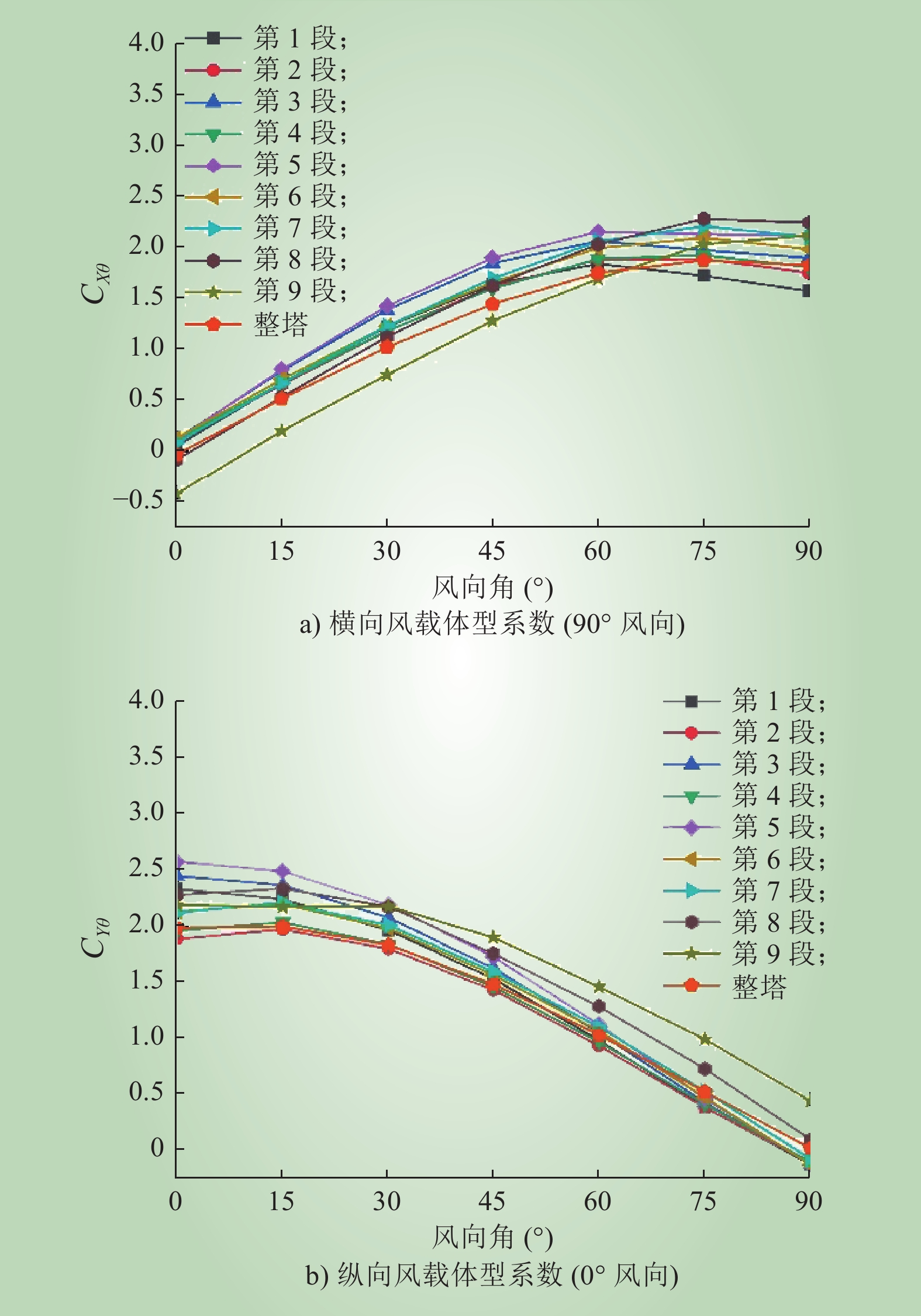
杨风利. 角钢输电铁塔横担角度风荷载系数取值研究[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34 (4): 150- 159.
|
|
YANG Fengli. Study on skewed wind load factor on cross-arms of angle steel transmission towers under skewed wind[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34 (4): 150- 159.
|
| 28 |
ZHANG D K, HU X Y, SONG X Q, et al. Investigation on aerodynamic characteristics for steel tubular cross-arms of transmission tower under skew wind[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2022, 222, 104914.
|
| 29 |
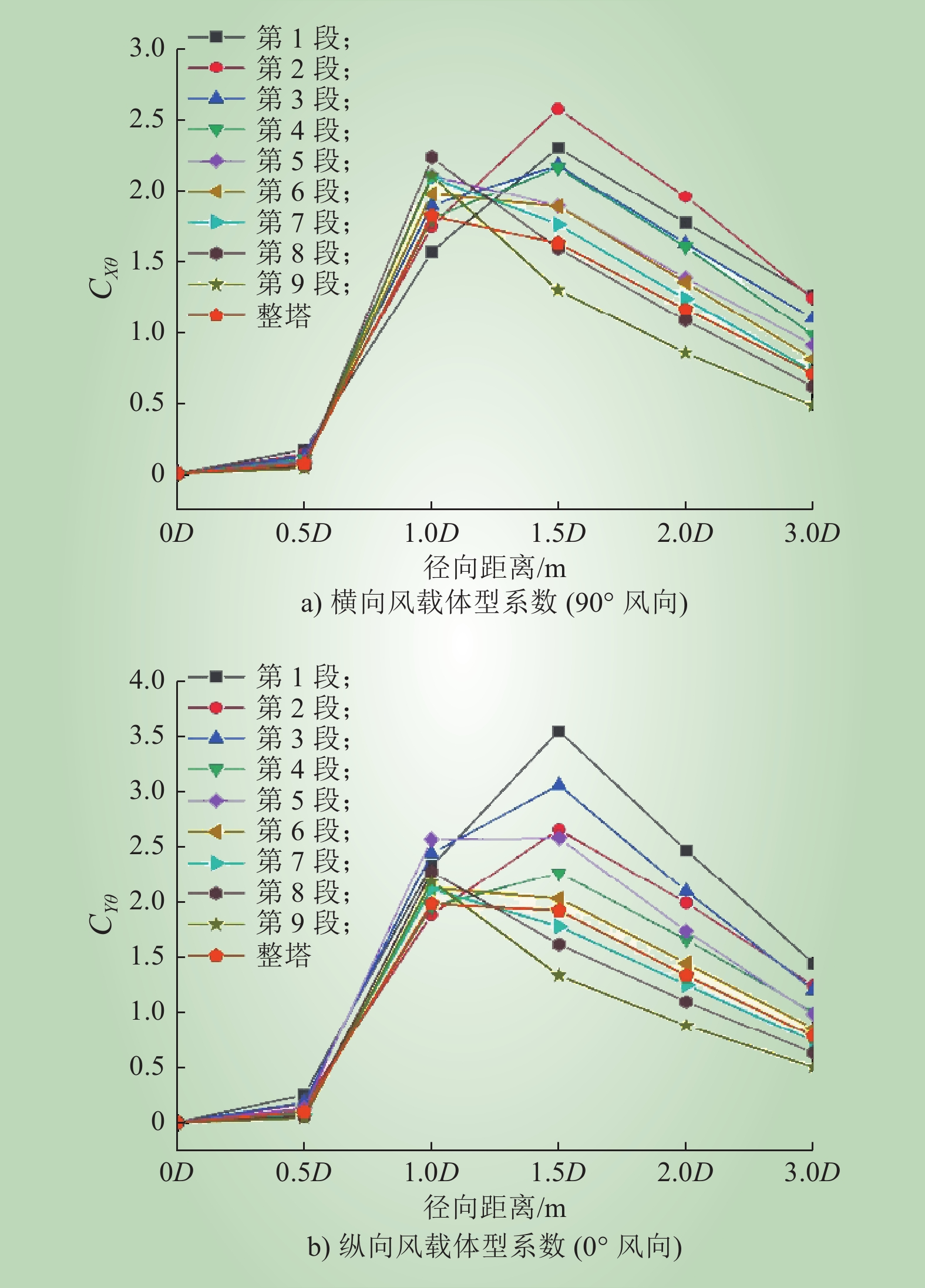
刘道永. 龙卷风作用方位对结构的荷载影响研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016.
|
|
LIU Daoyong. Study on the influence of tornado action direction on the load of structure[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016.
|
| 30 |
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 1000 kV架空输电线路设计规范: GB 50665—2011[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012.
|
|
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of 1000 kV overhead transmission line: GB 50665—2011[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2012.
|