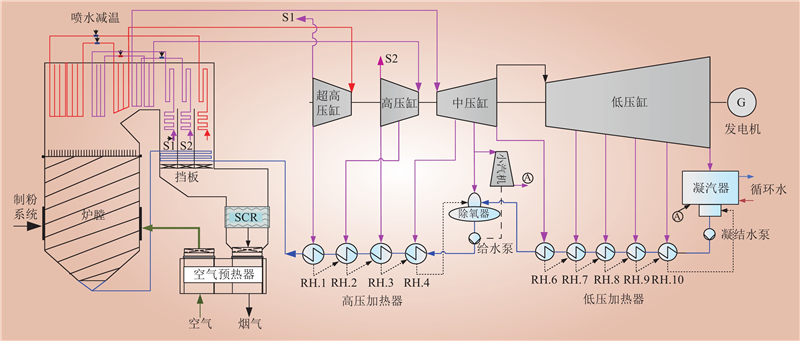
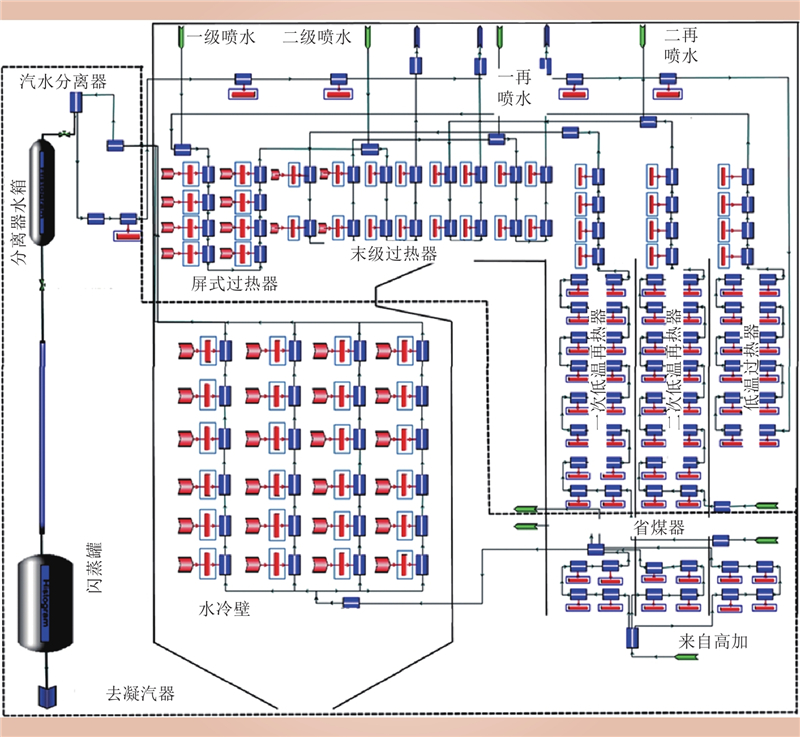
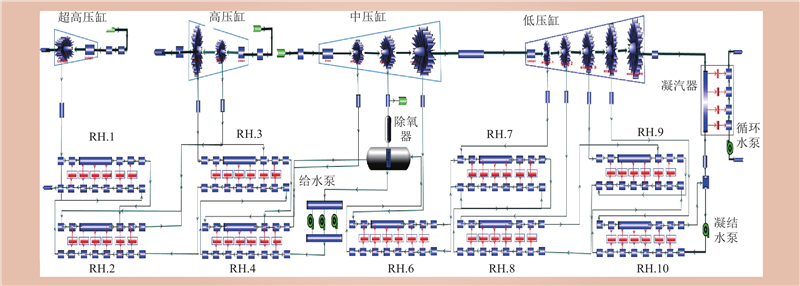
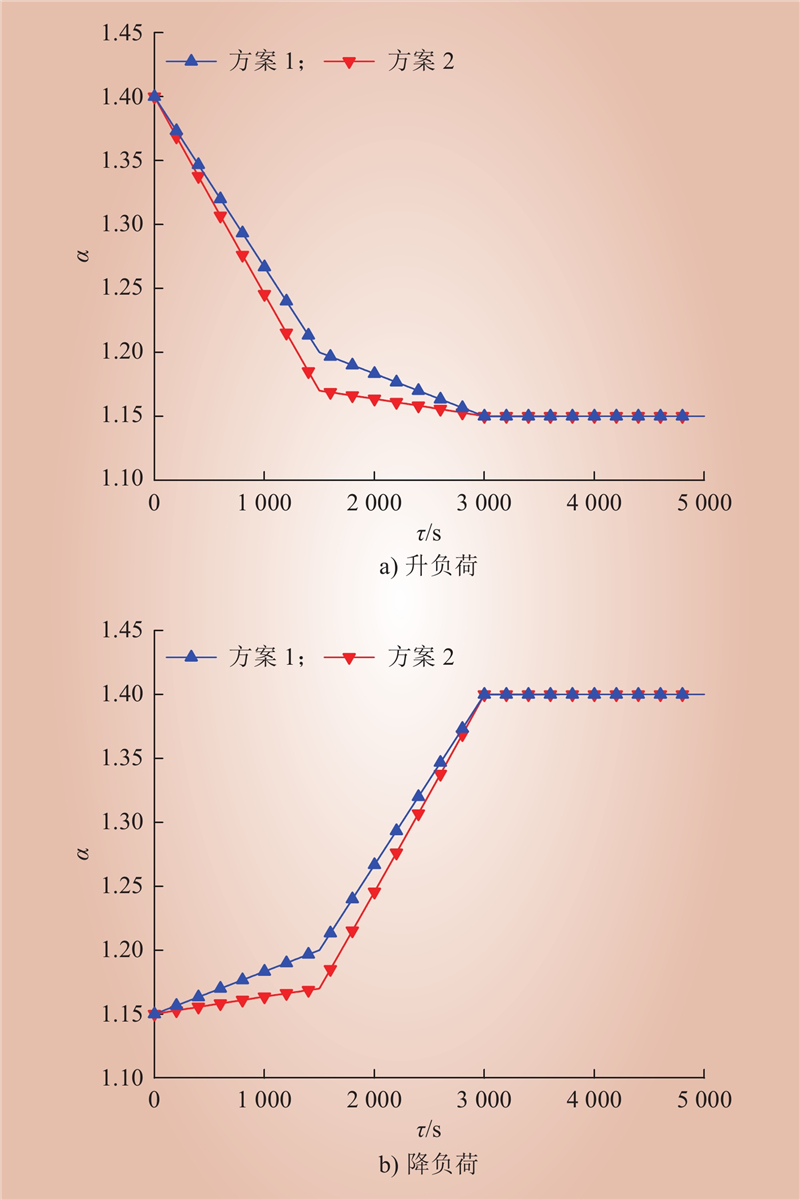
| 1 |
新华社. 习近平主持召开中央财经委员会第九次会议[EB/OL]. (2021-03-15) [2024-01-26]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/15/content_5593154.htm.
|
| 2 |
周云龙, 杨美, 杨金福, 等. 二次再热燃煤机组疏水梯级预热空气系统研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (S1): 177- 186.
|
|
ZHOU Yunlong, YANG Mei, YANG Jinfu, et al. Study on drainage cascade preheating air system in double reheat coal-fired unit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (S1): 177- 186.
|
| 3 |
李雄威, 王昕, 顾佳伟, 等. 考虑火电深度调峰的风光火储系统日前优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 1- 7, 48.
|
|
LI Xiongwei, WANG Xin, GU Jiawei, et al. Day-ahead optimal dispatching of wind-solar-thermal power storage system considering deep peak shaving of thermal power[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 1- 7, 48.
|
| 4 |
任大伟, 侯金鸣, 肖晋宇, 等. 支撑双碳目标的新型储能发展潜力及路径研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
|
REN Dawei, HOU Jinming, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Research on development potential and path of new energy storage supporting carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
| 5 |
董洁, 乔建强. “双碳” 目标下先进煤炭清洁利用发电技术研究综述[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 202- 212.
|
|
DONG Jie, QIAO Jianqiang. A review on advanced clean coal power generation technology under "carbon peaking and carbon neutrality" goal[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 202- 212.
|
| 6 |
李祥勇, 吴昕, 庞春凤, 等. 两种灵活性改造技术的热电特性对比研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 192- 200.
|
|
LI Xiangyong, WU Xin, PANG Chunfeng, et al. Comparative study of thermoelectric characteristics of two flexibility transformation technologies[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 192- 200.
|
| 7 |
国家发展改革委, 国家能源局. 关于印发《“十四五”现代能源体系规划》的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-03-22) [2024-01-26]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/202203/t20220322_1320016.html.
|
| 8 |
谢天, 梁凌, 张婷, 等. 火电机组瞬态特性研究现状综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (19): 6238- 6245.
|
|
XIE Tian, LIANG Ling, ZHANG Ting, et al. Status quo in research on transient characteristics of thermal power unit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (19): 6238- 6245.
|
| 9 |
赵征, 于悦波, 孙昊天. 基于凝结水节流的新型协调优化控制策略[J]. 动力工程学报, 2021, 41 (2): 107- 112, 128.
|
|
ZHAO Zheng, YU Yuebo, SUN Haotian. Optimization of a new coordinated control strategy based on condensate throttling[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2021, 41 (2): 107- 112, 128.
|
| 10 |
RICHTER M, OELJEKLAUS G, GÖRNER K. Improving the load flexibility of coal-fired power plants by the integration of a thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236, 607- 621.
|
| 11 |
崔晓宁, 赵志刚, 姜宁, 等. 1000 MW超超临界二次再热锅炉系统㶲分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2019, 39 (8): 605- 610, 617.
|
|
CUI Xiaoning, ZHAO Zhigang, JIANG Ning, et al. Exergy analysis of a 1000 MW ultra-supercritical double reheat boiler unit[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2019, 39 (8): 605- 610, 617.
|
| 12 |
姚丽萍. 超超临界二次再热机组热力系统优化与控制研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.
|
|
YAO Liping. Study on optimization and control of thermal system of ultra-supercritical secondary reheat unit [D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
|
| 13 |
蔡宝玲, 高海东, 王剑钊, 等. 二次再热超超临界机组动态特性分析及控制策略验证[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (19): 5288- 5299, 5411.
|
|
CAI Baoling, GAO Haidong, WANG Jianzhao, et al. Dynamic process characteristic analysis and control strategy verification on double-reheat ultra-supercritical coal-fired power units[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (19): 5288- 5299, 5411.
|
| 14 |
WU X, SHEN J, LI Y G, et al. Fuzzy modeling and predictive control of power plant steam temperature system[J]. IFAC, 2015, 48 (30): 397- 402.
|
| 15 |
WU X, SHEN J, LI Y G, et al. Fuzzy modeling and predictive control of superheater steam temperature for power plant[J]. ISA Transactions, 2015, 56, 241- 251.
|
| 16 |
FAN H J, XU W, ZHANG J, et al. Steam temperature regulation characteristics in a flexible ultra-supercritical boiler with a double reheat cycle based on a cell model[J]. Energy, 2021, 229, 120701.
|
| 17 |
YU J X, PETERSEN N, LIU P, et al. Hybrid modelling and simulation of thermal systems of in-service power plants for digital twin development[J]. Energy, 2022, 260, 125088.
|
| 18 |
GUO S S, LIU P, LI Z. Data reconciliation for the overall thermal system of a steam turbine power plant[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 165, 1037- 1051.
|
| 19 |
WANG C Y, QIAO Y Q, LIU M, et al. Enhancing peak shaving capability by optimizing reheat-steam temperature control of a double-reheat boiler[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 260, 114341.
|
| 20 |
WANG C Y, LIU Z F, FAN M Y, et al. Enhancing the flexibility and efficiency of a double-reheat coal-fired power unit by optimizing the steam temperature control: from simulation to application[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 217, 119240.
|
| 21 |
董竹林, 牛玉广, 董恩伏, 等. 适应火电机组灵活运行的滑压曲线优化方法[J]. 动力工程学报, 2020, 40 (3): 256- 264.
|
|
DONG Zhulin, NIU Yuguang, DONG Enfu, et al. Sliding pressure curve optimization for flexible operation of thermal power units[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2020, 40 (3): 256- 264.
|
| 22 |
WANG P, SI F Q, CAO Y, et al. Prediction of superheated steam temperature for thermal power plants using a novel integrated method based on the hybrid model and attention mechanism[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 203, 117899.
|
| 23 |
KIM H, KIM E K, KIM J, et al. Prediction-based feedforward control of superheated steam temperature of a power plant[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2015, 71, 351- 357.
|
| 24 |
WANG C Y, ZHAO Y L, LIU M, et al. Peak shaving operational optimization of supercritical coal-fired power plants by revising control strategy for water-fuel ratio[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 216, 212- 223.
|
| 25 |
谷俊杰, 杨智, 任晏伶, 等. 再热器喷水减温对机组煤耗率的影响研究[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 38 (1): 103- 106.
|
|
GU Junjie, YANG Zhi, REN Yanling, et al. Influence study of water spraying in reheaters desuperheating on unit coal consumption[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 38 (1): 103- 106.
|