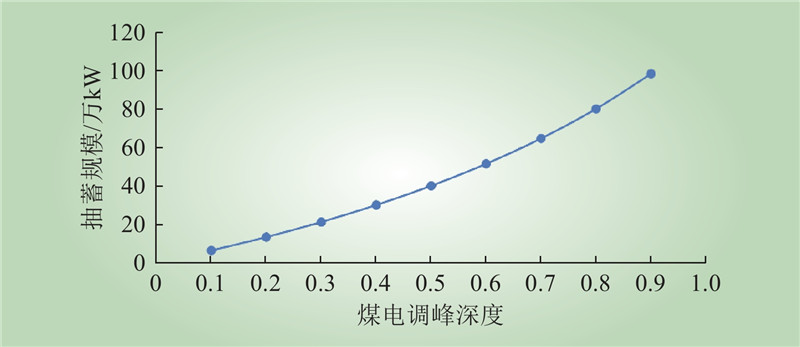
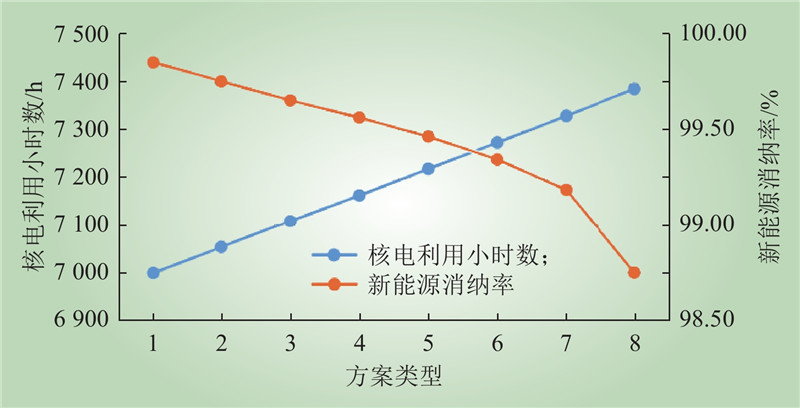
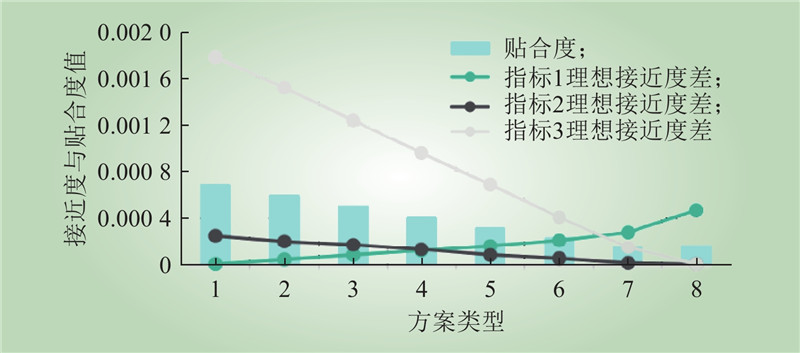
| 1 |
郭娟娟, 沈迪, 童朴, 等. 中国三代核电经济评价方法与参数优化[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 206- 212, 223.
|
|
GUO Juanjuan, SHEN Di, TONG Pu, et al. Economic evaluation method and parameter optimization for third generation nuclear power in China[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 206- 212, 223.
|
| 2 |
晁文浩, 袁至, 李骥. 计及电转气-风-火-核-碳捕集的多源联合系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 183- 194.
|
|
CHAO Wenhao, YUAN Zhi, LI Ji. Optimal dispatch of power system with P2G-wind-thermal-nuclear-carbon capture units[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 183- 194.
|
| 3 |
俞颖. 全球电力发展现状[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2025, 41 (1): 173.
|
| 4 |
徐浩然, 张瑾昀, 马歆, 等. 基于大语言模型的图检索增强生成技术在核电领域的应用与展望[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46 (3): 454- 466.
|
|
XU Haoran, ZHANG Jinyun, MA Xin, et al. Applications and prospects of graph retrieval-augmented generation technology based on large language models in the nuclear power field[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46 (3): 454- 466.
|
| 5 |
刘之琳, 许传龙, 郑海峰, 等. 德国关停核电前后保供应促消纳经验分析[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 145- 152.
|
|
LIU Zhilin, XU Chuanlong, ZHENG Haifeng, et al. Empirical analysis of ensuring electricity supply and promoting renewable power consumption before and after the shutdown of nuclear power plants: the Germany case[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 145- 152.
|
| 6 |
李洋, 尹逊虎, 张思, 等. 考虑多元发电资源灵活性的电力系统紧急调峰调度方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (8): 37- 45.
|
|
LI Yang, YIN Xunhu, ZHANG Si, et al. Emergency peak shaving dispatching method for power system considering flexibility of multiple power generation resources[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (8): 37- 45.
|
| 7 |
王妍心, 王蔚, 李华, 等. 新型电力系统抽水蓄能电站需求规模研究: 以陕西电网为例[J]. 北斗与空间信息应用技术, 2025, (1): 37- 40.
|
|
WANG Yanxin, WANG Wei, LI Hua, et al. Research on the demand scale of the pumped storage power station in the new power system: take Shanxi power grid as an example[J]. Beidou and Spatial Information Application Technology, 2025, (1): 37- 40.
|
| 8 |
王靖, 孙帆, 李晖, 等. 基于变速抽蓄的新能源送端电网能量平衡优化控制方法研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2024, 42 (7): 964- 971.
|
|
WANG Jing, SUN Fan, LI Hui, et al. Research on energy balance optimization control method of new energy sending end power grid based on variable speed pumping and storage[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2024, 42 (7): 964- 971.
|
| 9 |
朱军辉. 海水抽水蓄能与海上光伏一体化发电技术及经济性分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10 (2): 11- 17.
|
|
ZHU Junhui. Analysis of power generation technology and economy on the integration of seawater pump & storage and offshore PV[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2023, 10 (2): 11- 17.
|
| 10 |
何英静, 王湘, 但扬清, 等. 考虑源荷不确定性的风光水蓄互补系统优化调度策略[J]. 浙江电力, 2025, 44 (4): 103- 111.
|
|
HE Yingjing, WANG Xiang, DAN Yangqing, et al. An optimal scheduling strategy for a wind-solar-hydropower-pumped storage complementary system considering source-load uncertainty[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2025, 44 (4): 103- 111.
|
| 11 |
薛福, 马晓明, 游焰军. 储能技术类型及其应用发展综述[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2023, 45 (9): 48- 58.
|
|
XUE Fu, MA Xiaoming, YOU Yanjun. Energy storage technologies and their applications and development[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2023, 45 (9): 48- 58.
|
| 12 |
刘硕, 马兆兴, 刘金鑫, 等. 面向新能源消纳的新型电力系统优化运行策略[J]. 湖南电力, 2024, 44 (1): 59- 66.
|
|
LIU Shuo, MA Zhaoxing, LIU Jinxin, et al. Optimal operation strategies of new power system aimed at renewable energy system consumption[J]. Hunan Electric Power, 2024, 44 (1): 59- 66.
|
| 13 |
孙志媛, 彭博雅, 孙艳. 考虑多能互补的电力电量平衡优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
|
SUN Zhiyuan, PENG Boya, SUN Yan. Optimal dispatch strategy of power and electricity balance based on multi-energy complementation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
| 14 |
刘军, 李凌阳, 吴梦凯, 等. 分布式抽水蓄能电站与新能源发电联合参与现货市场的两阶段优化运行策略[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (2): 50- 58.
|
|
LIU Jun, LI Lingyang, WU Mengkai, et al. A two-stage optimal operation strategy of distributed pumped storage power plant and new energy power generation jointly participating in spot market[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (2): 50- 58.
|
| 15 |
秦正斌, 张午寅, 田海平, 等. 基于区域保供电和新能源消纳的常规抽水蓄能项目投资效益测算研究[J]. 湖南电力, 2025, 45 (1): 46- 53.
|
|
QIN Zhengbin, ZHANG Wuyin, TIAN Haiping, et al. Research on investment benefits calculation of conventional pumped storage projects based on regional power supply and new energy consumption[J]. Hunan Electric Power, 2025, 45 (1): 46- 53.
|
| 16 |
惠振国, 艾澜, 常鹏霞, 等. 计及风光出力相关性的风光水储互补系统优化调度[J]. 水电能源科学, 2024, 42 (8): 218- 222.
|
|
HUI Zhenguo, AI Lan, CHANG Pengxia, et al. Optimal scheduling of wind-solar-water-storage complementary system considering the correlation of wind-solar output[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2024, 42 (8): 218- 222.
|
| 17 |
刘世隆, 韦建溪, 田楠. 基于合理弃能的抽蓄-风-光-火联合发电系统多方案优化运行研究[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2025, 41 (2): 100- 106.
|
|
LIU Shilong, WEI Jianxi, TIAN Nan. Research on the multi-scheme optimal operation of the pumped storage-wind-solar-thermal combined power generation system based on rational abandonment of energy[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2025, 41 (2): 100- 106.
|
| 18 |
张智, 霍超, 郭尊, 等. 新型电力系统下抽水蓄能集群规划与运营关键问题综述及研究展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (15): 5810- 5832.
|
|
ZHANG Zhi, HUO Chao, GUO Zun, et al. Overview and research prospects of key issues in pumped storage cluster planning and operation under the new type power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (15): 5810- 5832.
|
| 19 |
田松峰, 姚静, 杨智好, 等. 基于混合储能的风光储联合发电系统优化调度策略及评价[J]. 热力发电, 2024, 53 (10): 21- 31.
|
|
TIAN Songfeng, YAO Jing, YANG Zhihao, et al. Optimal dispatching strategy and evaluation of wind-solar-storage combined power generation system based on hybrid energy storage[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2024, 53 (10): 21- 31.
|
| 20 |
CHEGARI B, TABAA M, SIMEU E, et al. Optimal energy management of a hybrid system composed of PV, wind turbine, pumped hydropower storage, and battery storage to achieve a complete energy self-sufficiency in residential buildings[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 126624- 126639.
|
| 21 |
赵洁, 刘涤尘, 雷庆生, 等. 核电机组参与电网调峰及与抽水蓄能电站联合运行研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31 (7): 1- 6.
|
|
ZHAO Jie, LIU Dichen, LEI Qingsheng, et al. Analysis of nuclear power plant participating in peak load regulation of power grid and combined operation with pumped storage power plant[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31 (7): 1- 6.
|
| 22 |
林国庆, 林礼清. 抽水蓄能电站与核电联合运行浅议[J]. 福建水力发电, 2016, (2): 28- 29, 32.
|
| 23 |
缪晓丹, 朱朱, 陈恺. 福建省核电经济性分析及“核蓄”联营初步探讨[J]. 南方能源建设, 2020, 7 (S1): 93- 96.
|
|
MIAO Xiaodan, ZHU Zhu, CHEN Kai. Economic analysis of nuclear power in fujian province and preliminary discussion on "nuclear power plant-pumped storage power plant" combined operation[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2020, 7 (S1): 93- 96.
|
| 24 |
张洪妹. 浅析福清核电调用调峰辅助服务方式研究: 核电与抽水蓄能、电化学储能一体化开发[J]. 中国能源, 2021, 43 (6): 75- 82.
|
|
ZHANG Hongmei. Brief analysis of Fuqing nuclear power plant peak shaving auxiliary services mode[J]. Energy of China, 2021, 43 (6): 75- 82.
|
| 25 |
罗佑坤, 钟鑫亮, 辛晟. 广东抽水蓄能电站与核电联营模式及效益研究[J]. 水电与新能源, 2022, 36 (11): 5- 7, 13.
|
|
LUO Youkun, ZHONG Xinliang, XIN Sheng. On the joint operation mode of pumped storage hydropower stations and nuclear power stations and its benefits[J]. Hydropower and New Energy, 2022, 36 (11): 5- 7, 13.
|
| 26 |
张志翔, 蒋龙, 严旭, 等. 基于主客观赋权的电力市场风险综合评价研究[J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10 (6): 160- 169.
|
|
ZHANG Zhixiang, JIANG Long, YAN Xu, et al. Research on comprehensive evaluation of electricity market risk based on subjective and objective weighting[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2023, 10 (6): 160- 169.
|
| 27 |
王磊, 董平, 何玉涛, 等. 基于熵权法的电化学储能电站安全隐患数据分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2024, 31 (6): 9- 15, 25.
|
|
WANG Lei, DONG Ping, HE Yutao, et al. Data analysis of potential safety hazard of electrochemical energy storage power station based on entropy weight method[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2024, 31 (6): 9- 15, 25.
|