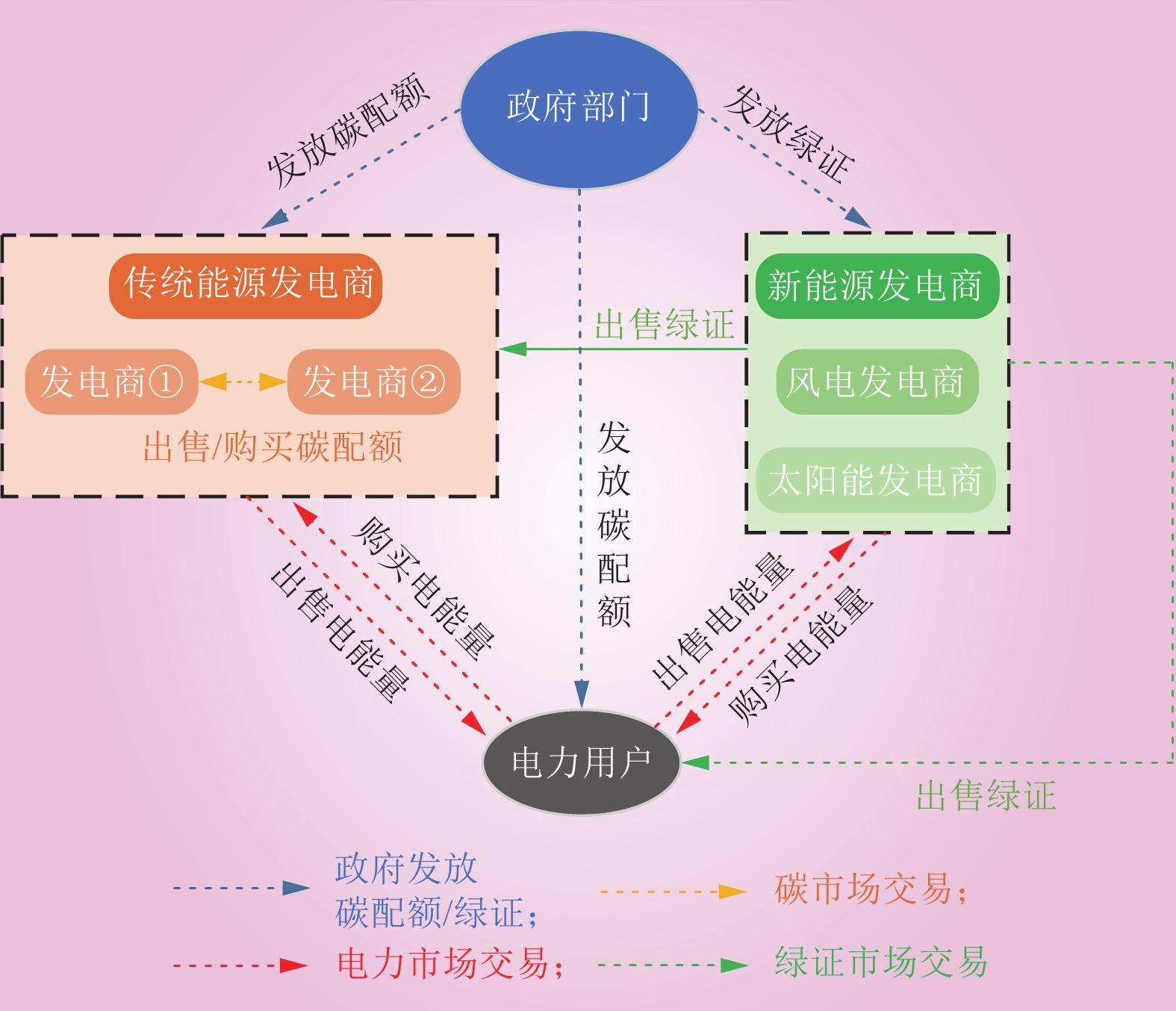
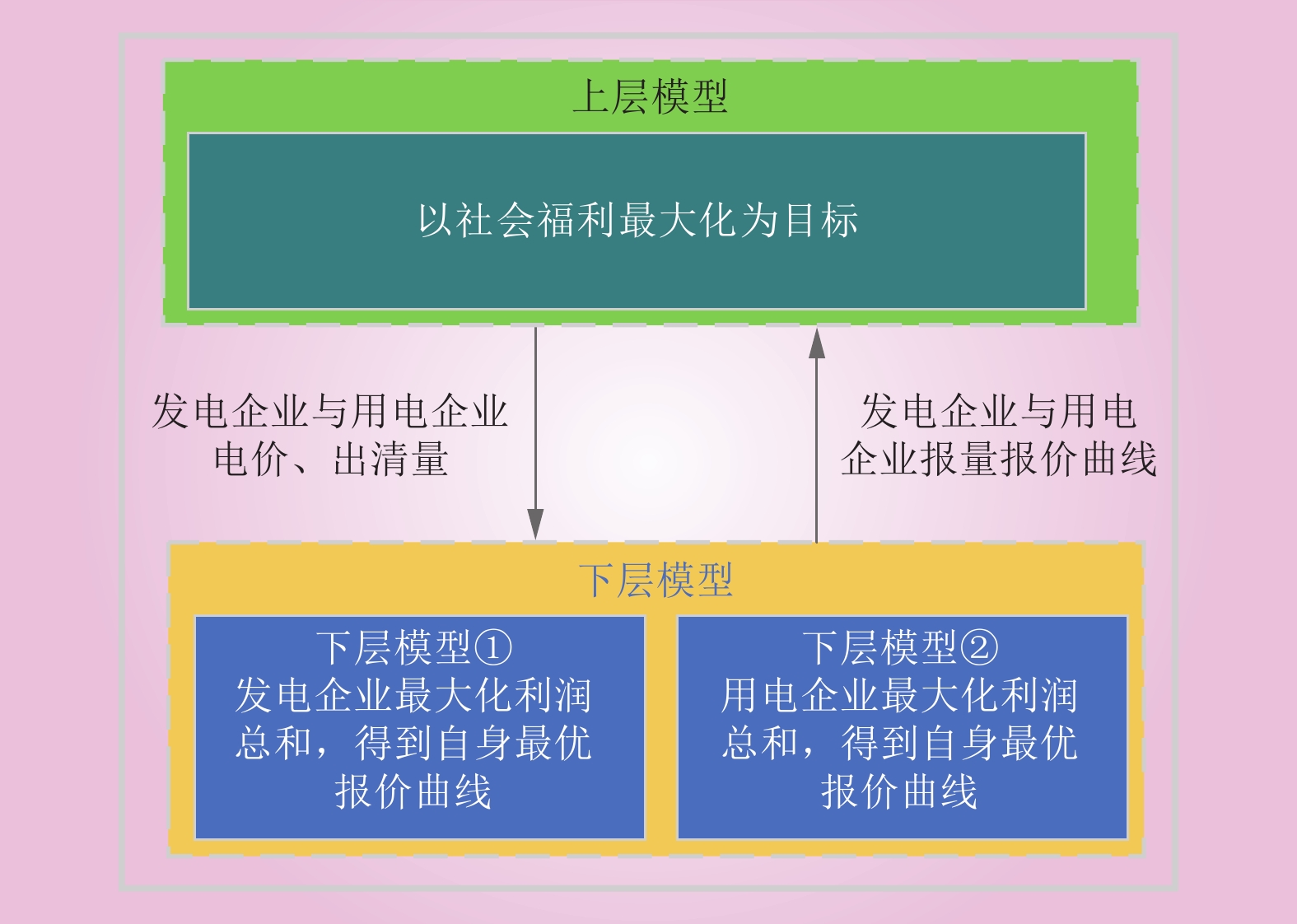
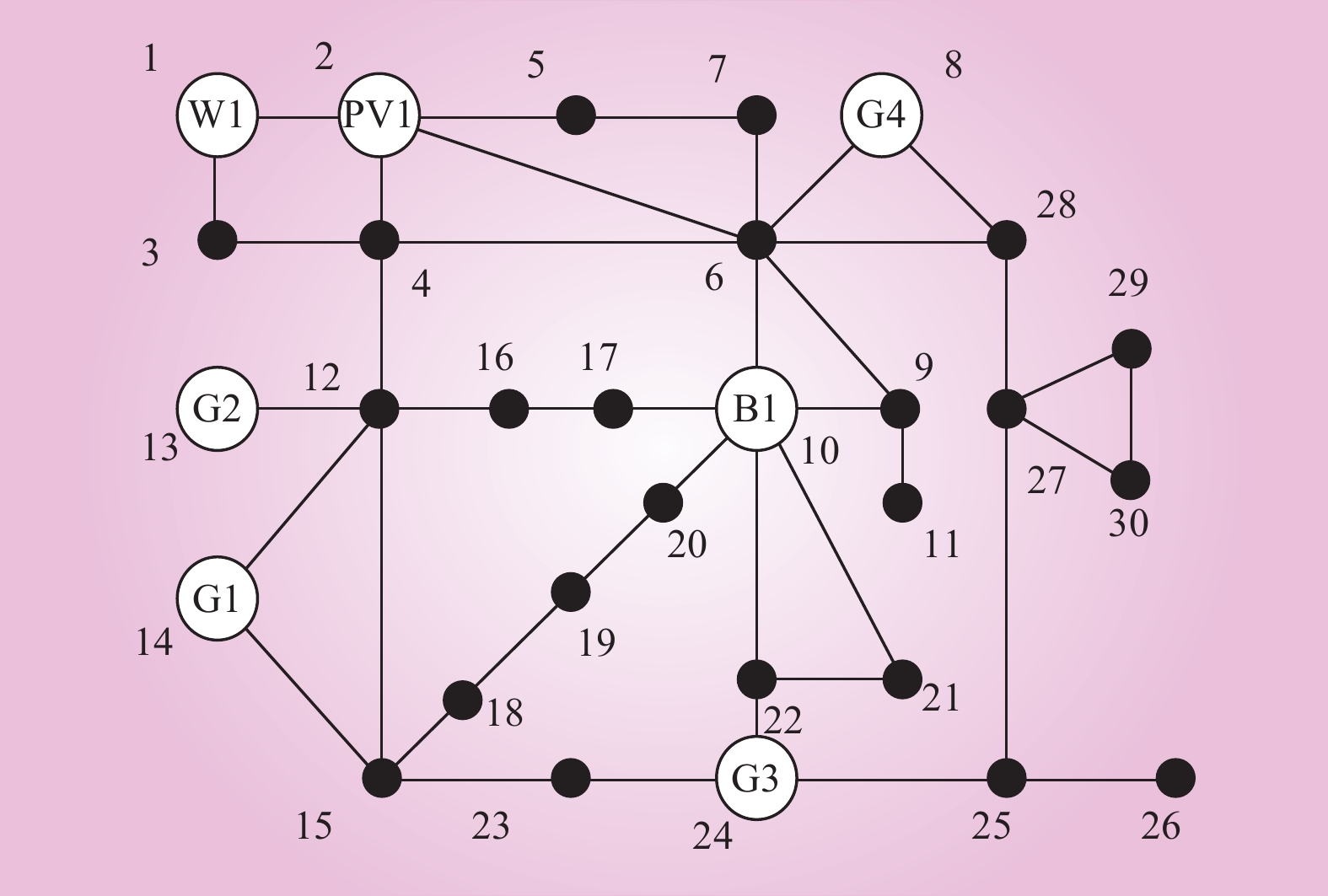
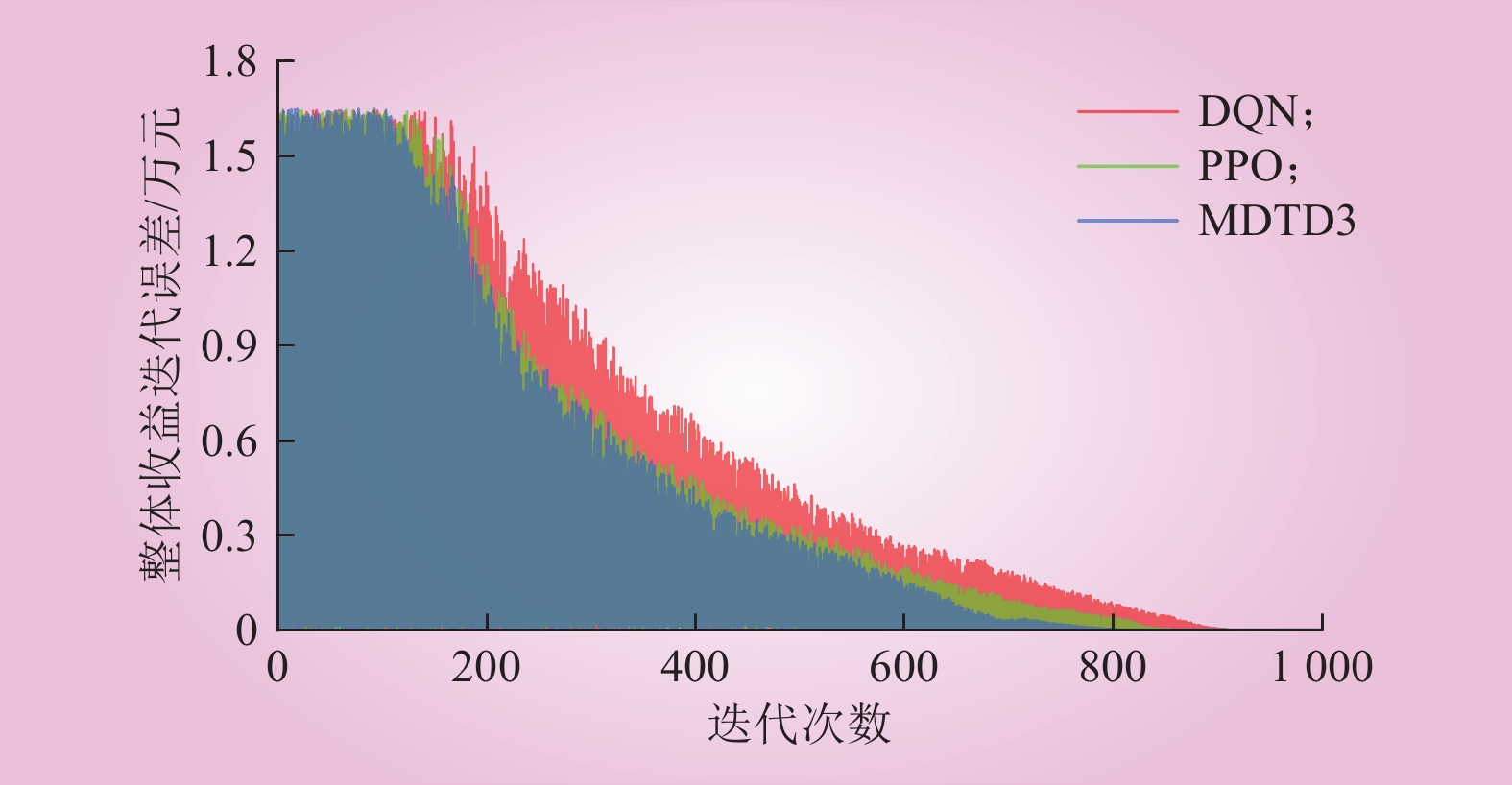
| 1 |
国家能源局. 国家能源局发布2023年全国电力工业统计数据[EB/OL]. (2024-01-26) [2024-10-09]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-01/26/c_1310762246.
|
| 2 |
汤芳, 代红才, 张宁, 等. 能耗双控向碳排放双控转变影响分析及推进路径设计[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 255- 261.
|
|
TANG Fang, DAI Hongcai, ZHANG Ning, et al. Effect analysis and promotion path design for transformation from energy consumption "dual control" to carbon "dual control"[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 255- 261.
|
| 3 |
国务院. 《2024—2025年节能降碳行动方案》[EB/OL]. (2024-05-23) [2024-10-09]. https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/2024/issue_11406/202406/content_6958082.html.
|
| 4 |
尚楠, 陈政, 冷媛. 电碳市场背景下典型环境权益产品衔接互认机制及关键技术[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (7): 2558- 2578.
|
|
SHANG Nan, CHEN Zheng, LENG Yuan. Mutual recognition mechanism and key technologies of typical environmental interest products in power and carbon markets[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (7): 2558- 2578.
|
| 5 |
冯昌森, 谢方锐, 文福拴, 等. 基于智能合约的绿证和碳联合交易市场的设计与实现[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (23): 1- 11.
|
|
FENG Changsen, XIE Fangrui, WEN Fushuan, et al. Design and implementation of joint trading market for green power certificate and carbon based on smart contract[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (23): 1- 11.
|
| 6 |
尚楠, 陈政, 卢治霖, 等. 电力市场、碳市场及绿证市场互动机理及协调机制[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (1): 142- 154.
|
|
SHANG Nan, CHEN Zheng, LU Zhilin, et al. Interaction principle and cohesive mechanism between electricity market, carbon market and green power certificate market[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (1): 142- 154.
|
| 7 |
董亚杰. 绿色证书与碳排放权交易协同实施对电力市场的政策效果分析[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2022.
|
|
DONG Yajie. Analysis of the policy effect of the coordinated implementation of green certificates and carbon emission trading on the power[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2022.
|
| 8 |
王心昊, 蒋艺璇, 陈启鑫, 等. 可交易减排价值权证比较分析和衔接机制研究[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 594- 602.
|
|
WANG Xinhao, JIANG Yixuan, CHEN Qixin, et al. On tradeable certificates of emissions reduction and their interactions[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 594- 602.
|
| 9 |
邱忠涛, 金艳鸣, 徐沈智. 全国碳市场扩容下电力平均排放因子选择对高耗能产业的影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 1- 7.
|
|
QIU Zhongtao, JIN Yanming, XU Shenzhi. Impacts of electricity emission factor selection on high energy-consuming industries with the expanded national carbon market[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 1- 7.
|
| 10 |
李祥光, 谭青博, 李帆琪, 等. 电碳耦合对煤电机组现货市场结算电价影响分析模型[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 113- 125.
|
|
LI Xiangguang, TAN Qingbo, LI Fanqi, et al. Analysis model to study the influence of electrocarbon coupling on settlement price of coal power units in spot market[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 113- 125.
|
| 11 |
王晛, 王胜彩, 张少华. 电-碳-绿证交易耦合下新能源发电商参与投标竞争的多市场博弈分析[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (10): 4125- 4138.
|
|
WANG Xian, WANG Shegncai , ZHANG Shaohua. Game analysis of coupled electricity-carbon-green certificate markets with strategic bidding of renewable generators[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (10): 4125- 4138.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG X Y, GUO X P, ZHANG X P. Assessing the policy synergy among power, carbon emissions trading and tradable green certificate market mechanisms on strategic GENCOs in China[J]. Energy, 2023, 278, 127833.
|
| 13 |
YAN S Z, WANG W Q, LI X Z, et al. Stochastic optimal scheduling strategy of cross-regional carbon emissions trading and green certificate trading market based on Stackelberg game[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 219, 119268.
|
| 14 |
赵会茹, 赵一航, 武昭原, 等. 电力市场、碳排放权交易市场以及核证自愿减排市场耦合下发电商竞价策略[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (10): 123- 135.
|
|
ZHAO Huiru, ZHAO Yihang, WU Zhaoyuan, et al. Bidding strategy of power generators under the linkage of electricity market, carbon emission trading market, and certified emission reduction market[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (10): 123- 135.
|
| 15 |
姚军, 何姣, 吴永飞, 等. 考虑碳交易和绿证交易制度的电力批发市场能源优化[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 190- 195.
|
|
YAO Jun, HE Jiao, WU Yongfei, et al. Energy optimization of electricity wholesale market considering carbon emissions trading and green power certificate trading mechanism[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 190- 195.
|
| 16 |
周建华, 梁昌誉, 史林军, 等. 计及阶梯式碳交易机制的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (2): 77- 87.
|
|
ZHOU Jianhua, LIANG Changyu, SHI Linjun, et al. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy system considering the ladder-type carbon trading mechanism[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (2): 77- 87.
|
| 17 |
郭静蓉, 向月, 吴佳婕, 等. 考虑CCUS电转气技术及碳市场风险的电–气综合能源系统低碳调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (4): 1290- 1302.
|
|
GUO Jingrong, XIANG Yue, WU Jiajie, et al. Low-carbon optimal scheduling of integrated electricity-gas energy systems considering CCUS-P2G technology and risk of carbon market[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (4): 1290- 1302.
|
| 18 |
TAN Q L, DING Y H, ZHENG J, et al. The effects of carbon emissions trading and renewable portfolio standards on the integrated wind–photovoltaic–thermal power-dispatching system: real case studies in China[J]. Energy, 2021, 222, 119927.
|
| 19 |
汪鹏. 风光新能源发电商参与多市场耦合交易模型研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京), 2023.
|
|
WANG Peng. Research on the models of wind and photovoltaic power generation companies participating in multi-market coupled transaction[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2023.
|
| 20 |
王泽森, 石岩, 唐艳梅, 等. 考虑LCA能源链与碳交易机制的综合能源系统低碳经济运行及能效分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (6): 1614- 1626, 1858.
|
|
WANG Zesen, SHI Yan, TANG Yanmei, et al. Low carbon economy operation and energy efficiency analysis of integrated energy systems considering LCA energy chain and carbon trading mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (6): 1614- 1626, 1858.
|
| 21 |
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 企业温室气体排放核算与报告指南铝冶炼行业[EB/OL]. (2024-09-14) [2024-10-09]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202403/t20240315_1068508.html.
|
| 22 |
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 《温室气体自愿减排交易管理办法(试行)》[EB/OL]. (2023-10-29) [2024-10-09]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk02/202310/t20231020_1043694.html.
|