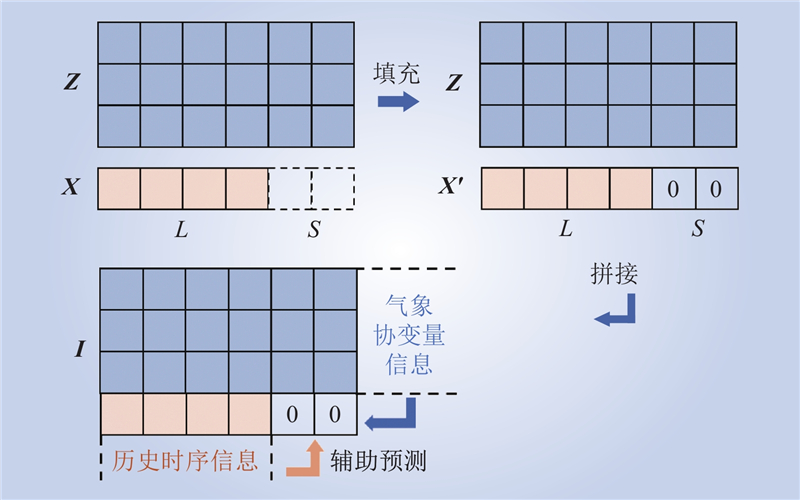
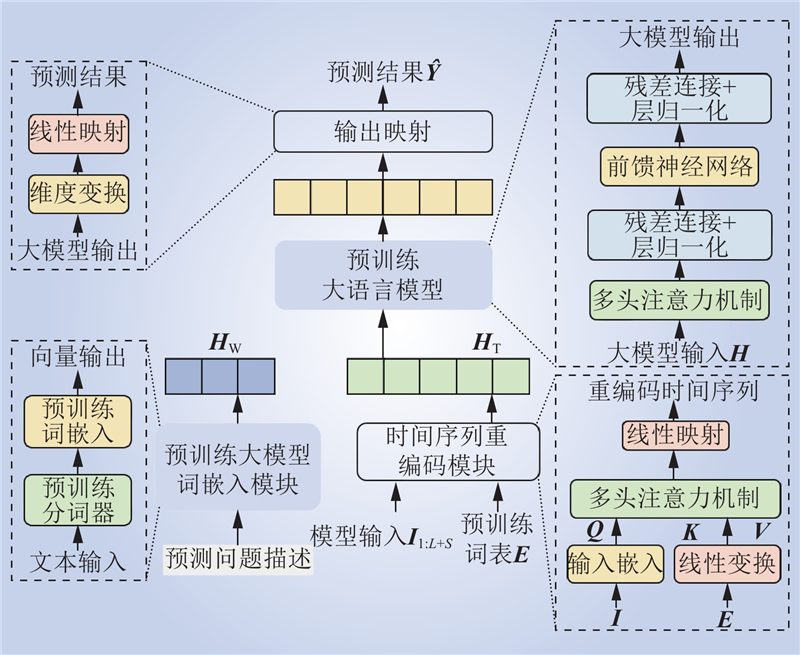
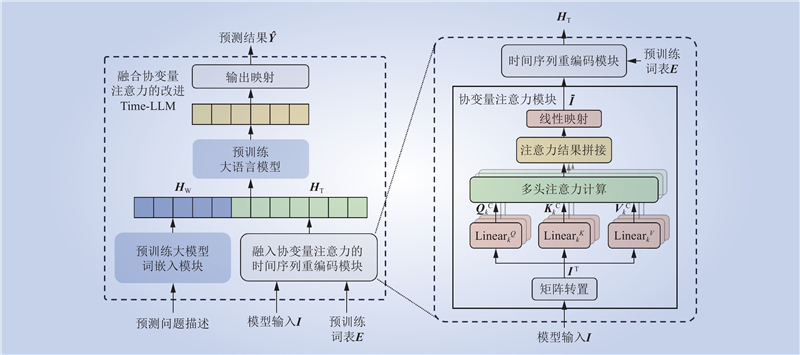
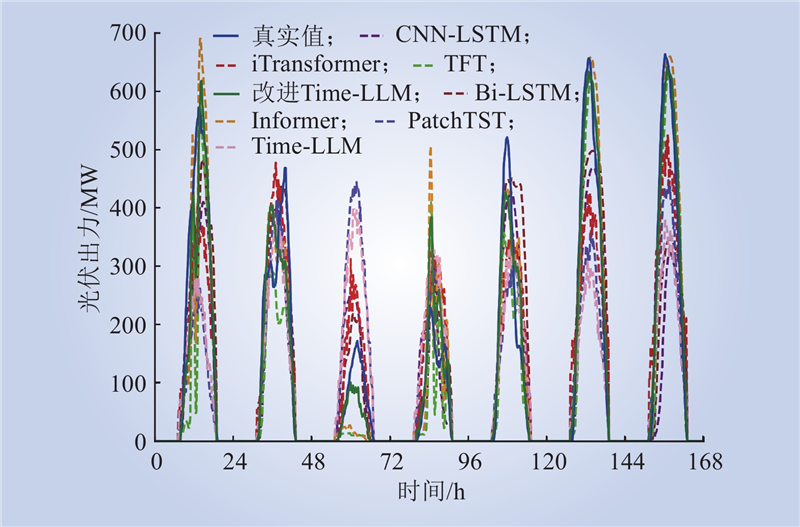
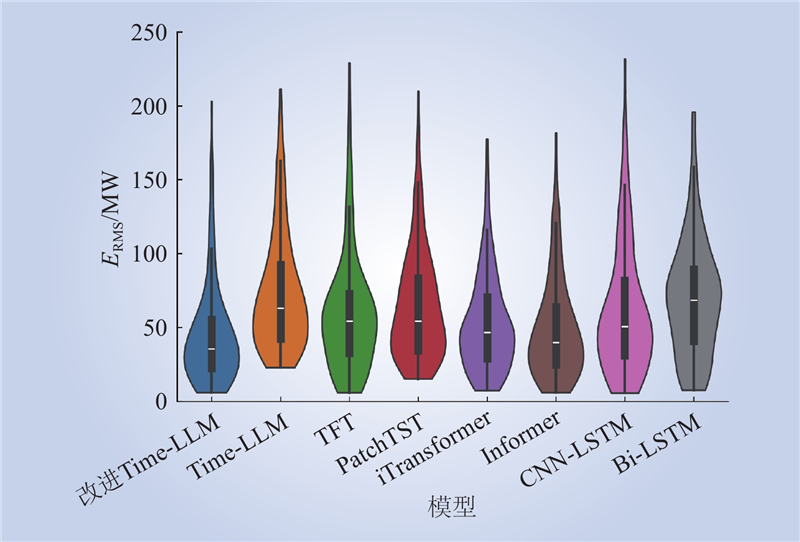
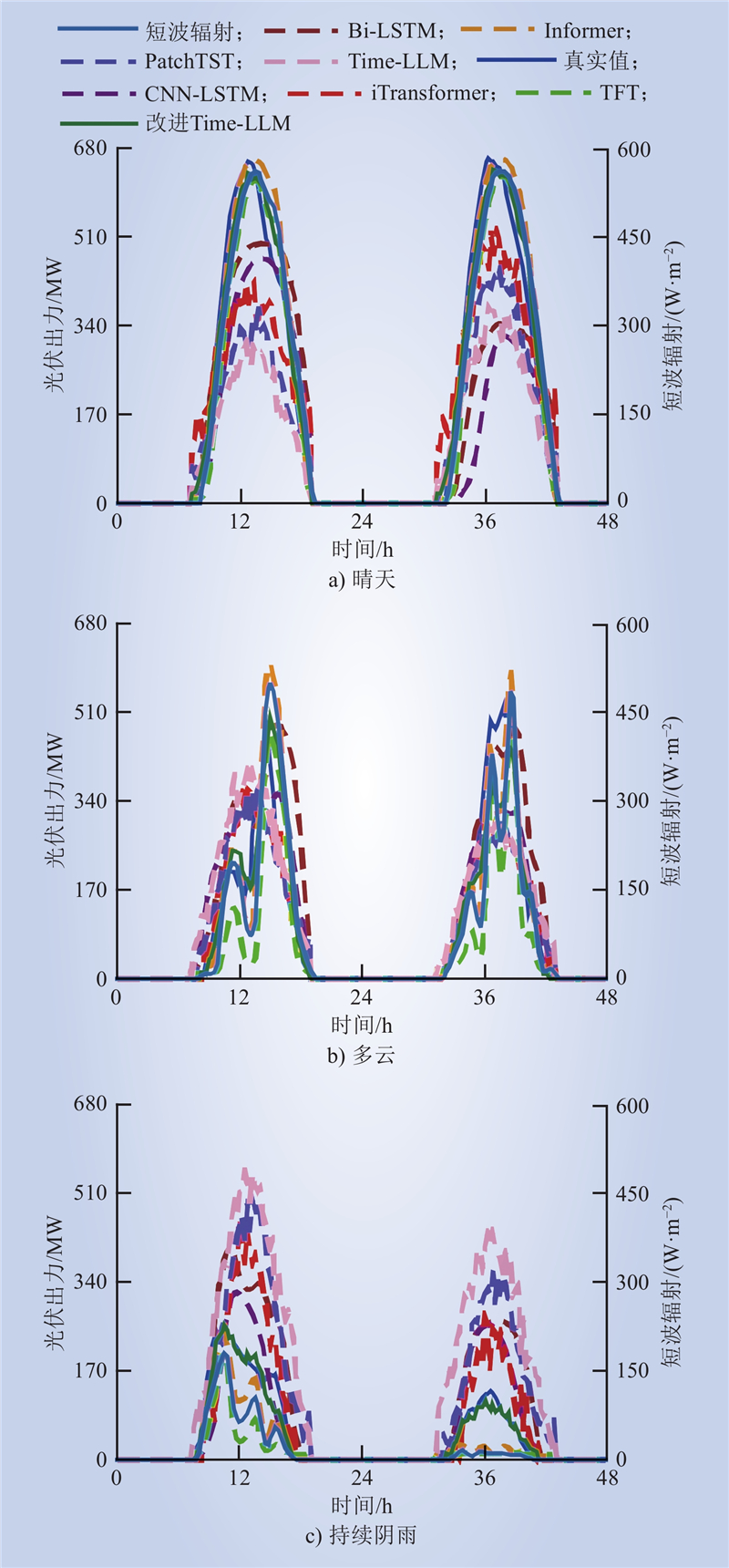
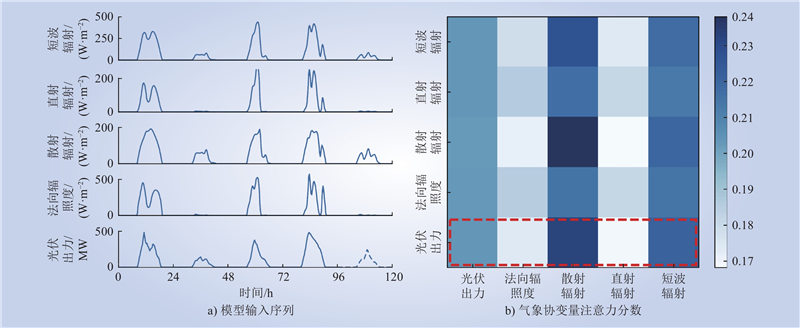
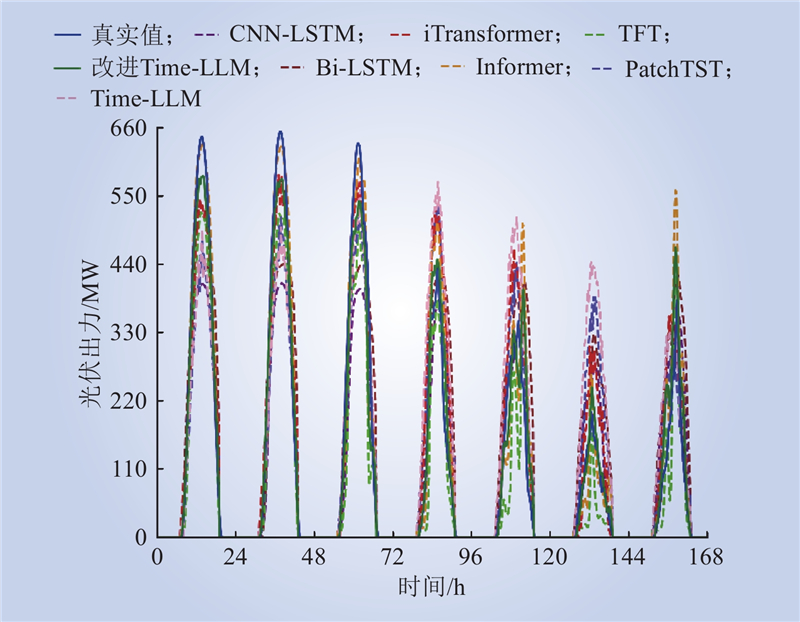
| 1 |
SUN H B, GUO Q L, SHEN X W, et al. Energy Internet: redefinition and categories[J]. Energy Internet, 2024, 1 (1): 3- 8.
|
| 2 |
FAN S X, GUO J B, MA S C, et al. Enabling artificial intelligence-based scenario application in new type power systems[J]. Energy Internet, 2024, 1 (1): 9- 13.
|
| 3 |
刘大贵, 王维庆, 张慧娥, 等. 基于隐马尔科夫修正的光伏中长期电量预测及调度计划应用[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (2): 840- 848.
|
|
LIU Dagui, WANG Weiqing, ZHANG Huie, et al. Mid-long term available quantity of electricity forecasting with error calibration by hidden Markov model in photovoltaic and application of dispatching plan[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (2): 840- 848.
|
| 4 |
解振学, 林帆, 王若谷, 等. 基于时序动态回归的超短期光伏发电功率预测方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (7): 45- 51.
|
|
XIE Zhenxue, LIN Fan, WANG Ruogu, et al. Very short-term photovoltaic power forecasting method based on time series dynamic regression[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (7): 45- 51.
|
| 5 |
彭曙蓉, 陈慧霞, 孙万通, 等. 基于改进LSTM的光伏发电功率预测方法研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (11): 296- 302.
|
|
PENG Shurong, CHEN Huixia, SUN Wantong, et al. Research on photovoitaic power prediction method based on improved LSTM[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (11): 296- 302.
|
| 6 |
李丰君, 王磊, 赵健, 等. 基于天气融合和LSTM网络的分布式光伏短期功率预测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 149- 154.
|
|
LI Fengjun, WANG Lei, ZHAO Jian, et al. Research on distributed photovoltaic short-term power prediction method based on weather fusion and LSTM-Net[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 149- 154.
|
| 7 |
龙小慧, 秦际赟, 张青雷, 等. 基于相似日聚类及模态分解的短期光伏发电功率组合预测研究[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2948- 2957.
|
|
LONG Xiaohui, QIN Jiyun, ZHANG Qinglei, et al. Short-term photovoltaic power prediction study based on similar day clustering and modal decomposition[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2948- 2957.
|
| 8 |
何威, 苏中元, 史金林, 等. 基于双重注意力GRU与相似修正的光伏功率预测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (3): 480- 487.
|
|
HE Wei, SU Zhongyuan, SHI Jinlin, et al. Photovoltaic power forecasting based on dual-attention-GRU and similarity modification[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (3): 480- 487.
|
| 9 |
姜建国, 杨效岩, 毕洪波. 基于VMD-FE-CNN-BiLSTM的短期光伏发电功率预测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (7): 462- 473.
|
|
JIANG Jianguo, YANG Xiaoyan, BI Hongbo. Photovoltaic power forecasting method based on VMD-FE-CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (7): 462- 473.
|
| 10 |
冯裕祺, 李辉, 李利娟, 等. 基于CNN-GRU的光伏电站电压轨迹预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 163- 171.
|
|
FENG Yuqi, LI Hui, LI Lijuan, et al. Voltage trajectory prediction of photovoltaic power station based on CNN-GRU[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 163- 171.
|
| 11 |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2017, 30.
|
| 12 |
ZHOU H Y, ZHANG S H, PENG J Q, et al. Informer: beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35 (12): 11106- 11115.
|
| 13 |
NIE Y Q, NGUYEN N H. , SINTHONG P, et al. A time series is worth 64 words: Long-term forecasting with transformers[C]//The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations. 2022.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG Y H, YAN J C. Crossformer: transformer utilizing cross-dimension dependency for multivariate time series forecasting[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023.
|
| 15 |
LIU Y, WU H X, WANG J M, et al. Non-stationary transformers: exploring the stationarity in time series forecasting[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, 35, 9881- 9893.
|
| 16 |
ZHOU T, MA Z Q, WEN Q S, et al. FEDformer: frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, 2022 : 27268–27286.
|
| 17 |
梁睿, 金沫含, 朱慧君, 等. 基于多场景聚类和可解释时间融合Transformer网络的乡村地区净负荷区间预测[J/OL]. 电网技术, 1–13 [2025-03-28]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.TM.20250327.1802.012.html.
|
|
LIANG Rui, JIN Mohan, ZHU Huijun, et al. Net load interval forecasting in rural areas based on multi-scenario clustering and explainable temporal fusion transformers network[J/OL]. Power System Technology, 1–13 [2025-03-28]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.TM.20250327.1802.012.html.
|
| 18 |
张倩, 蒙飞, 李涛, 等. 基于周期信息增强的Informer光伏发电功率预测[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 186- 193.
|
|
ZHANG Qian, MENG Fei, LI Tao, et al. Informer photovoltaic power generation forecasting based on cycle information enhancement[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 186- 193.
|
| 19 |
邓芳明, 刘涛, 王锦波, 等. 基于地基云图与气象因素多模态融合的光伏功率预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (18): 7193- 7206.
|
|
DENG Fangming, LIU Tao, WANG Jinbo, et al. Research on photovoltaic power prediction based on multimodal fusion of ground cloud map and meteorological factors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (18): 7193- 7206.
|
| 20 |
LIU Y, HU T G, ZHANG H R, et al. iTransformer: Inverted transformers are effective for time series forecasting[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations.
|
| 21 |
LIANG Y X, WEN H M, NIE Y Q, et al. Foundation models for time series analysis: a tutorial and survey[C]//Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Barcelona Spain. ACM, 2024: 6555–6565.
|
| 22 |
XUE H, SALIM F D. PromptCast: a new prompt-based learning paradigm for time series forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024, 36 (11): 6851- 6864.
|
| 23 |
WANG X L, FENG M K, QIU J, et al. From news to forecast: integrating event analysis in LLM-based time series forecasting with reflection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024, 37, 58118- 58153.
|
| 24 |
TANG H, ZHANG C, JIN M Y, et al. Time series forecasting with LLMs: understanding and enhancing model capabilities[J]. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2025, 26 (2): 109- 118.
|
| 25 |
ZHENG L N, DONG C, ZHANG W E, et al. Understanding why large language models can be ineffective in time series analysis: the impact of modality alignment[C]//Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining V. 2. Toronto ON, Canada. ACM, 2025: 4026–4037.
|
| 26 |
JIN M, WANG S Y, MA L T, et al. Time-LLM: Time series forecasting by reprogramming large language models[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations.
|
| 27 |
ELIA. Photovoltaic power production estimation and forecast on Belgian grid (Historical)[EB/OL]. (2025-02-15)[2025-05-27]. https://opendata.elia.be/explore/dataset/ods032/information.
|
| 28 |
OPEN-METEO. Weather forecast API[EB/OL]. (2025-02-15)[2025-05-27]. https://open-meteo.com/en/docs.
|
| 29 |
刘洋, 于海东, 刘文彬, 等. 基于DTW-两阶四分位的分布式光伏发电异常数据辨识[J]. 热力发电, 2024, 53(7): 34–44.
|
|
LIU Yang, YU Haidong, LIU Wenbin, et al. Abnormal data identification for distributed photovoltaic generation based on DTW and two-stage quartile[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2024, 53(7): 163–171.
|
| 30 |
DIEBOLD F X, MARIANO R S. Comparing predictive accuracy[J]. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 2002, 20 (1): 134- 144.
|
| 31 |
LIM B, ARIK S Ö, LOEFF N, et al. Temporal fusion transformers for interpretable multi-horizon time series forecasting[J]. International Journal of Forecasting, 2021, 37 (4): 1748- 1764.
|