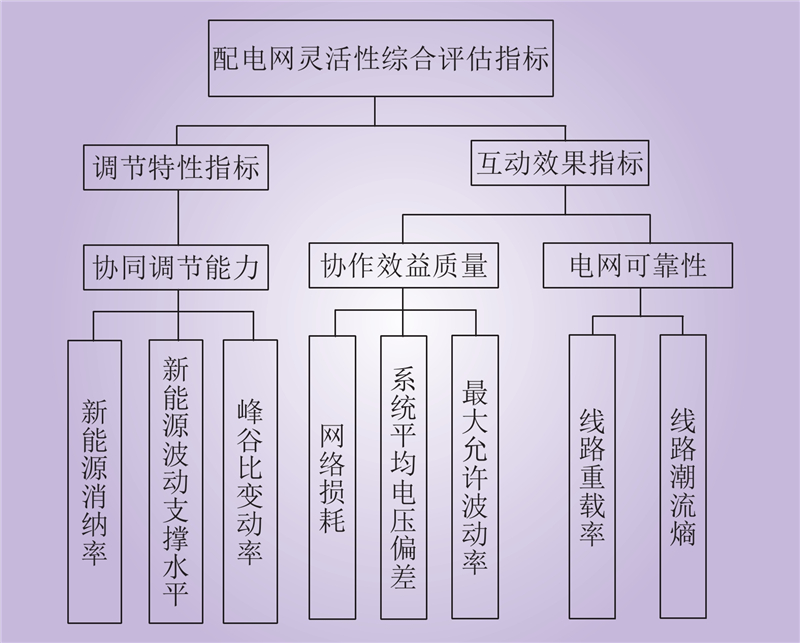
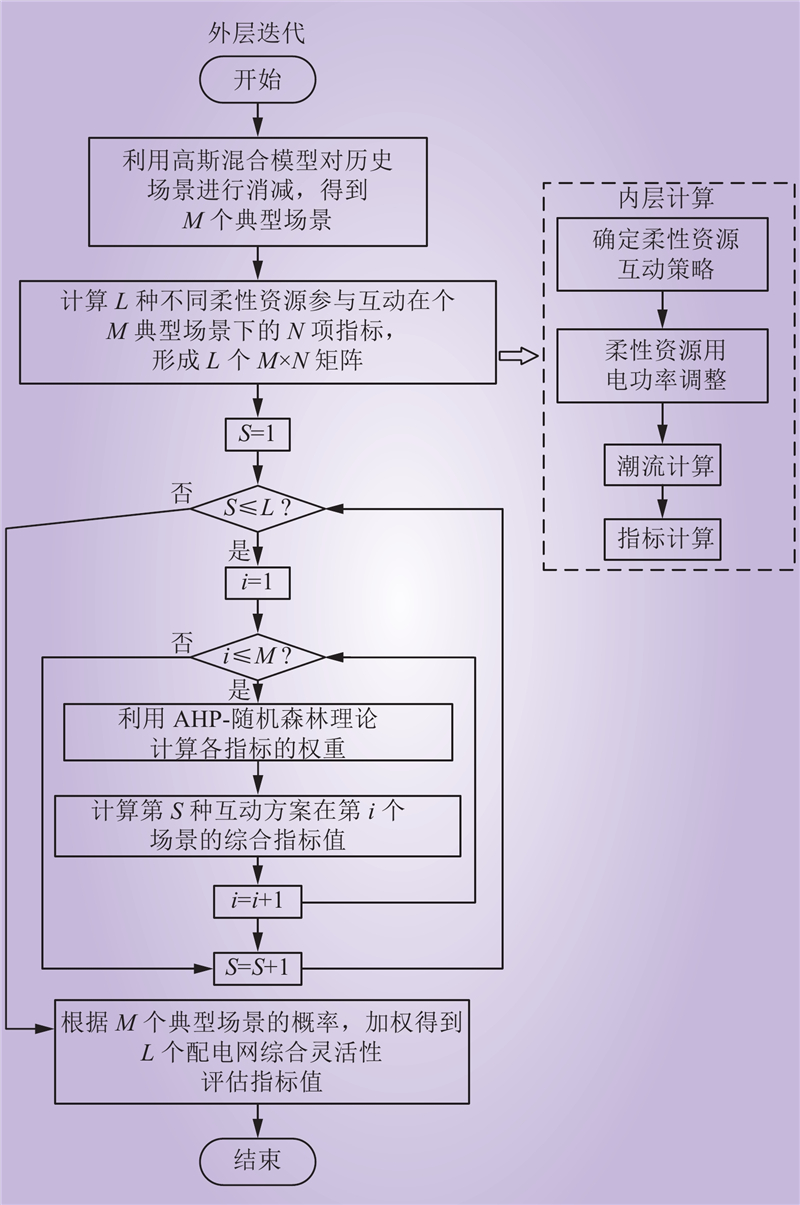
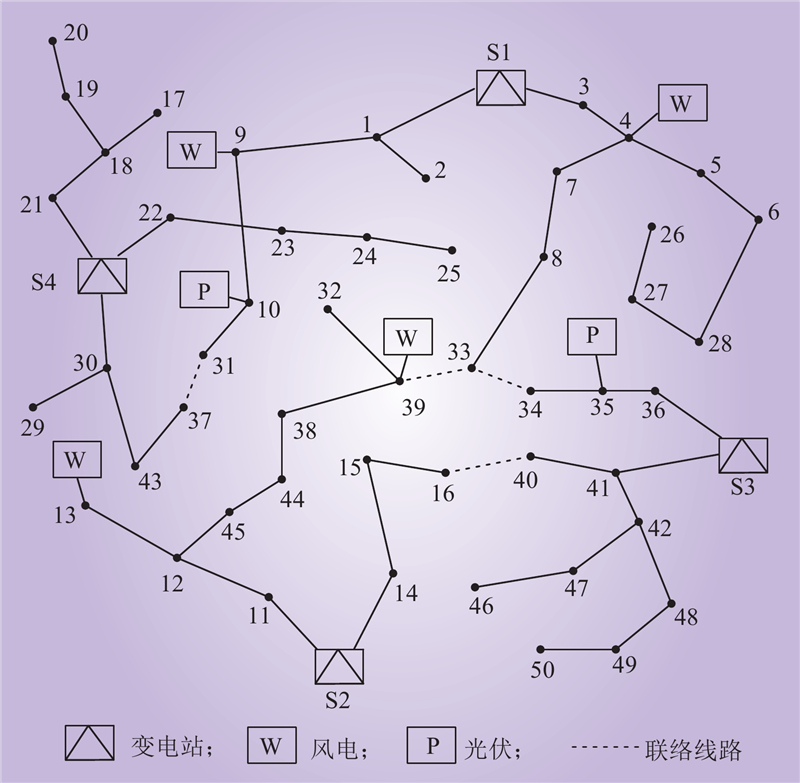
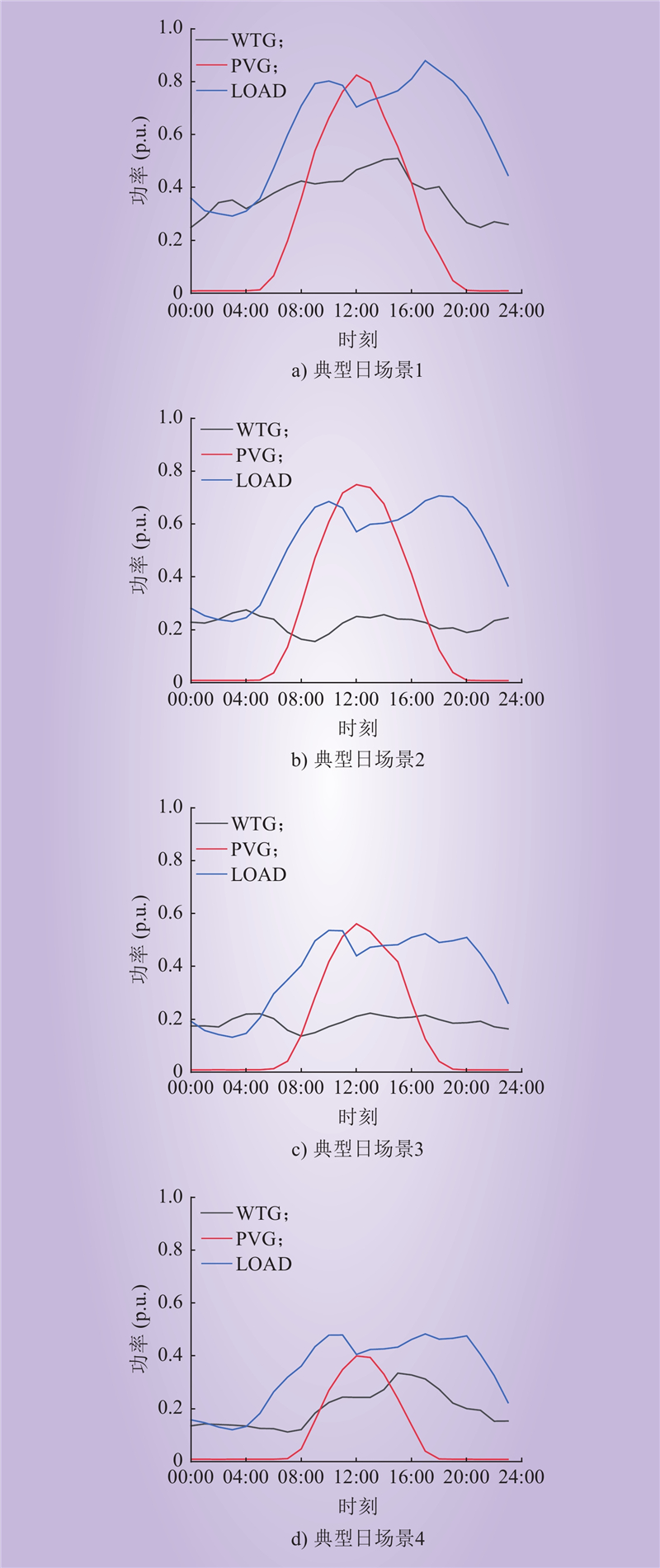
| 1 |
郑国光. 支撑“双碳” 目标实现的问题辨识与关键举措研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 1- 8.
|
|
ZHENG Guoguang. Problem identification and key measures to support the achievement of carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 1- 8.
|
| 2 |
叶宇剑, 袁泉, 汤奕. 面向双碳目标的交通网-电网耦合网络中电动汽车负荷低碳优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 72- 79.
|
|
YE Yujian, YUAN Quan, TANG Yi. Electric vehicle charging demand low carbon optimization in traffic-grid coupling networks towards "dual carbon" goal[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 72- 79.
|
| 3 |
王彩霞, 时智勇, 梁志峰, 等. 新能源为主体电力系统的需求侧资源利用关键技术及展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (16): 37- 48.
|
|
WANG Caixia, SHI Zhiyong, LIANG Zhifeng, et al. Key technologies and prospects of demand-side resource utilization for power systems dominated by renewable energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (16): 37- 48.
|
| 4 |
卓映君, 周保荣, 姚文峰, 等. “双碳” 目标下南方区域能源电力消费及负荷特性预测[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (9): 132- 140.
|
|
ZHUO Yingjun, ZHOU Baorong, YAO Wenfeng, et al. Prediction of energy and electricity consumption and load characteristics in the southern region under the carbon peak and carbon neutrality target[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (9): 132- 140.
|
| 5 |
彭道刚, 税纪钧, 王丹豪, 等. “双碳” 背景下虚拟电厂研究综述[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (5): 602- 615.
|
|
PENG Daogang, SHUI Jijun, WANG Danhao, et al. Review of virtual power plant under the background of "dual carbon"[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (5): 602- 615.
|
| 6 |
任海波, 余波, 王奎, 等. “双碳” 背景下抽水蓄能电站的发展与展望[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2022, 40 (3): 25- 30.
|
|
REN Haibo, YU Bo, WANG Kui, et al. Development and prospect of pumped storage power station under double-carbon background[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2022, 40 (3): 25- 30.
|
| 7 |
刘鹏, 崔雪. 双碳背景下考虑市场份额偏好的发电侧市场均衡分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (2): 9- 17, 39.
|
|
LIU Peng, CUI Xue. Equilibrium analysis of power generation market considering market share preference un-der carbon-neutral goal[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (2): 9- 17, 39.
|
| 8 |
GE S Y, XU Z Y, LIU H, et al. Flexibility evaluation of active distribution networks considering probabilistic characteristics of uncertain variables[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2019, 13 (14): 3148- 3157.
|
| 9 |
米伟铭, 叶鹏, 张明理, 等. 基于云模型的新型配电系统灵活性评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (6): 2532- 2540.
|
|
MI Weiming, YE Peng, ZHANG Mingli, et al. Novel flexibility evaluation for distribution systems based on cloud models[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (6): 2532- 2540.
|
| 10 |
LIU S K, LIU L H, FAN Y P, et al. An integrated scheme for online dynamic security assessment based on partial mutual information and iterated random forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (4): 3606- 3619.
|
| 11 |
高亚静, 朱静, 程华新, 等. 计及不确定性因素基于多场景的主动配电系统短期供电能力评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (22): 6076- 6085.
|
|
GAO Yajing, ZHU Jing, CHENG Huaxin, et al. Evaluation on the short-term power supply capacity of active distribution system based on multiple scenarios considering uncertainties[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (22): 6076- 6085.
|
| 12 |
马杰, 李秋燕, 丁岩, 等. 含高渗透率可再生能源的配电网灵活性评价指标体系及计算方法[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2020, 32 (9): 99- 104, 112.
|
|
MA Jie, LI Qiuyan, DING Yan, et al. Flexibility evaluation index system and calculation method for distribution network with High-permeability renewable energy[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2020, 32 (9): 99- 104, 112.
|
| 13 |
陈垚煜, 江全元, 周自强, 等. 考虑典型场景的配电网调控方案灵活性评估方法[J]. 电力建设, 2019, 40 (7): 34- 40.
|
|
CHEN Yaoyu, JIANG Quanyuan, ZHOU Ziqiang, et al. An evaluation method on the flexibility of regulation methods in distribution network considering typical scene sets[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2019, 40 (7): 34- 40.
|
| 14 |
李亚平, 周竞, 鞠平, 等. 柔性负荷互动影响量化评估方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (17): 26- 32, 67.
|
|
LI Yaping, ZHOU Jing, JU Ping, et al. Quantitative assessment method for interactive impact of flexible load[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (17): 26- 32, 67.
|
| 15 |
陈海鹏, 周越豪, 赵畅, 等. 考虑高载能负荷参与的多时间尺度风电消纳调度[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 39- 51.
|
|
CHEN Haipeng, ZHOU Yuehao, ZHAO Chang, et al. Multi-time scale wind power consumption scheduling with high energy load participation is considered[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (6): 39- 51.
|
| 16 |
张蓬, 吕恭祥, 刘志杰, 等. 含电能路由器的配电网转供灵活性量化分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57 (5): 513- 520.
|
|
ZHANG Peng, LÜ Gongxiang, LIU Zhijie, et al. Load transfer flexibility analysis of distribution network with electric energy routers[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57 (5): 513- 520.
|
| 17 |
潘忠志, 孔宁, 王燕涛. 改进新能源消纳的配电网资源优化配置研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (6): 71- 78.
|
|
PAN Zhongzhi, KONG Ning, WANG Yantao. Joint optimal allocation method of energy-load-storage in power SupplyArea to improve new energy consumption capacity[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (6): 71- 78.
|
| 18 |
凡鹏飞, 李宝琴, 侯江伟, 等. 配电网分布式电源经济可承载力评估[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 196- 202.
|
|
FAN Pengfei, LI Baoqin, HOU Jiangwei, et al. Economic capacity assessment of renewables in distribution networks[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 196- 202.
|
| 19 |
杨彪, 颜伟, 莫静山. 考虑源荷功率随机性和相关性的主导节点选择与无功分区方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
|
YANG Biao, YAN Wei, MO Jingshan. Pilot-bus selection and network partitioning method considering randomness and correlation of source-load power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
| 20 |
李彬, 白雪峰, 王京菊, 等. 新型电力负荷管理系统发展的关键支撑技术研究[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (2): 1- 6.
|
|
LI Bin, BAI Xuefeng, WANG Jingju, et al. Research on key supporting technology for development of new power load management system[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (2): 1- 6.
|
| 21 |
MIRANDA V, RANITO J V, PROENCA L M. Genetic algorithms in optimal multistage distribution network planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2002, 9 (4): 1927- 1933.
|