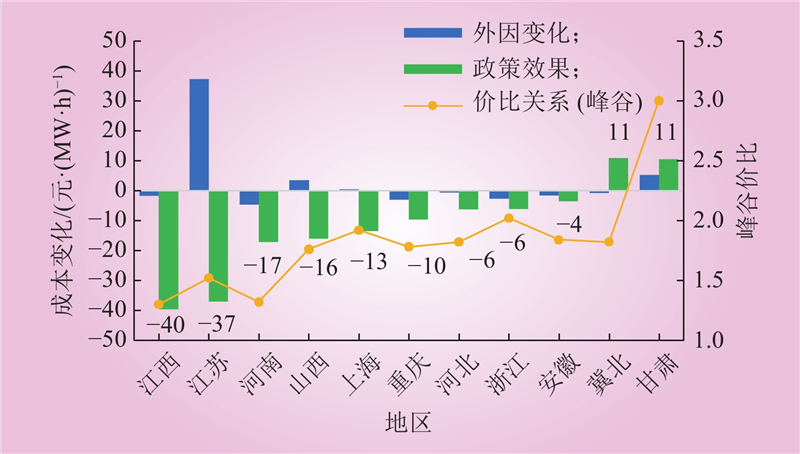
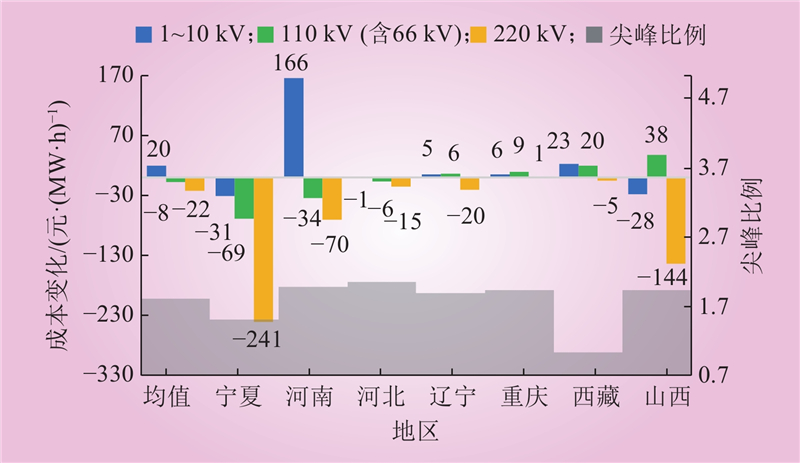
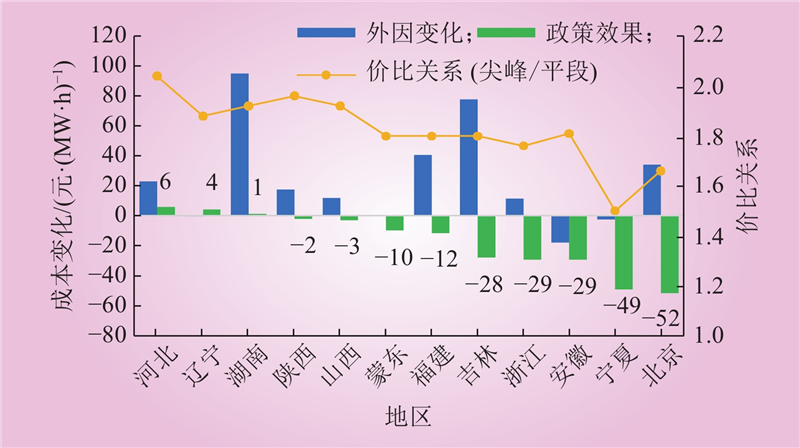
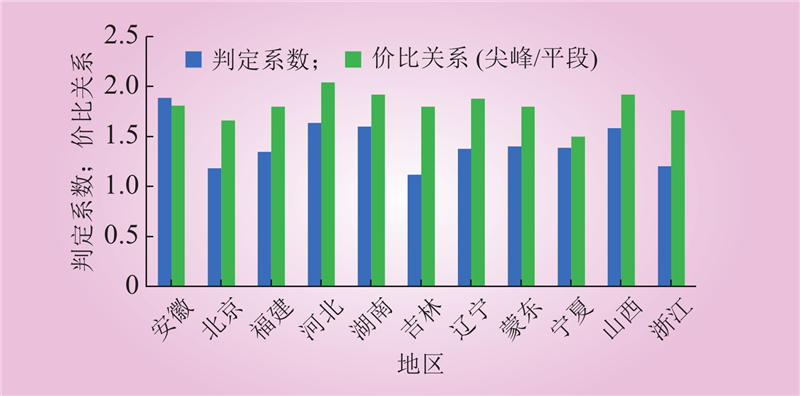
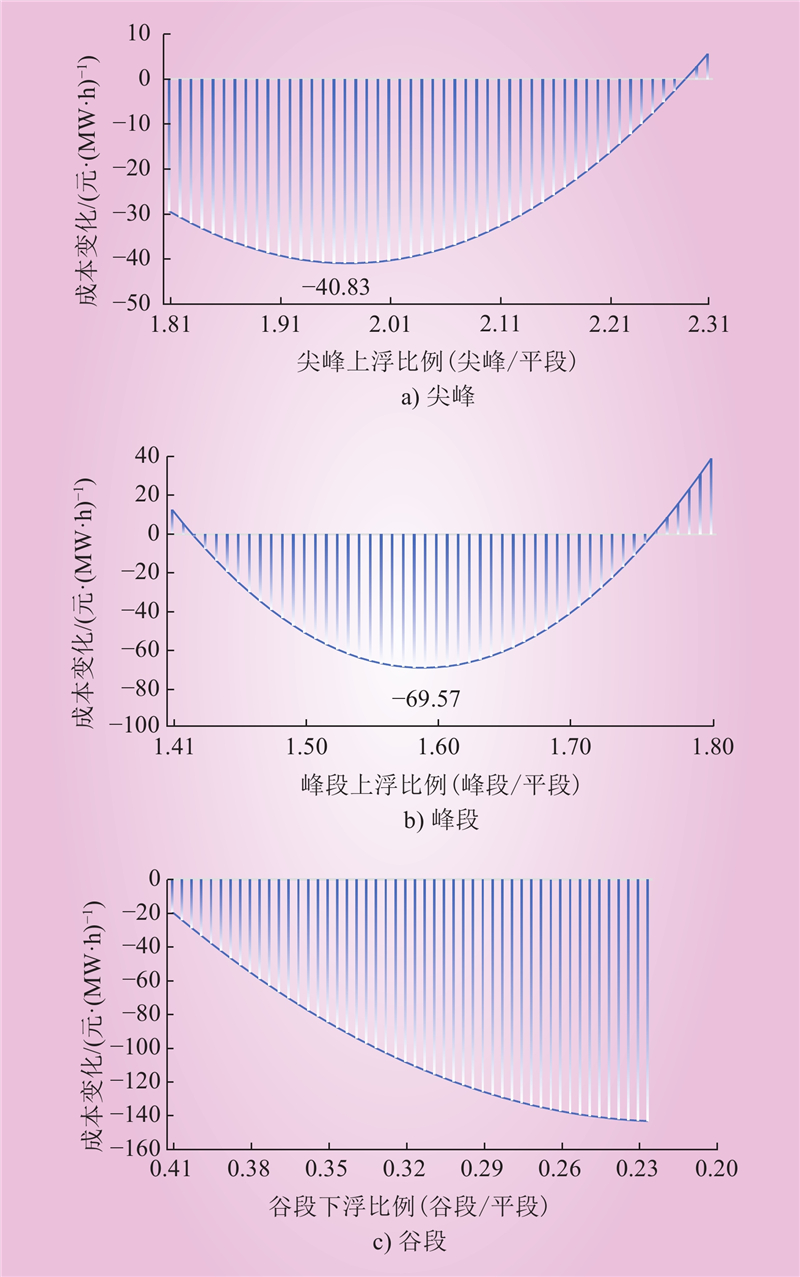
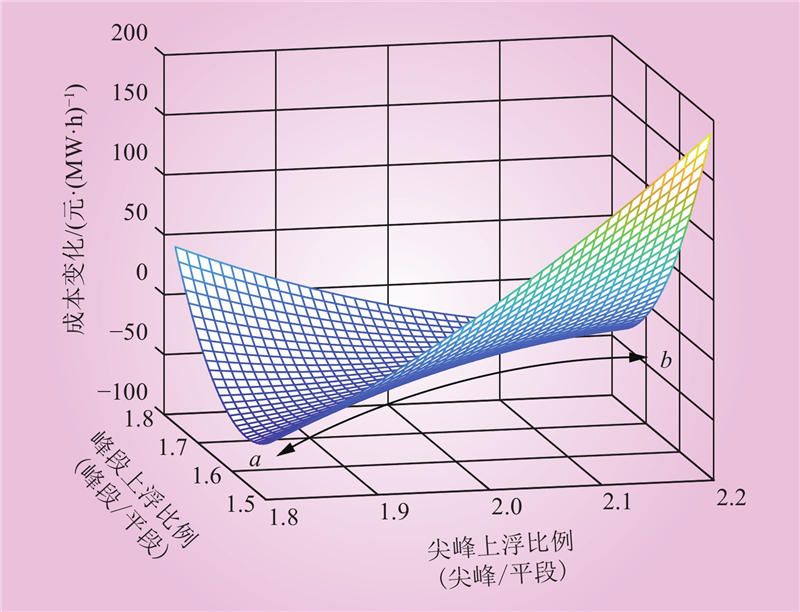
| 1 |
李东东, 汪露璐, 王维等. 考虑源荷互动的综合能源系统多目标双层规划[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (2): 527- 542.
|
|
LI Dongdong, WANG Luwei, WANG Wei, et al. Multi-objective bi-level planning for integrated energy systems considering source-load interaction[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (2): 527- 542.
|
| 2 |
万灿, 宋永华. 新能源电力系统概率预测理论与方法及其应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (1): 2- 16.
|
|
WAN Can, SONG Yonghua. Theories, methodologies and applications of probabilistic forecasting for power systems with renewable energy sources[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (1): 2- 16.
|
| 3 |
柳启俊. 面向智能电网的需求侧响应及其居民电价研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2016.
|
|
LIU Qijun. Electrical demand response in smart grid and its research of residential electrovalency[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2016.
|
| 4 |
欧华钰. 需求响应背景下分时电价研究综述[J]. 电气开关, 2023, 61 (5): 6- 11, 17.
|
|
OU Huayu. Summary of time-of-use research in a demand response environment[J]. Electric Switchgear, 2023, 61 (5): 6- 11, 17.
|
| 5 |
黄剑平. 基于用户响应行为的峰谷分时电价优化策略研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2022.
|
|
HUANG Jianping. Research on the optimization strategy for time-of-use prices based on customer response behavior[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2022.
|
| 6 |
黄刚. V2G模式下峰谷电价方案评估模型研究[D]. 宜昌: 三峡大学, 2018.
|
|
HUANG Gang. Study on the evaluation model of peak valley electricity price scheme under V2G model[D]. Yichang: China Three Gorges University, 2018.
|
| 7 |
付强. 考虑峰谷分时电价影响的电网规划及其经济效益分析研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2018.
|
|
FU Qiang. Research on power grid planning considering influence of peak-valley time-of-use power price and its economic benefits analysis[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2018.
|
| 8 |
李国荣. 基于用户需求响应的分时电价优化研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2023.
|
|
LI Guorong. Research on time-of-use price optimization based on user's demand response[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023.
|
| 9 |
汪磊, 杨贺钧, 马英浩, 等. 考虑多重评价指标的多时段分时电价优化模型[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (6): 54- 59.
|
|
WANG Lei, YANG Hejun, MA Yinghao, et al. Optimization model of multi-period time of use strategy considering multiple assessment indices[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (6): 54- 59.
|
| 10 |
王星华, 刘升伟, 陈豪君, 等. 考虑用户差异性的售电公司需求响应电价模型[J]. 电力建设, 2019, 40 (9): 116- 123.
|
|
WANG Xinghua, LIU Shengwei, CHEN Haojun, et al. Demand response pricing model for power sales companies considering user differences[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2019, 40 (9): 116- 123.
|
| 11 |
谈金晶, 王蓓蓓, 李扬. 基于多智能体的用户分时电价响应模型[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36 (2): 257- 263.
|
|
TAN Jinjing, WANG Beibei, LI Yang. Modeling of user response to time-of-use price based on multi-agent technology[J]. Power System Technology, 2012, 36 (2): 257- 263.
|
| 12 |
石宇航. 降低企业用电成本案例分析[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2018, (13): 44- 45.
|
| 13 |
方彬楠, 冉黎黎. 引导工商业错峰用电 北京分时电价进阶[N]. 北京商报, 2023-08-22(002).
|
| 14 |
张延伟, 高昌辉. 中国省域间碳排放权交易机制检验——基于双重差分法[J]. 时代经贸, 2023, 20 (9): 5- 9.
|
| 15 |
杨新梅, 周瑞辉. 设立国家高新区能否驱动城市绿色发展: 基于双重差分法的经验数据[J]. 中国环境管理, 2023, 15 (3): 51- 61.
|
|
YANG Xinmei, ZHOU Ruihui. Can national high-tech zones drive urban green development? —empirical data based on DID[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 15 (3): 51- 61.
|
| 16 |
张科, 熊子怡, 黄细嘉, 等. 红色旅游发展与革命老区城乡收入差距——基于双重差分法的经验分析[J]. 中国农村经济, 2023, (5): 103- 121.
|
|
ZHANG Ke, XIONG Ziyi, HUANG Xijia, et al. Red tourism and urban-rural income gap in old revolutionary base areas: an empirical analysis based on the difference-in-differences method[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2023, (5): 103- 121.
|
| 17 |
赖玲玲, 程跃. 战略性新兴产业政策对企业创新绩效的影响研究——基于双重差分法的准自然实验[J]. 现代管理科学, 2022, (5): 98- 108.
|
| 18 |
翟玉鹏, 曹俊文. 基于双重差分法的我国差别电价政策对电力消费强度影响研究[J]. 电力与能源, 2018, 39 (6): 725- 732.
|
|
ZHAI Yupeng, CAO Junwen. Influence of China's differential price policy on electricity consumption intensity based on difference-in-difference method[J]. Power & Energy, 2018, 39 (6): 725- 732.
|
| 19 |
刘力铭. 分时电价项目下负荷削峰效果的影响因子识别与分析研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学(保定), 2019.
|
|
LIU Liming. Research on identification and analysis of impact factors for peak demand reduction under the time of use programs [D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University, 2019.
|
| 20 |
唐文升, 王阳, 张煜等. 基于多维价格弹性系数的分时电价对负荷特性影响机理[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (2): 202- 211.
|
|
TANG Wensheng, WANG Yang, ZHANG Yu, et al. Influence mechanism of time-of-use electricity prices on industry load characteristics based on multi-dimensional price elasticity coefficient matrix[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (2): 202- 211.
|
| 21 |
田佳垚, 冯自平, 胡亚飞等. 基于多元回归模型的燃气热泵系统制热性能分析[J]. 热能动力工程, 2023, 38 (6): 129- 136.
|
|
TIAN Jiayao, FENG Ziping, HU Yafei, et al. Analysis of heating performance of gas engine-driven heat pump system based on multiple regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2023, 38 (6): 129- 136.
|