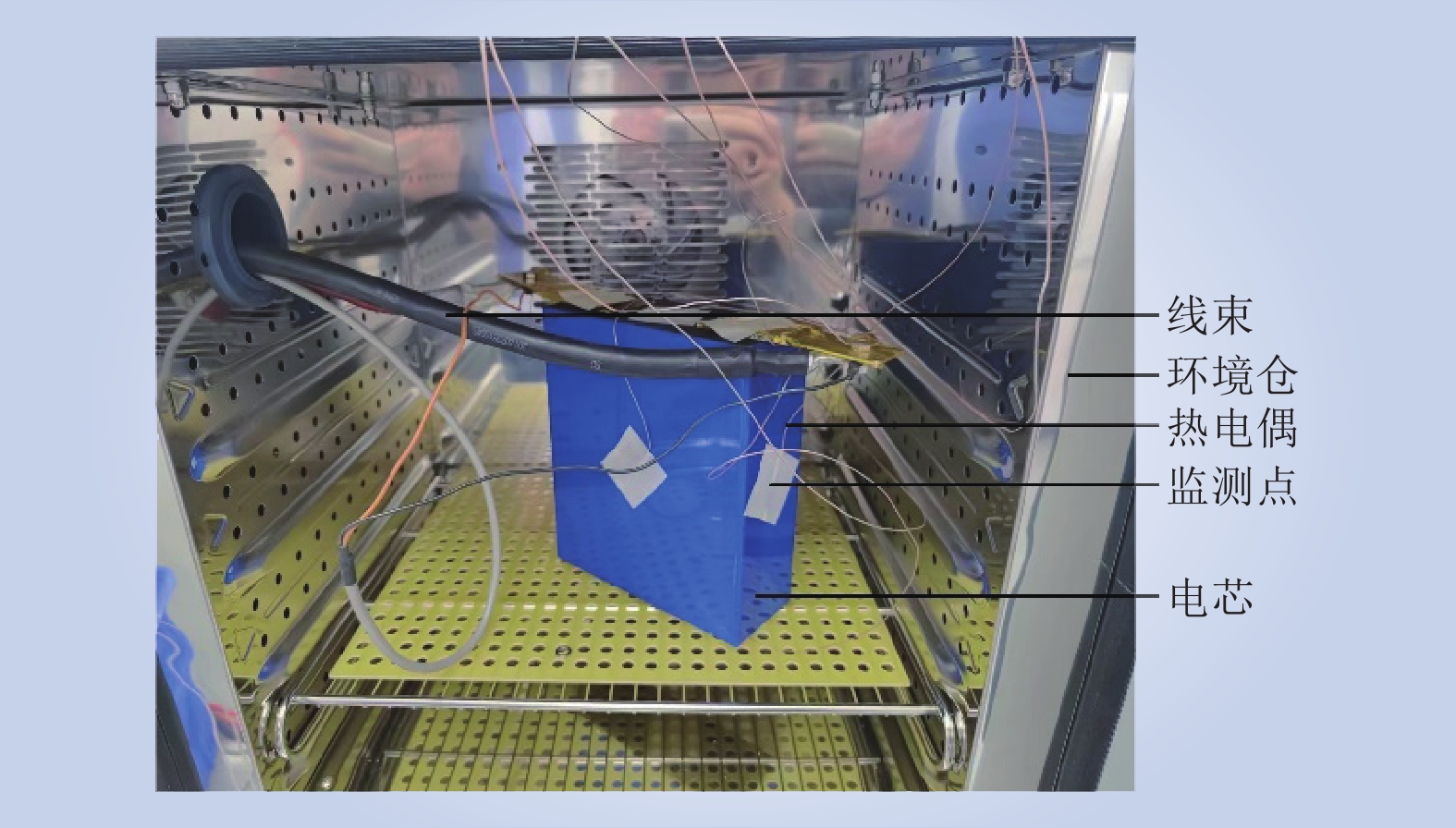
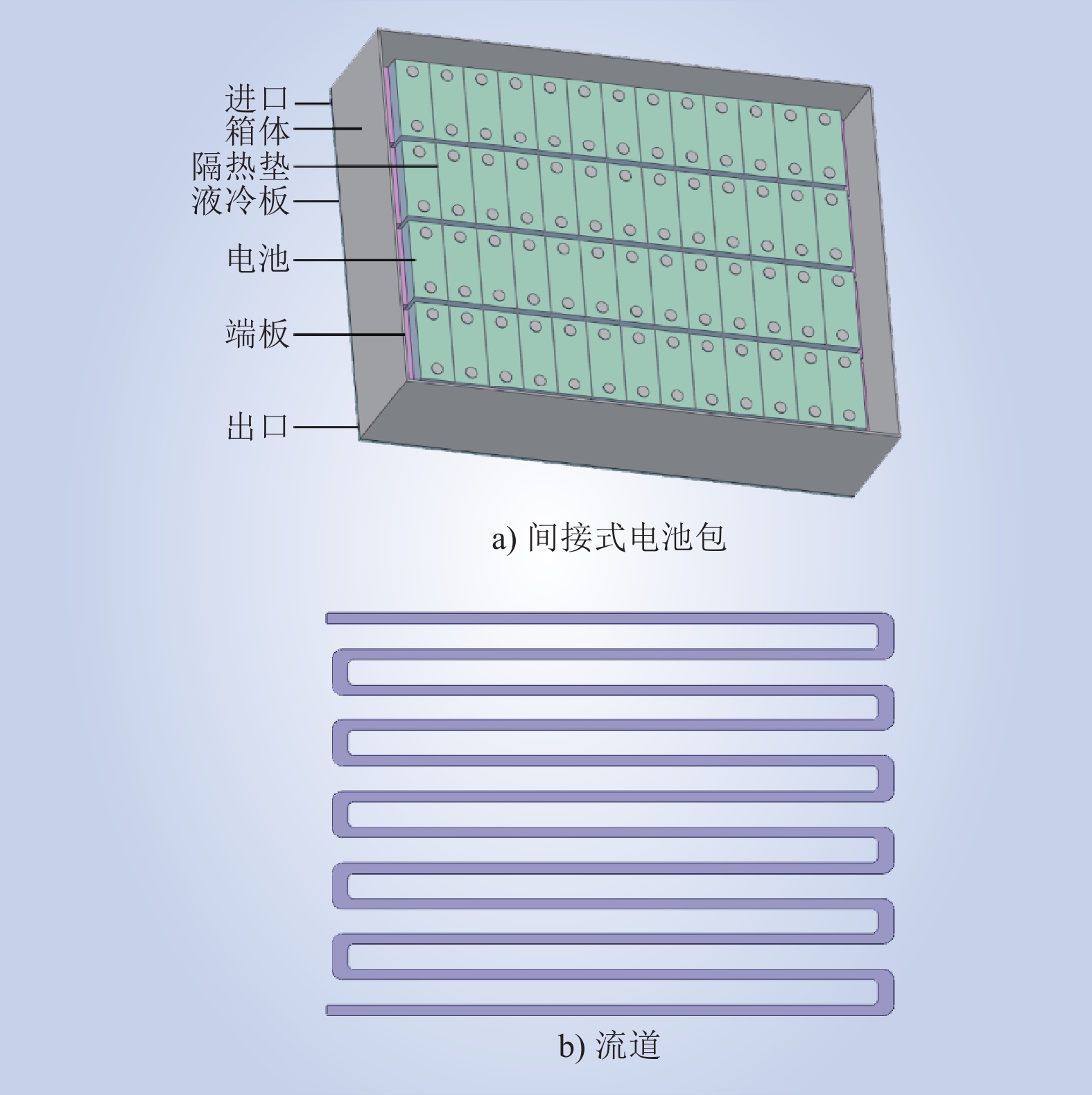
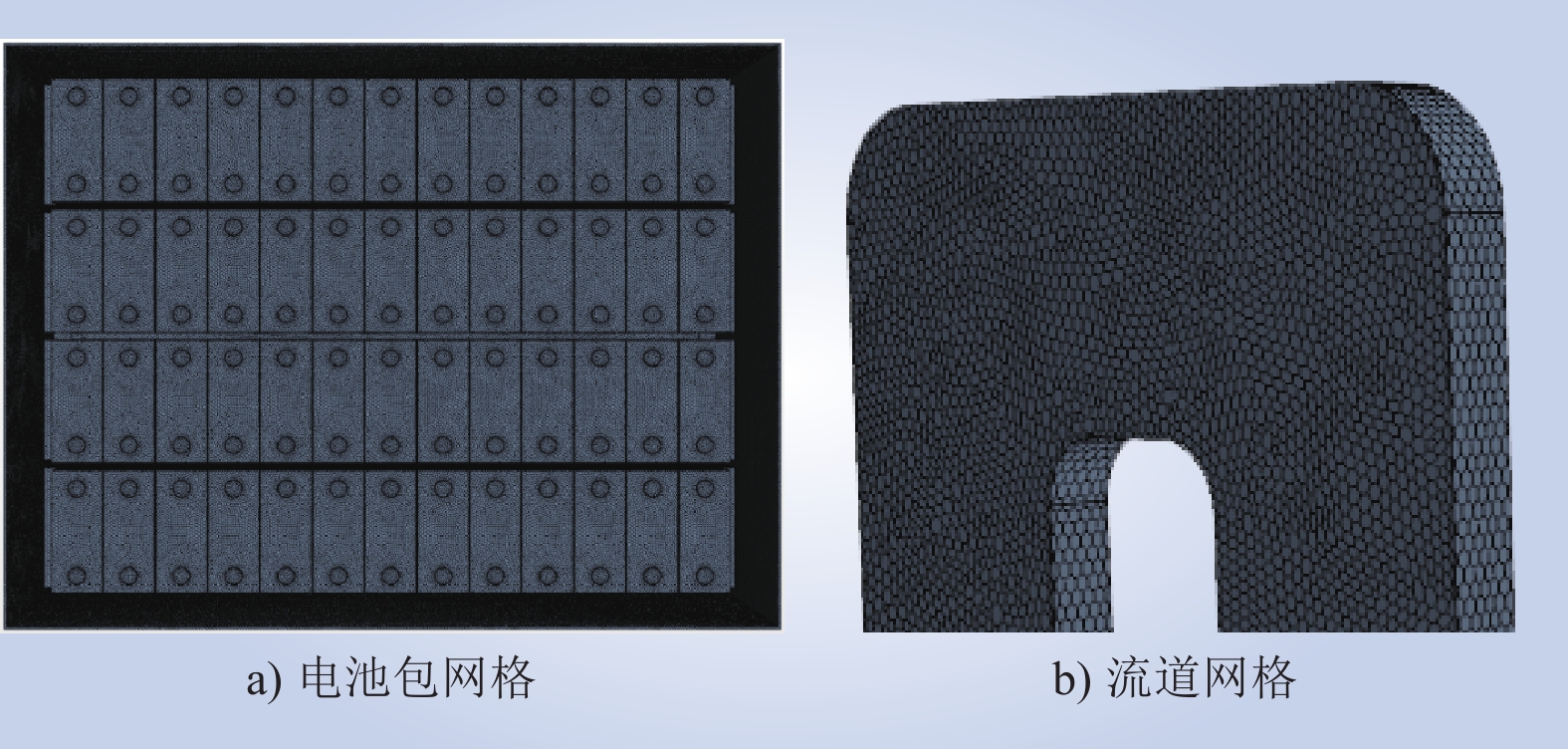
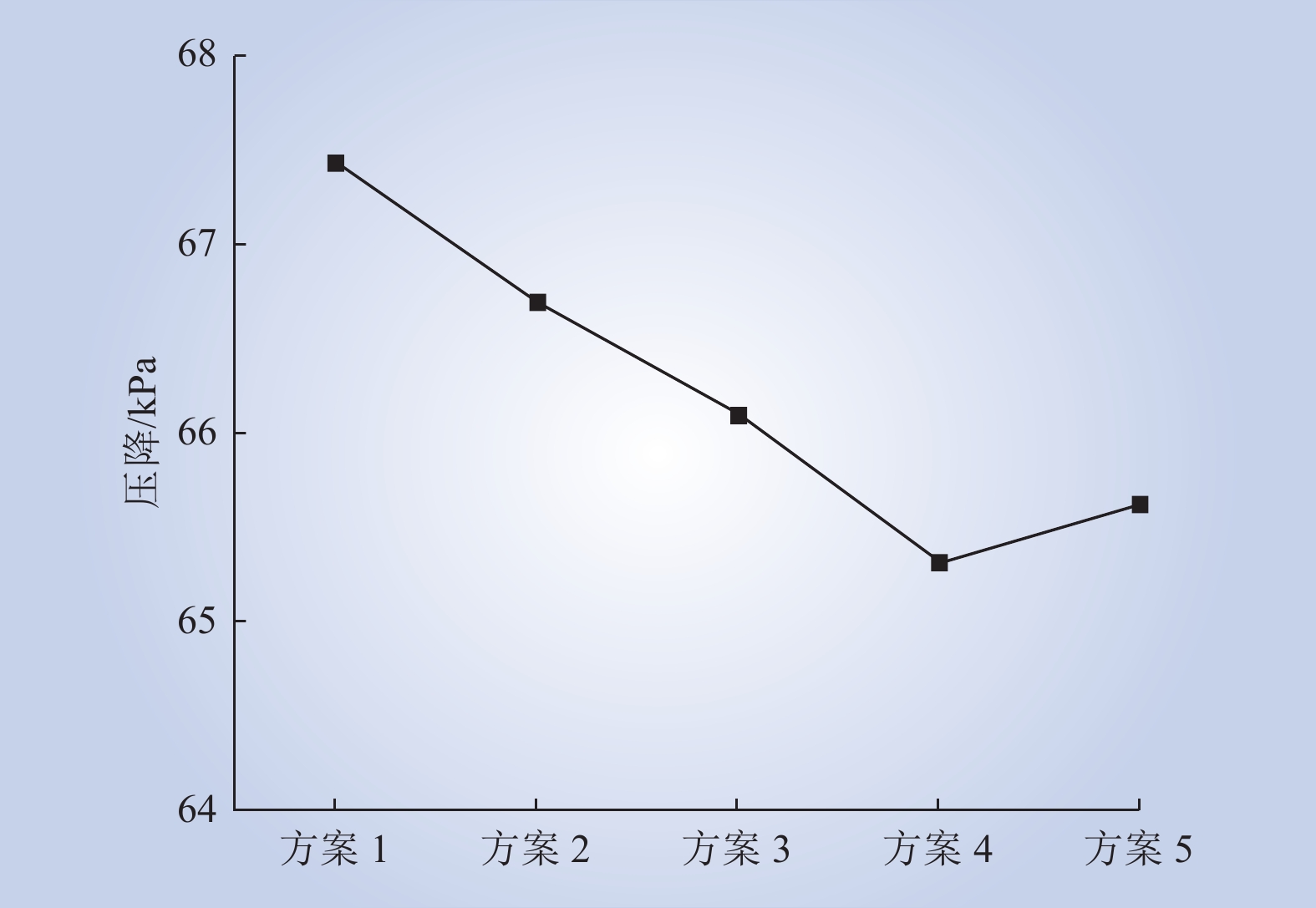
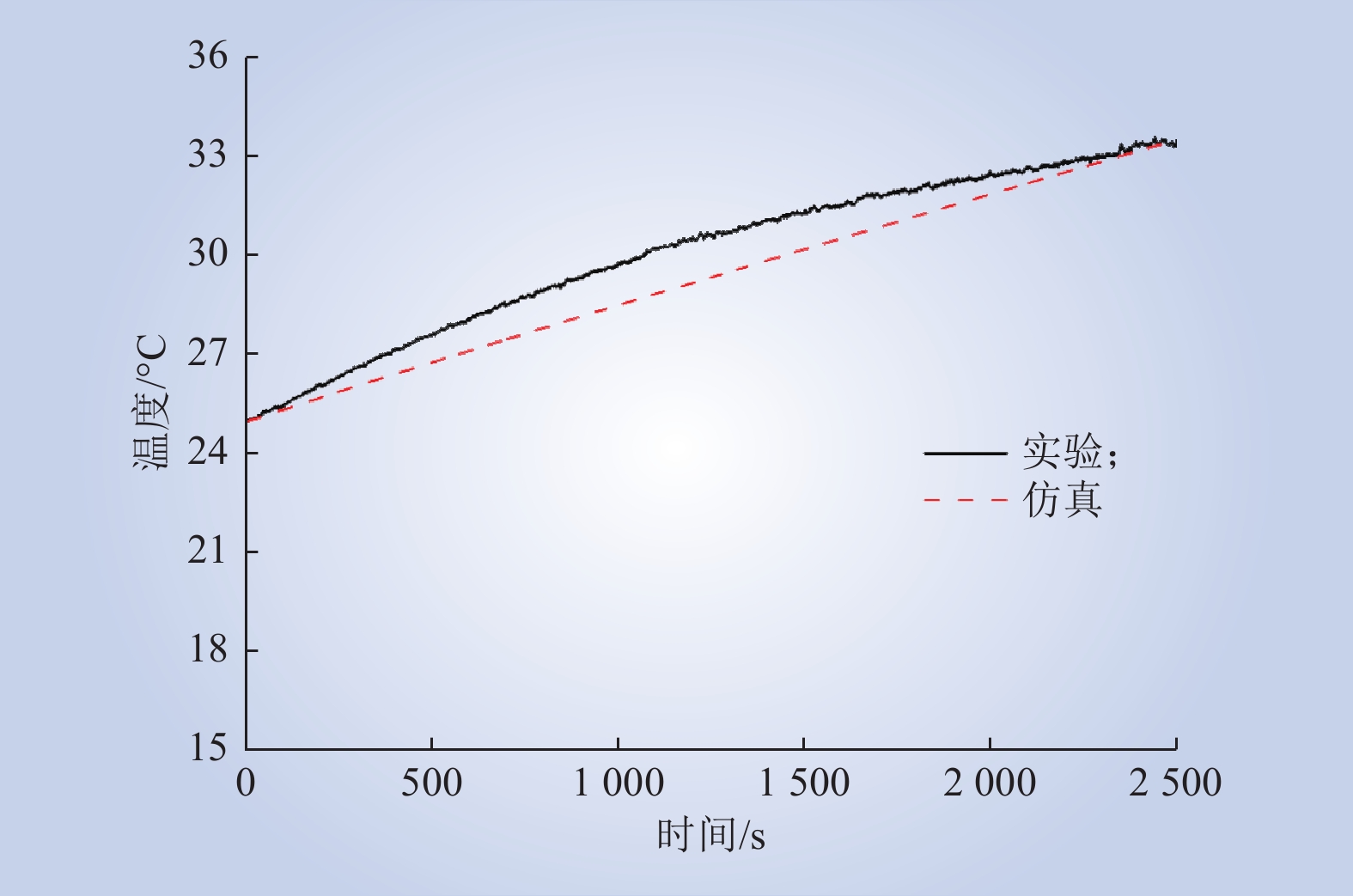
| 1 |
杨续来, 袁帅帅, 杨文静, 等. 锂离子动力电池能量密度特性研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59 (6): 239- 254.
|
|
YANG Xulai, YUAN Shuaishuai, YANG Wenjing, et al. Research progress on energy density of Li-ion batteries for EVs[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59 (6): 239- 254.
|
| 2 |
郎伟强, 楼鑫, 叶加炜, 等. 新能源系统中的储能技术分析[J]. 电子技术, 2022, 51 (10): 172- 173.
|
|
LANG Weiqiang, LOU Xin, YE Jiawei, et al. Analysis of energy storage technology in new energy system[J]. Electronic Technology, 2022, 51 (10): 172- 173.
|
| 3 |
俞恩科, 陈梁金. 大规模电力储能技术的特性与比较[J]. 浙江电力, 2011, 30 (12): 4- 8.
|
|
YU Enke, CHEN Liangjin. Characteristics and comparison of large-scale electric energy storage technologies[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2011, 30 (12): 4- 8.
|
| 4 |
刘阳, 滕卫军, 谷青发, 等. 规模化多元电化学储能度电成本及其经济性分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12 (1): 312- 318.
|
|
LIU Yang, TENG Weijun, GU Qingfa, et al. Scaled-up diversified electrochemical energy storage LCOE and its economic analysis[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12 (1): 312- 318.
|
| 5 |
KIM J, OH J, LEE H. Review on battery thermal management system for electric vehicles[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 149, 192- 212.
|
| 6 |
VISHNUMURTHY K A, GIRISH K H. A comprehensive review of battery technology for E-mobility[J]. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2021, 98 (10): 100173.
|
| 7 |
TERADA N, YANAGI T, ARAI S, et al. Development of lithium batteries for energy storage and EV applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 100 (1/2): 80- 92.
|
| 8 |
DOYLE M, FULLER T F, NEWMAN J. Modeling of galvanostatic charge and discharge of the lithium/polymer/insertion cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1993, 140 (6): 1526- 1533.
|
| 9 |
CHEN Z Y, XIONG R, SUN F C. Research status and analysis for battery safety accidents in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55 (24): 93.
|
| 10 |
BAI F F, CHEN M B, SONG W J, et al. Thermal management performances of PCM/water cooling-plate using for lithium-ion battery module based on non-uniform internal heat source[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 126, 17- 27.
|
| 11 |
CHEN K, WU W X, YUAN F, et al. Cooling efficiency improvement of air-cooled battery thermal management system through designing the flow pattern[J]. Energy, 2019, 167, 781- 790.
|
| 12 |
PESARAN A A. Battery thermal models for hybrid vehicle simulations[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 110 (2): 377- 382.
|
| 13 |
FAN Y Q, BAO Y, LING C, et al. Experimental study on the thermal management performance of air cooling for high energy density cylindrical lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 155, 96- 109.
|
| 14 |
CHEN D F, JIANG J C, KIM G H, et al. Comparison of different cooling methods for lithium ion battery cells[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 94, 846- 854.
|
| 15 |
ZHAO Q A, WU H W, WANG Z H, et al. Numerical research on lithium-ion battery thermal management utilizing a novel cobweb-like channel cooling plate exchanger[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2022, 10, 992779.
|
| 16 |
孔为, 金劲涛, 陆西坡, 等. 对称蛇形流道锂离子电池冷却性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11 (7): 2258- 2265.
|
|
KONG Wei, JIN Jintao, LU Xipo, et al. Study on cooling performance of lithium ion batteries with symmetrical serpentine channel[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11 (7): 2258- 2265.
|
| 17 |
WU M S, HUNG Y H, WANG Y Y, et al. Heat dissipation behavior of the nickel/metal hydride battery[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147 (3): 930.
|
| 18 |
WU W X, WANG S F, WU W, et al. A critical review of battery thermal performance and liquid based battery thermal management[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 182, 262- 281.
|
| 19 |
ROE C, FENG X N, WHITE G, et al. Immersion cooling for lithium-ion batteries-a review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 525, 231094.
|
| 20 |
NELSON P, DEES D, AMINE K, et al. Modeling thermal management of lithium-ion PNGV batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 110 (2): 349- 356.
|
| 21 |
DENG Y W, FENG C L, JIAQIANG E, et al. Effects of different coolants and cooling strategies on the cooling performance of the power lithium ion battery system: a review[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 142, 10- 29.
|
| 22 |
田钧, 高帅. 基于浸没式技术的纯电动汽车电池包热管理方案解析[J]. 汽车电器, 2023, (5): 6- 8.
|
|
TIAN Jun, GAO Shuai. Solution analysis of battery pack thermal management for pure electric vehicle based on immersion technology[J]. Auto Electric Parts, 2023, (5): 6- 8.
|
| 23 |
CHEN S C, WAN C C, WANG Y Y. Thermal analysis of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 140 (1): 111- 124.
|
| 24 |
JARRETT A, KIM I Y. Design optimization of electric vehicle battery cooling plates for thermal performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196 (23): 10359- 10368.
|
| 25 |
路帅. 锂离子动力电池模组热场仿真及散热控制[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
LU Shuai. Thermal field simulation and heat dissipation control of lithium ion power battery module[D]. Jilin: Northeast Dianli University, 2021.
|
| 26 |
BERNARDI D, PAWLIKOWSKI E, NEWMAN J. A general energy balance for battery systems[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132 (1): 5- 12.
|
| 27 |
吕超, 张爽, 朱世怀, 等. 储能锂离子电池包强制风冷系统热仿真分析与优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (12): 48- 55.
|
|
LÜ Chao, ZHANG Shuang, ZHU Shihuai, et al. Thermal simulation analysis and optimization of forced air cooling system for energy storage lithium-ion battery pack[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (12): 48- 55.
|
| 28 |
王明强, 郭月明, 许淘淘, 等. 锂离子动力电池组发热功率试验研究[J]. 汽车零部件, 2020, (5): 69- 72.
|
|
WANG Mingqiang, GUO Yueming, XU Taotao, et al. Experiment research on the heating power of lithium-ion battery module[J]. Automobile Parts, 2020, (5): 69- 72.
|
| 29 |
HUO Y T, RAO Z H, LIU X J, et al. Investigation of power battery thermal management by using mini-channel cold plate[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 89, 387- 395.
|
| 30 |
STERN F, WILSON R V, COLEMAN H W, et al. Comprehensive approach to verification and validation of CFD simulations—part 1: methodology and procedures[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2001, 123 (4): 793- 802.
|
| 31 |
安富强, 赵洪量, 程志, 等. 纯电动车用锂离子电池发展现状与研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2019, 41 (1): 22- 42.
|
|
AN Fuqiang, ZHAO Hongliang, CHENG Zhi, et al. Development status and research progress of power battery for pure electric vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2019, 41 (1): 22- 42.
|
| 32 |
卢子敬, 李子寿, 郭相国, 等. 基于多目标人工蜂鸟算法的电-氢混合储能系统最优配置[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 33- 42.
|
|
LU Zijing, LI Zishou, GUO Xiangguo, et al. Optimal configuration of electricity-hydrogen hybrid energy storage system based on multi-objective artificial hummingbird algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 33- 42.
|
| 33 |
张媛, 夏向阳, 岳家辉, 等. 基于电池簇放电电量的电池堆不一致性在线监测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215, 227.
|
|
ZHANG Yuan, XIA Xiangyang, YUE Jiahui, et al. Online monitoring method of battery stack inconsistency based on discharge quantity of battery clusters[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215, 227.
|
| 34 |
余斌, 宋兴荣, 周挺, 等. 基于梅尔倒谱系数特征集的储能变流器开路故障诊断方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 34- 42.
|
|
YU Bin, SONG Xingrong, ZHOU Ting, et al. Open circuit fault diagnosis method of energy storage converter based on Mel cepstrum coefficient feature set[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 34- 42.
|
| 35 |
黎冲, 王成辉, 王高, 等. 基于数据驱动的锂离子电池健康状态估计技术[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|
|
LI Chong, WANG Chenghui, WANG Gao, et al. Technology of lithium-ion battery state-of-health assessment based on data-driven[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|