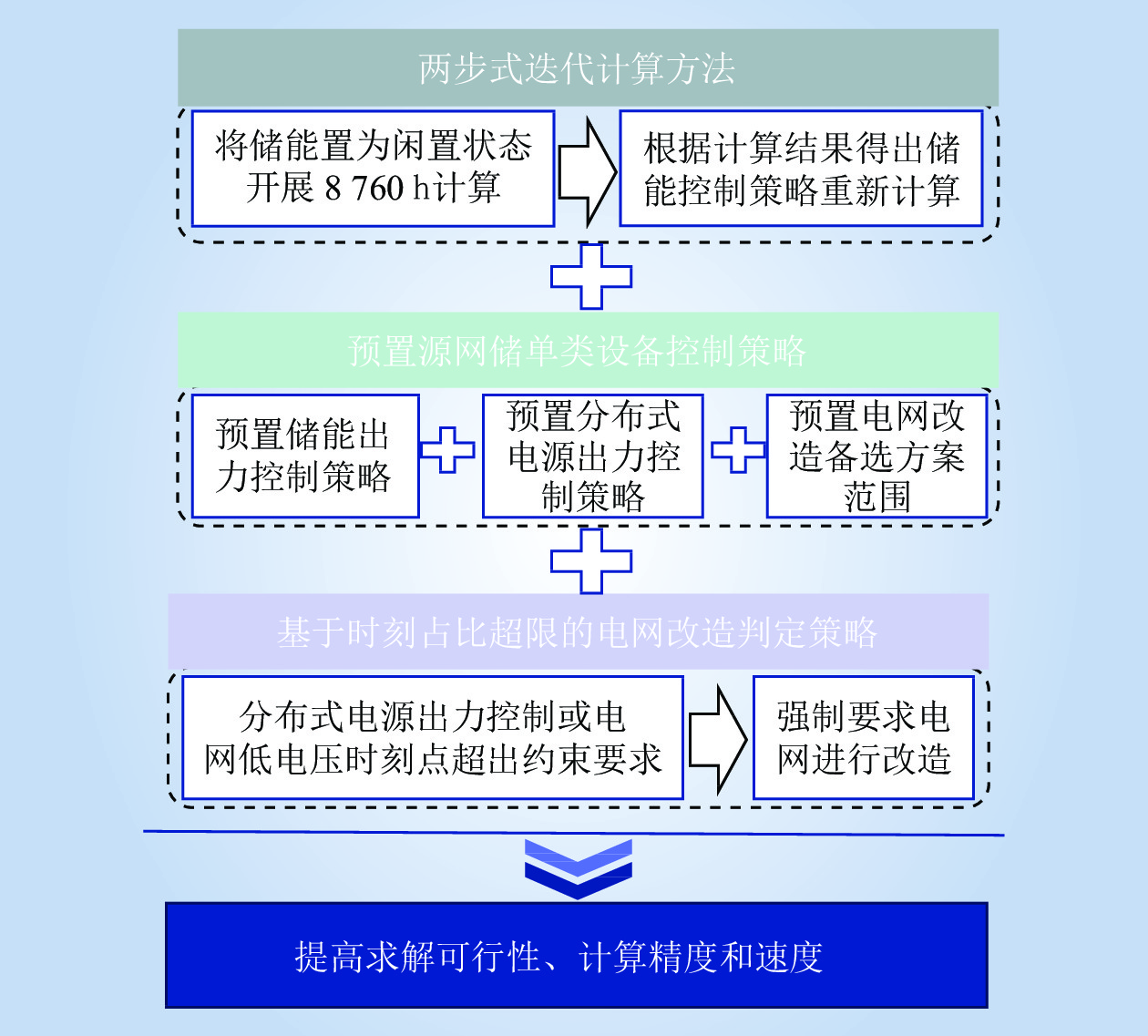
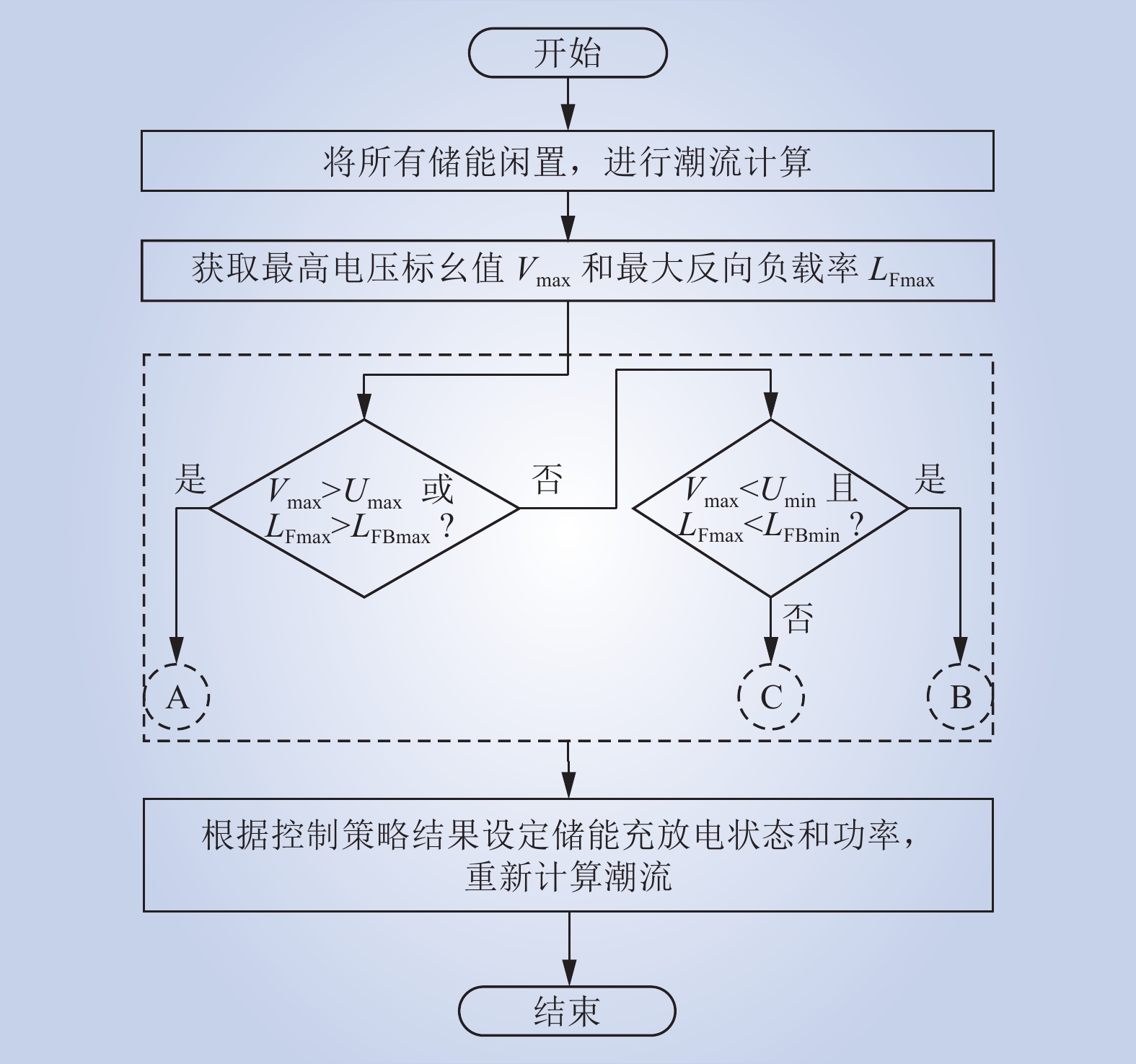
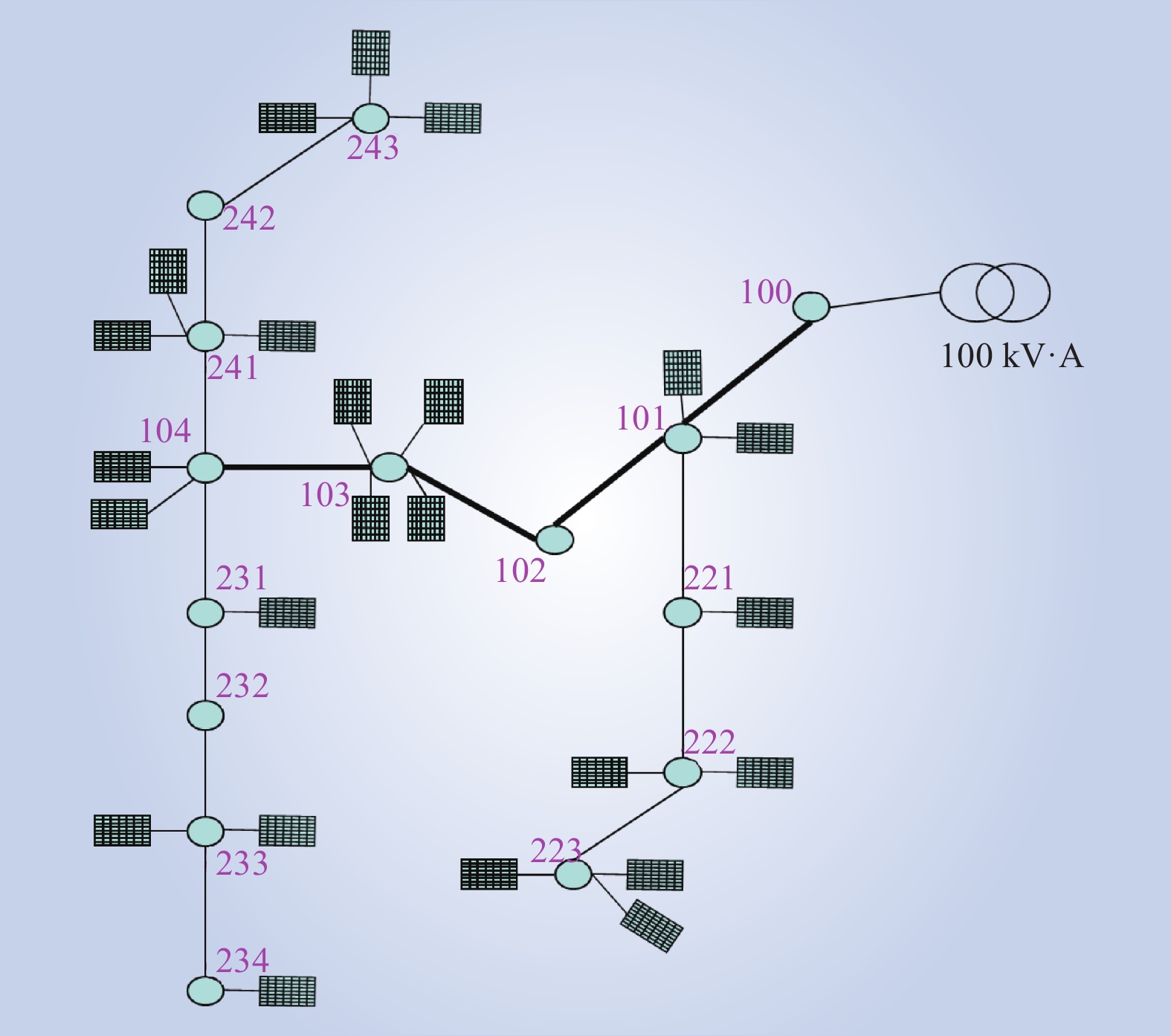
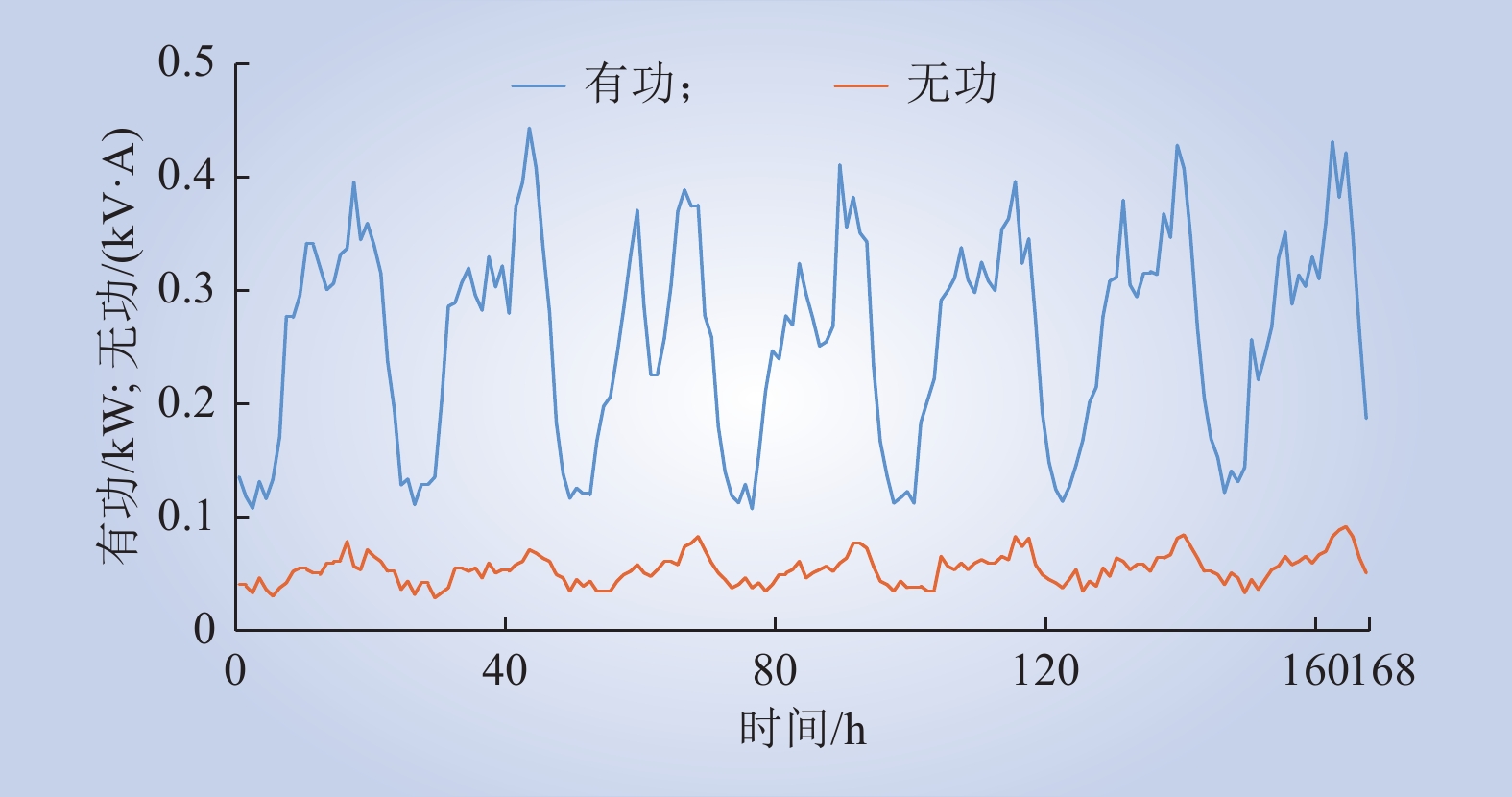
| 1 |
张珍珍, 吕清泉, 张健美. “双碳” 目标下分布式光伏发电技术的研究进展及展望[J]. 太阳能, 2023, (1): 17- 21.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenzhen, LYU Qingquan, ZHANG Jianmei. Research progress and prospect of distributed PV power generation technology under the goal of emission peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Solar Energy, 2023, (1): 17- 21.
|
| 2 |
丁明, 王伟胜, 王秀丽, 等. 大规模光伏发电对电力系统影响综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (1): 1- 14.
|
|
DING Ming, WANG Weisheng, WANG Xiuli, et al. A review on the effect of large-scale PV generation on power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (1): 1- 14.
|
| 3 |
国家发展和改革委员会, 国家能源局, 等. “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发改能源〔2021〕1445号)[Z].
|
| 4 |
黄碧斌, 洪博文, 胡静, 等. 分布式光伏发电技术特性及对电力系统的影响[J]. 大众科技, 2016, 18 (1): 41- 43.
|
|
HUANG Bibin, HONG Bowen, HU Jing, et al. Technical characteristics of distributed photovoltaic power generation and its effects on power system[J]. Popular Science & Technology, 2016, 18 (1): 41- 43.
|
| 5 |
赵波, 肖传亮, 徐琛, 等. 基于渗透率的区域配电网分布式光伏并网消纳能力分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (21): 105- 111.
|
|
ZHAO Bo, XIAO Chuanliang, XU Chen, et al. Penetration based accommodation capacity analysis on distributed photovoltaic connection in regional distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (21): 105- 111.
|
| 6 |
黄碧斌, 李琼慧, 高菲, 等. 高渗透率分布式光伏发电接入农村电网的成本分析[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2017, 29 (6): 102- 106.
|
|
HUANG Bibin, LI Qionghui, GAO Fei, et al. Cost analysis of distributed photovoltaic integration with high penetration rate in rural network[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29 (6): 102- 106.
|
| 7 |
丁琦欣, 覃洪培, 万灿, 等. 基于机会约束规划的配电网分布式光伏承载能力评估[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
|
DING Qixin, QIN Hongpei, WAN Can, et al. Chance-constrained optimization-based distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity assessment of distribution networks[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
| 8 |
丁浩然, 张博, 唐巍, 等. 考虑源-网-荷-储协同的配电台区分布式光伏消纳能力评估[J]. 供用电, 2023, 40 (3): 2- 8, 31.
|
|
DING Haoran, ZHANG Bo, TANG Wei, et al. Evaluation of distributed photovoltaic consumption capacity of distribution station area considering source-network-load-storage collaboration[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2023, 40 (3): 2- 8, 31.
|
| 9 |
李世辉, 王琪, 贾晓卜, 等. 考虑热泵负荷和分布式光伏的配微网协调调度[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
|
LI Shihui, WANG Qi, JIA Xiaobo, et al. Coordinated scheduling of distribution networks and microgrids considering heat pump load and distributed photovoltaic[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
| 10 |
李振坤, 鲍新雨, 邵宇鹰, 等. 考虑多种调压措施的分布式光伏消纳能力研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46 (8): 10- 16.
|
|
LI Zhenkun, BAO Xinyu, SHAO Yuying, et al. Studying accommodation ability of distributed photovoltaic considering various voltage regulation measures[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46 (8): 10- 16.
|
| 11 |
张光儒, 任浩栋, 马振祺, 等. 提升配电网承载力和调节能力的整县分布式光伏储能配置方法[J]. 电气技术, 2022, 23 (11): 49- 55, 61.
|
|
ZHANG Guangru, REN Haodong, MA Zhenqi, et al. County-wide distributed photovoltaic energy storage configuration method to improve the carrying capacity and regulation capacity of distribution network[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2022, 23 (11): 49- 55, 61.
|
| 12 |
国务院办公厅. 关于转发国家发展改革委 国家能源局关于促进新时代新能源高质量发展实施方案的通知(国办函〔2022〕39号)[Z].
|
| 13 |
孙充勃, 李敬如, 罗凤章, 等. 考虑分布式电源接入的配电系统典型算例设计[J]. 电力建设, 2020, 41 (10): 47- 62.
|
|
SUN Chongbo, LI Jingru, LUO Fengzhang, et al. Typical case design of distribution system considering DG integration[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2020, 41 (10): 47- 62.
|
| 14 |
陈璨, 白明辉, 张婉明, 等. 分布式光伏边界渗透率快速定位及消纳方案择优[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 40- 50.
|
|
CHEN Can, BAI Minghui, ZHANG Wanming, et al. Fast positioning of marginal hosting capacity and optimal selection of accommodation scheme for distributed PVs[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 40- 50.
|
| 15 |
蒋向兵, 汤波, 余光正, 等. 面向新能源就地消纳的园区储能与电价协调优化方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (5): 51- 64.
|
|
JIANG Xiangbing, TANG Bo, YU Guangzheng, et al. Coordination and optimization method of park-level energy storage and electricity price for local accommodation of renewable energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (5): 51- 64.
|
| 16 |
李翠萍, 东哲民, 李军徽, 等. 提升配电网新能源消纳能力的分布式储能集群优化控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (23): 76- 83.
|
|
LI Cuiping, DONG Zhemin, LI Junhui, et al. Optimal control strategy of distributed energy storage cluster for prompting renewable energy accomodation in distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (23): 76- 83.
|
| 17 |
饶萍, 向月, 姚昊天, 等. 市场环境下配电网分布式光储协同规划[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 178- 188.
|
|
RAO Ping, XIANG Yue, YAO Haotian, et al. Collaborative planning for distribution network and PV-ESS in the marketization environment[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 178- 188.
|
| 18 |
黄碧斌, 李琼慧, 高菲. 计及电网改造的高渗透率分布式光伏优化规划[J]. 电力建设, 2015, 36 (10): 82- 87.
|
|
HUANG Bibin, LI Qionghui, GAO Fei. Distributed photovoltaic optimal planning with high permeability considering grid reinforcement[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2015, 36 (10): 82- 87.
|
| 19 |
梁志峰, 夏俊荣, 孙檬檬, 等. 数据驱动的配电网分布式光伏承载力评估技术研究[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (7): 2430- 2439.
|
|
LIANG Zhifeng, XIA Junrong, SUN Mengmeng, et al. Data driven assessment of distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity in distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (7): 2430- 2439.
|
| 20 |
国家能源局. 分布式电源接入电网承载力评估导则: DL/T 2041—2019[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社.
|
| 21 |
黄碧斌, 李琼慧. 储能支撑大规模分布式光伏接入的价值评估[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2016, 36 (6): 88- 93.
|
|
HUANG Bibin, LI Qionghui. Value assessment for energy storage in supporting large-scale integration of distributed PVs[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36 (6): 88- 93.
|