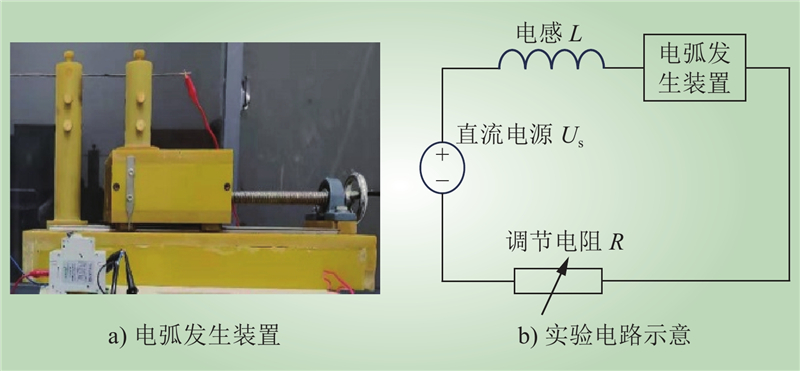
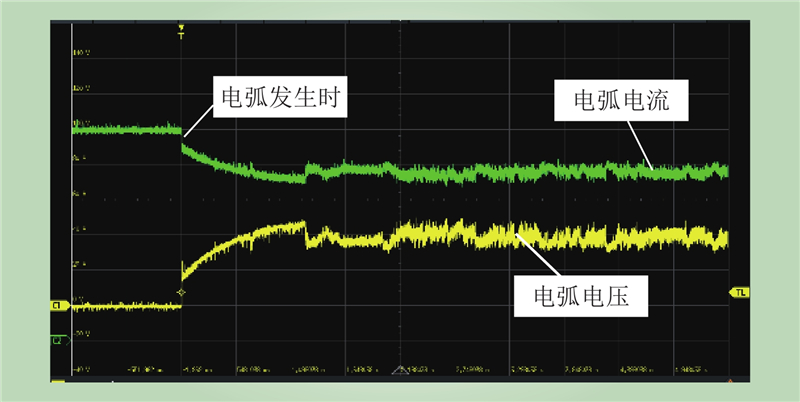
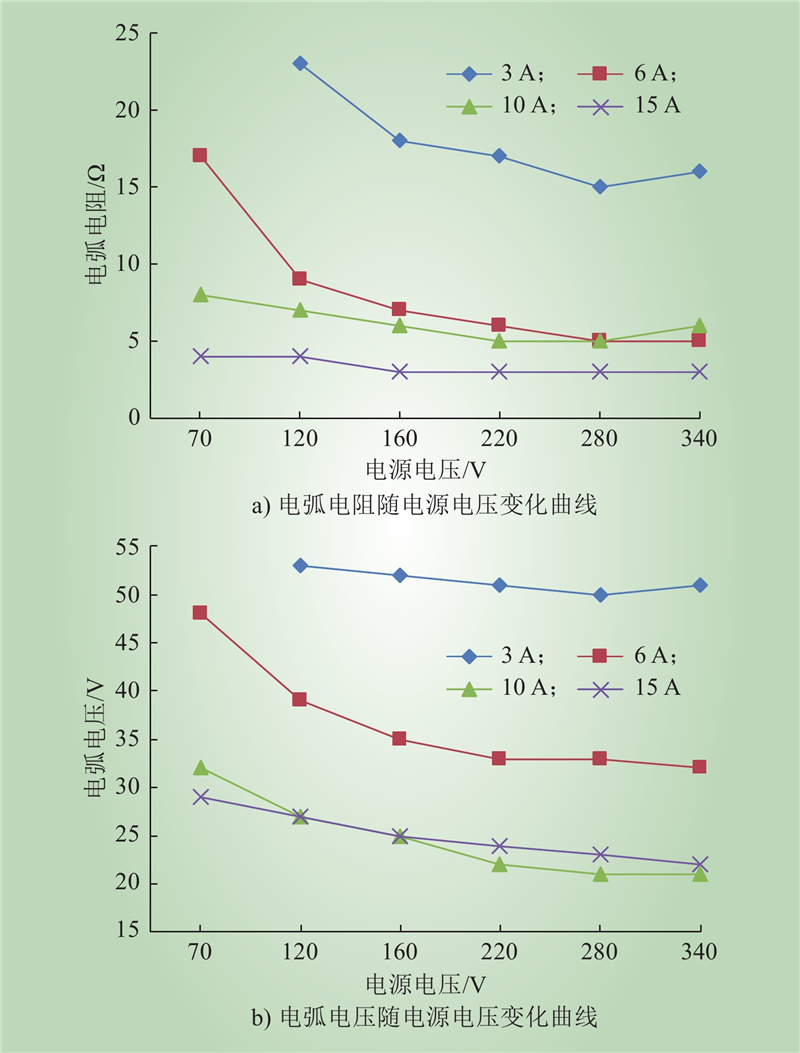
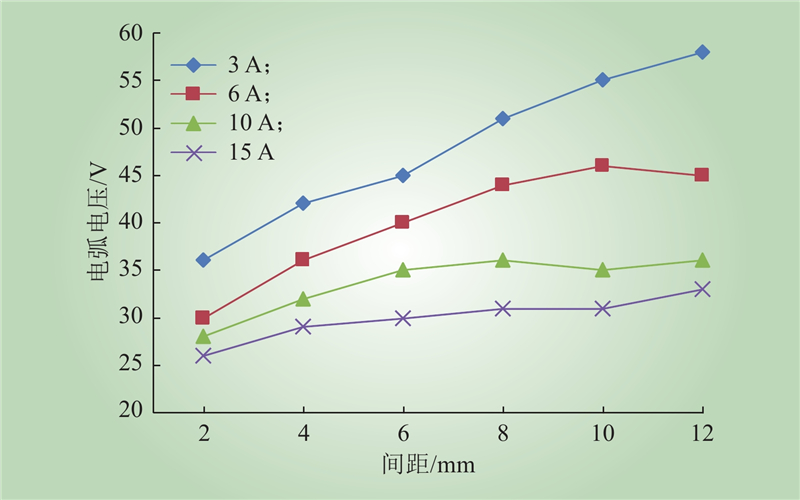
| 1 |
徐晶,赵亮,张梁,等. 考虑移动储能接入的柔性配电网运行优化策[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 184- 191.
|
|
XU Jing, ZHAO Liang, ZHANG Liang,et al. Operation optimization method for flexible distribution network considering the integration of mobile energy storage[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 184- 191.
|
| 2 |
陆翌, 宣佳卓, 陈骞, 等. 基于成本分析的柔性直流配电网综合规划方案研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57 (19): 33- 39.
|
|
LU Yi, XUAN Jiazhuo, CHEN Qian, et al. Comprehensive approach for flexible DC distribution network planning based on cost analysis[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57 (19): 33- 39.
|
| 3 |
付宇, 白浩, 李跃, 等. 面向高比例光伏消纳的低压交直流混合配电网时-空协调优化方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (1): 84- 93.
|
|
FU Yu, BAI Hao, LI Yue, et al. Spatial-temporal coordinated optimization method of low voltage hybrid AC/DC distribution network for accommodation of high-proportion PVs[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (1): 84- 93.
|
| 4 |
黄龑, 郝迎鹏, 汪慧娴, 等. 基于二阶统一模型的分布式发电并网同步控制研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 41- 50.
|
|
HUANG Yan, HAO Yingpeng, WANG Huixian, et al. Research on synchronization control of distributed generation based on second-order unified model[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 41- 50.
|
| 5 |
王军龙, 杨欢红, 张劲松, 等. 基于低能量直流的真空断路器短路开断能力评估[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (7): 23- 28, 44.
|
|
WANG Junlong, YANG Huanhong, ZHANG Jinsong, et al. Short-circuit breaking capacity evaluation of vacuum circuit breaker based on low-energy DC[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (7): 23- 28, 44.
|
| 6 |
蔺华,王子龙,郭振华,等. 考虑弧长动态变化的配电网电弧接地故障建模及辨识[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (7): 31- 39.
|
|
LIN Hua, WANG Zilong, GUO Zhenhua, et al. Modeling and identification of a distribution network arc grounding fault considering arc length dynamic variation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (7): 31- 39.
|
| 7 |
SEKIKAWA J. An experimental equation for dependence of duration of breaking arcs on supply voltage with constant circuit resistance[J]. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 2005, 88 (8): 1584- 1589.
|
| 8 |
李阳, 刘浩军, 何冰, 等. GIS/GIL内部电弧试验中电弧外部效应检测方法[J]. 电气应用, 2021, 40 (2): 61- 64.
|
|
LI Yang, LIU Haojun, HE Bing, et al. Detection method for external effect of the internal arc fault test of GIS/GIL[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2021, 40 (2): 61- 64.
|
| 9 |
SCHOEPF T J, NAIDU M, GOPALAKRISHNAN S. Mitigation and analysis of arc faults in automotive DC networks[C]//Proceedings of the Forty-Ninth IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts. Washington, DC, USA. IEEE, 2003: 163–171.
|
| 10 |
刘小军, 熊庆, 汲胜昌, 等. 针对串联直流电弧的电容电流时频检测方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2018, 52 (12): 152- 158, 166.
|
|
LIU Xiaojun, XIONG Qing, JI Shengchang, et al. Detection method for series DC arc using time-frequency domain characteristics of capacitive current[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2018, 52 (12): 152- 158, 166.
|
| 11 |
DARGATZ M, FORNAGE M. Method and apparatus for detection and control of DC arc faults: EP2741B88B1[P]. 2012.
|
| 12 |
崔芮华, 李泽, 佟德栓. 基于相空间重构和PCA的航空电弧故障检测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (14): 5054- 5065.
|
|
CUI Ruihua, LI Ze, TONG Deshuan. Arc fault detection based on phase space reconstruction and principal component analysis in aviation power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (14): 5054- 5065.
|
| 13 |
LE V, YAO X, MILLER C, et al. Series DC arc fault detection based on ensemble machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35 (8): 7826- 7839.
|
| 14 |
黄宵宵, 吴春华, 李智华, 等. 光伏系统直流电弧故障检测方法对比研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41 (8): 204- 214.
|
|
HUANG Xiaoxiao, WU Chunhua, LI Zhihua, et al. Comparison of DC arc fault detection methods for photovoltaic system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41 (8): 204- 214.
|
| 15 |
吴春华, 黄宵宵, 李智华, 等. 光伏系统直流微弱电弧信号检测研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (20): 6025- 6033, 6183.
|
|
WU Chunhua, HUANG Xiaoxiao, LI Zhihua, et al. Research on DC weak arc signal detection in photovoltaic system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (20): 6025- 6033, 6183.
|
| 16 |
XIA K, GUO H T, HE S, et al. Binary classification model based on machine learning algorithm for the DC serial arc detection in electric vehicle battery system[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2019, 12 (1): 112- 119.
|
| 17 |
孔德钱, 张新燕, 童涛, 等. 基于差分进化算法与BP神经网络的变压器故障诊断[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57 (5): 57- 61.
|
|
KONG Deqian, ZHANG Xinyan, TONG Tao, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis based on differential evolution algorithm and BP neural network[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57 (5): 57- 61.
|
| 18 |
熊庆, 陈维江, 汲胜昌, 等. 低压直流系统故障电弧特性、检测和定位方法研究进展综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (18): 6015- 6027.
|
|
XIONG Qing, CHEN Weijiang, JI Shengchang, et al. Review of research progress on characteristics, detection and localization approaches of fault arc in low voltage DC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (18): 6015- 6027.
|
| 19 |
NOTTINGHAM W B. A new equation for the static characteristic of the normal electric arc[J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1923, XLII, 302- 310.
|
| 20 |
GB/T 35727—2017. 中低压直流配电电压导则[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
|
| 21 |
苗硕, 李奇南, 查鲲鹏, 等. 基于加窗FFT的风电场自适应振荡抑制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 112- 123.
|
|
MIAO Shuo, LI Qinan, ZHA Kunpeng, et al. Adaptive oscillation suppression strategy for wind farms based on windowed FFT[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 112- 123.
|
| 22 |
余高旺, 方陈, 樊占峰, 等. 基于汉宁窗的配电网同步相量测量装置算法及应用[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (6): 18- 24.
|
|
YU Gaowang, FANG Chen, FAN Zhanfeng, et al. Research and application of algorithm for distribution network synchronous phasor measurement unit based on Hanning window[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (6): 18- 24.
|
| 23 |
赵振兵, 强一凡, 李信, 等. 基于改进循环神经网络的配电网超短期功率预测方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (5): 144- 154.
|
|
ZHAO Zhenbing, QIANG Yifan, LI Xin, et al. Ultra-short-term power prediction method of distribution network based on improved recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (5): 144- 154.
|
| 24 |
李宏仲, 叶翔宇, 付国. 信号分解技术在新能源发电功率预测中的应用评述[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (4): 3- 15.
|
|
LI Hongzhong, YE Xiangyu, FU Guo. Review on the application of signal decompositon technology in power prediction of new energy power generation[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (4): 3- 15.
|
| 25 |
蒋意珏, 唐毓, 骆杨, 等. 基于加速度传感器的电缆防盗检测算法研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57 (21): 54- 60, 69.
|
|
JIANG Yijue, TANG Yu, LUO Yang, et al. Research on anti-theft detection algorithm of cable based on acceleration sensor[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57 (21): 54- 60, 69.
|