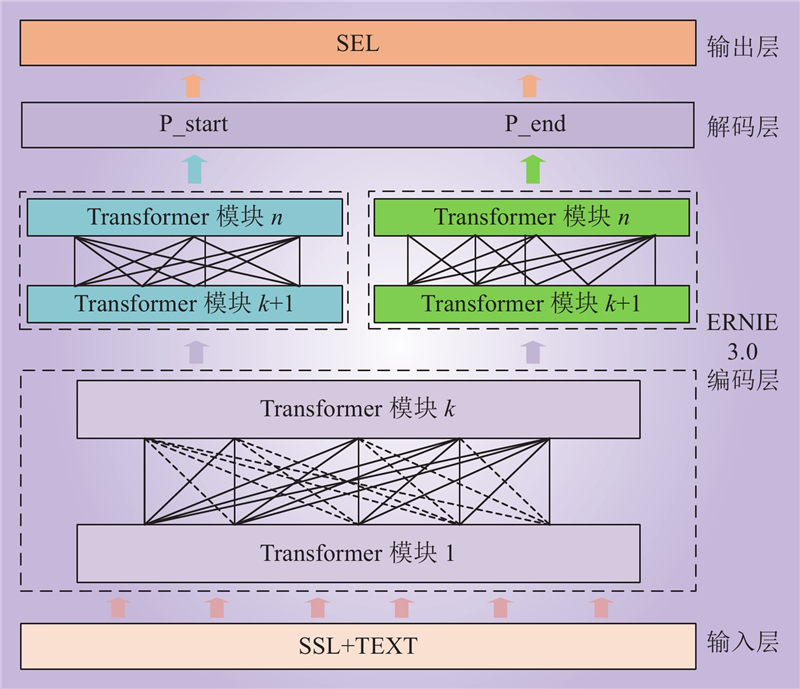
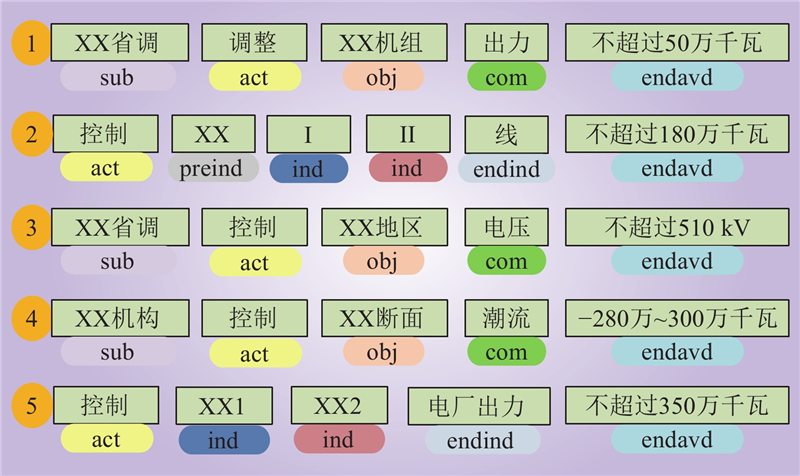
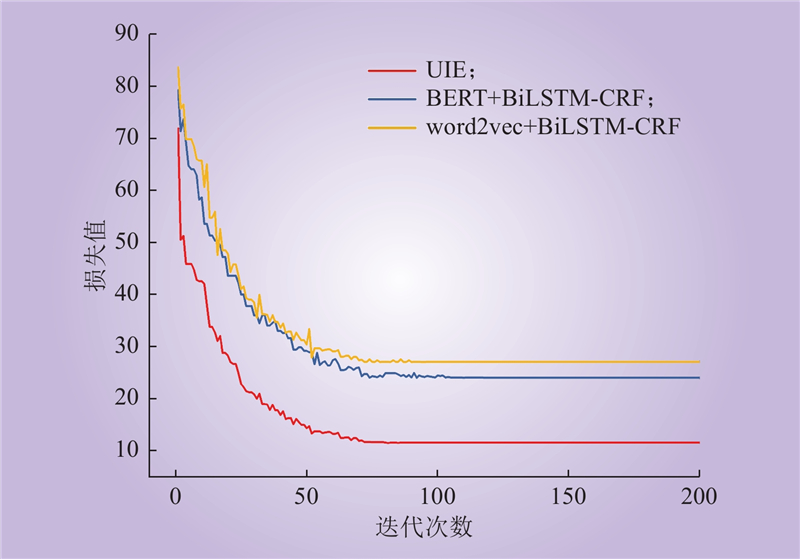
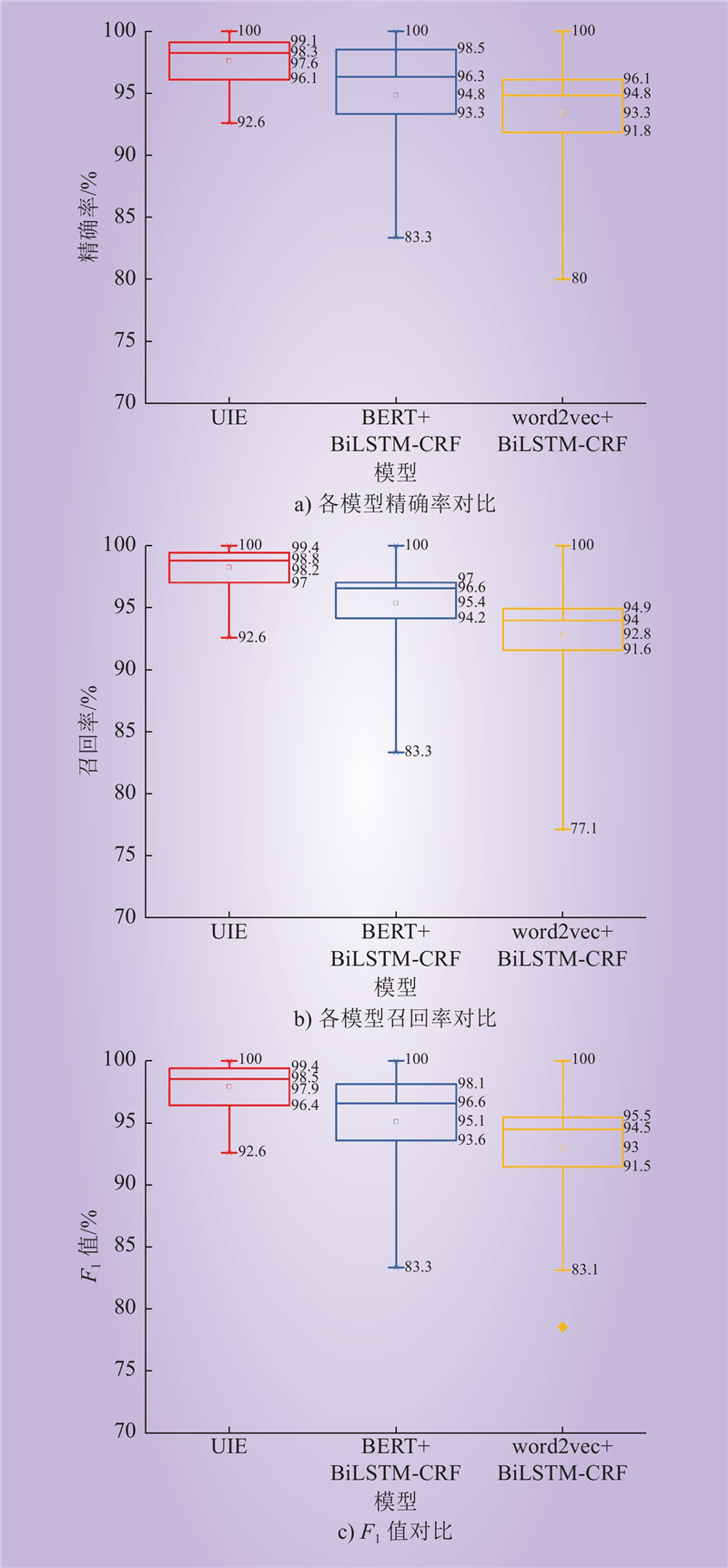
| 1 |
陈国平, 李明节, 许涛. 特高压交直流电网系统保护及其关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (22): 2- 10.
|
|
CHEN Guoping, LI Mingjie, XU Tao. System protection and its key technologies of UHV AC and DC power grid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (22): 2- 10.
|
| 2 |
李明节, 陶洪铸, 许洪强, 等. 电网调控领域人工智能技术框架与应用展望[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (2): 393- 400.
|
|
LI Mingjie, TAO Hongzhu, XU Hongqiang, et al. The technical framework and application prospect of artificial intelligence application in the field of power grid dispatching and control[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (2): 393- 400.
|
| 3 |
许洪强, 姚建国, 南贵林, 等. 未来电网调度控制系统应用功能的新特征[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (1): 1- 7.
|
|
XU Hongqiang, YAO Jianguo, NAN Guilin, et al. New features of application function for future dispatching and control systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (1): 1- 7.
|
| 4 |
张晓华, 冯长有, 王永明, 等. 电网调控机器人设计思路[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (13): 1- 8.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaohua, FENG Changyou, WANG Yongming, et al. Design ideas of robotic dispatcher for power grid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (13): 1- 8.
|
| 5 |
陶洪铸, 翟明玉, 许洪强, 等. 适应调控领域应用场景的人工智能平台体系架构及关键技术[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (2): 412- 419.
|
|
TAO Hongzhu, ZHAI Mingyu, XU Hongqiang, et al. Architecture and key technologies of artificial intelligence platform oriented for power grid dispatching and control application scenarios[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (2): 412- 419.
|
| 6 |
王福贺, 海威, 张越, 等. 电网线路故障处置智能调度机器人研究及应用[J]. 电气自动化, 2021, 43 (3): 1- 3, 23.
|
|
WANG Fuhe, HAI Wei, ZHANG Yue, et al. Research and application of intelligent dispatching robots handling grid line faults[J]. Electrical Automation, 2021, 43 (3): 1- 3, 23.
|
| 7 |
余建明, 王小海, 张越, 等. 面向智能调控领域的知识图谱构建与应用[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (3): 29- 35.
|
|
YU Jianming, WANG Xiaohai, ZHANG Yue, et al. Construction and application of knowledge graph for intelligent dispatching and control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (3): 29- 35.
|
| 8 |
胡怀伟, 富英, 张越, 等. 基于自然语言理解的故障处置预案语义建模研究及应用[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2022, 20 (5): 68- 73.
|
|
HU Huaiwei, FU Ying, ZHANG Yue, et al. Research and application of semantic modeling of fault handling plan based on natural language understanding[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2022, 20 (5): 68- 73.
|
| 9 |
戴宇欣, 张俊, 季知祥, 等. 基于功能缺陷文本的电力系统二次设备智能诊断与辅助决策[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 40 (8): 1537- 1562.
|
|
DAI Yuxin, ZHANG Jun, JI Zhixiang, et al. Intelligent diagnosis and auxiliary decision of power system secondary equipment based on functional defect text[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 40 (8): 1537- 1562.
|
| 10 |
. [J]. 2014, 40 (8): 1537- 1562.
|
|
YANG Jinfeng, YU Qiubin, GUAN Yi, et al. An overview of research on electronic medical record oriented named entity recognition and entity relation extraction[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40 (8): 1537- 1562.
|
| 11 |
鲁华永, 袁越, 郭泓佐, 等. 基于正则表达式的变电站集中监控信息解析方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (5): 78- 83.
|
|
LU Huayong, YUAN Yue, GUO Hongzuo, et al. Regular expressions based information analytic method for substation centralized monitoring[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (5): 78- 83.
|
| 12 |
李慧林, 柴玉梅, 孙穆祯. 面向文本命名实体识别的深层网络模型[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2019, 40 (1): 50- 57.
|
|
LI Huilin, CHAI Yumei, SUN Muzhen. Deep network model for text named entity recognition[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2019, 40 (1): 50- 57.
|
| 13 |
陈斌, 周勇, 刘兵. 基于卷积双向长短期记忆网络的事件触发词抽取[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45 (1): 153- 158.
|
|
CHEN Bin, ZHOU Yong, LIU Bing. Event trigger word extraction based on convolutional bidirectional long short term memory network[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45 (1): 153- 158.
|
| 14 |
吴文涛, 李培峰, 朱巧明. 基于混合神经网络的实体和事件联合抽取方法[J]. 中文信息学报, 2019, 33 (8): 77- 83.
|
|
WU Wentao, LI Peifeng, ZHU Qiaoming. Joint extraction of entities and events by a hybrid neural network[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2019, 33 (8): 77- 83.
|
| 15 |
江叶峰, 孙少华, 仇晨光, 等. 电网故障处置预案文本中的命名实体识别研究[J]. 电力工程技术, 2021, 40 (5): 177- 183.
|
|
JIANG Yefeng, SUN Shaohua, QIU Chenguang, et al. Named entity recognition in power fault disposal preplan text[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40 (5): 177- 183.
|
| 16 |
单连飞, 张越. 电网调度专业语料库构建方法研究及应用[J]. 机械与电子, 2022, 40 (4): 73- 76, 80.
|
|
SHAN Lianfei, ZHANG Yue. Research and application for construction method of power grid dispatching professional corpus[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2022, 40 (4): 73- 76, 80.
|
| 17 |
丁禹, 尚学伟, 米为民. 基于深度学习的电网调控文本知识抽取方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (24): 161- 168.
|
|
DING Yu, SHANG Xuewei, MI Weimin. Deep learning based knowledge extraction method for text of power grid dispatch and control[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (24): 161- 168.
|
| 18 |
佟佳弘, 武志刚, 管霖, 等. 电力调度文本的自然语言理解与解析技术及应用[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (11): 4148- 4156.
|
|
TONGJIA Hong, WU Zhigang, GUAN Lin, et al. Power dispatching text analysis and application based on natural language understanding[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (11): 4148- 4156.
|
| 19 |
蒋晨, 王渊, 胡俊华, 等. 基于深度学习的电力实体信息识别方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (6): 2141- 2149.
|
|
JIANG Chen, WANG Yuan, HU Junhua, et al. Power entity information recognition based on deep learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (6): 2141- 2149.
|
| 20 |
LU Y J, LIU Q, DAI D, et al. Unified structure generation for universal information extraction[EB/OL]. 2022: arXiv: 2203.12277.https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12277.pdf.
|
| 21 |
SUN Y, WANG S H, FENG S K, et al. ERNIE 3.0: large-scale knowledge enhanced pre-training for language understanding and generation[EB/OL]. 2021: arXiv: 2107.02137.https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.02137.pdf.
|
| 22 |
BONETTA G, CANCELLIERE R, LIU D, et al. Retrieval-augmented transformer-XL for close-domain dialog generation[J]. The International FLAIRS Conference Proceedings, 2021, 34 (1): 2021.
|
| 23 |
纪鹏志, 李光肖, 王琳, 等. 基于Transformer深度学习网络的主动配电网多元源荷灾损辨识方法[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(3): 56–65.
|
|
JI Pengzhi, LI Guangxiao, WANG Lin, et al. Transformer-based evaluation method of power outage in active distribution networks with multiple sources and loads[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44(3): 56–65.
|
| 24 |
DAI Z H, YANG Z L, YANG Y M, et al. Transformer-XL: attentive language models beyond a fixed-length context[EB/OL]. 2019: arXiv: 1901.02860.https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860.pdf
|
| 25 |
LI X, FENG J, MENG Y, et al. A unified MRC framework for named entity recognition[C]//Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020. DOI:10.18653/V1/2020.ACL-MAIN.519.
|
| 26 |
YANG R Q, ZHANG J H, GAO X, et al. Simple and effective text matching with richer alignment features[C]//Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Florence, Italy. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019: 4699–4709.
|