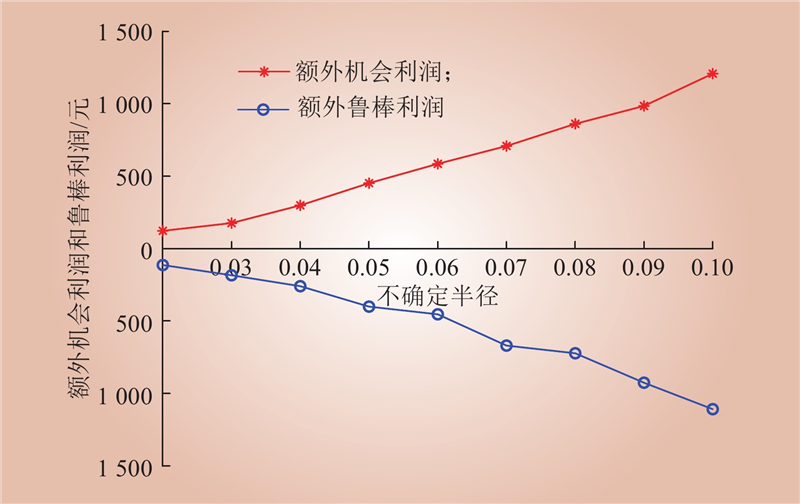
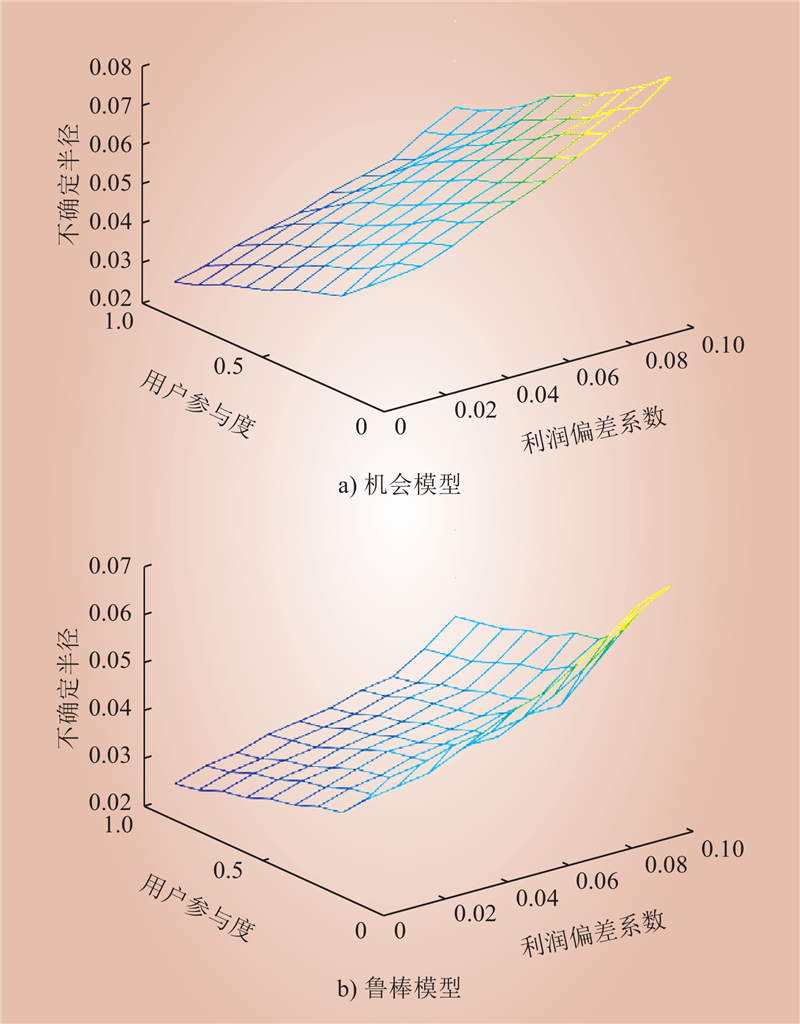
| 1 |
李东东, 王啸林, 沈运帷, 等. 考虑多重不确定性的含需求响应及电碳交易的虚拟电厂优化调度策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (5): 210- 217, 251.
|
|
LI Dongdong, WANG Xiaolin, SHEN Yunwei, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy of virtual power plant with demand response and electricity-carbon trading considering multiple uncertainties[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (5): 210- 217, 251.
|
| 2 |
李昭昱, 艾芊. 分时电价下居民用户用电需求响应估计方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (10): 121- 127.
|
|
LI Zhaoyu, AI Qian. Demand response estimation method of electricity consumption for residential customer under time of use price[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (10): 121- 127.
|
| 3 |
任正某, 王剑, 王金锋, 等. 基于负荷聚合商的需求侧应用方法研究[J]. 电气时代, 2023, (4): 77- 80.
|
|
REN Zhengmou, WANG Jian, WANG Jinfeng, et al. Research on demand-side application method based on load aggregator[J]. Electrical Age, 2023, (4): 77- 80.
|
| 4 |
柏颖, 刘晓峰, 陈雪颖. 面向需求响应日前市场投标的负荷聚合商决策动力学分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (24): 95- 103.
|
|
BAI Ying, LIU Xiaofeng, CHEN Xueying. Dynamics analysis on decision-making of load aggregator for day-ahead demand response market bidding[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (24): 95- 103.
|
| 5 |
谭鸣骢, 王玲玲, 蒋传文, 等. 考虑负荷聚合商调节潜力的需求响应双层优化模型[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 32- 44.
|
|
TAN Mingcong, WANG Lingling, JIANG Chuanwen, et al. A dual-layer optimization model for demand response considering the regulation potential of load aggregators[J]. Electric Power in China, 2022, 55 (10): 32- 44.
|
| 6 |
杨苹, 曾凯林, 余雁琳, 等. 电能量市场下负荷聚合商参与负荷削减投标策略[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (1): 2- 10.
|
|
YANG Ping, ZENG Kailin, YU Yanlin, et al. Strategy of load aggregator participating in load curtailment bidding under power market[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (1): 2- 10.
|
| 7 |
张晶晶, 蒋峰, 吴红斌, 等. 计及CVaR的负荷聚合商双重市场投标策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (12): 153- 158.
|
|
ZHANG Jingjing, JIANG Feng, WU Hongbin, et al. Dual market bidding strategy of load aggregator based on CVaR[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (12): 153- 158.
|
| 8 |
贾雨龙, 米增强, 余洋, 等. 计及不确定性的柔性负荷聚合商随机-鲁棒投标决策模型[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34 (19): 4096- 4107.
|
|
JIA Yulong, MI Zengqiang, YU Yang, et al. Stochastic-robust decision-making model for flexible load aggregator considering uncertainties[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34 (19): 4096- 4107.
|
| 9 |
张晓东, 艾欣, 潘玺安. 考虑用户可调度潜力的负荷聚合商优化调度策略[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50 (1): 28- 37.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaodong, AI Xin, PAN Xi'an. Optimal scheduling strategy of load aggregators considering user's scheduling potential[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 50 (1): 28- 37.
|
| 10 |
谢雨奇, 曾伟, 马瑞. 考虑用户响应度模糊控制的需求响应双层博弈模型[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (6): 30- 38.
|
|
XIE Yuqi, ZENG Wei, MA Rui. Two-layer game model for demand response considering fuzzy control of user responsiveness[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (6): 30- 38.
|
| 11 |
王秀慧, 赵浩辰, 谭忠富. 计及负荷聚合商的综合能源系统双层主从博弈运行优化[J]. 可再生能源, 2023, 41 (11): 1554- 1562.
|
|
WANG Xiuhui, ZHAO Haochen, TAN Zhongfu. Optimization study of integrated energy system hierarchical stackelberg game operation with load aggregator[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2023, 41 (11): 1554- 1562.
|
| 12 |
刘晓峰, 陈雪颖, 柏颖, 等. 计及多重影响因素的居民需求响应行为分析[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (6): 116- 124.
|
|
LIU Xiaofeng, CHEN Xueying, BAI Ying, et al. Analysis of residents' demand response behavior considering multiple influencing factors[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (6): 116- 124.
|
| 13 |
周亦洲, 李想, 沈思辰, 等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的产消者多市场产品分布式交易[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (23): 122- 130.
|
|
ZHOU Yizhou, LI Xiang, SHEN Sichen, et al. Distributed trading of multi-market products for producers and consumers based on information gap decision theory[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (23): 122- 130.
|
| 14 |
孙伟卿, 郑钰琦, 薛贵挺. 考虑响应率差异的需求响应交易机制设计与效果分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (22): 83- 94.
|
|
SUN Weiqing, ZHENG Yuqi, XUE Guiting. Design and effect analysis of demand response transaction mechanism considering response rate difference[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (22): 83- 94.
|
| 15 |
杨伟宏, 秦阳, 吴兵兵. 环境感知的新冠肺炎传播态势的建模与分析[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38 (7): 2077- 2080.
|
|
YANG Weihong, QIN Yang, WU Bingbing. Modeling and analysis of environment-aware COVID-19 transmission[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38 (7): 2077- 2080.
|
| 16 |
张婕, 孙伟卿, 刘唯. 考虑需求响应收益的售电商实时电价决策模型[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (2): 492- 504.
|
|
ZHANG Jie, SUN Weiqing, LIU Wei. Real time pricing considering demand response revenue of electricity sellers[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (2): 492- 504.
|
| 17 |
曹昉, 李欣宁, 刘思佳, 等. 基于消费者参考价格决策及用户黏性的售电套餐优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (14): 67- 74.
|
|
CAO Fang, LI Xinning, LIU Sijia, et al. Optimization of sales package for end-users based on user stickiness and reference pricing decision of consumers[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (14): 67- 74.
|
| 18 |
高锋阳, 袁成, 李昭君, 等. 近似贝叶斯计算结合马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛的概率潮流计算[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42 (11): 265- 272.
|
|
GAO Fengyang, YUAN Cheng, LI Zhaojun, et al. Probabilistic load flow method using approximate Bayesian computation and Markov chain Monte Carlo[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42 (11): 265- 272.
|
| 19 |
LI Q, WANG Z, WU B, et al. Competition and cooperation: dynamical interplay diffusion between social topic multiple messages in multiplex networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2019, 6 (3): 467- 478.
|
| 20 |
张靖琛, 江全元, 耿光超, 等. 基于区块链的负荷聚合商及居民用户多方共治交易模式[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (1): 109- 118.
|
|
ZHANG Jingchen, JIANG Quanyuan, GENG Guangchao, et al. Blockchain-based multi-party co-governance transaction mode for load aggregator and residential users[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (1): 109- 118.
|
| 21 |
庞贺元. 负荷聚合商参与风光消纳调度策略研究[J]. 机电工程技术, 2023, 52 (2): 114- 117.
|
|
PANG Heyuan. Research on load aggregator's participation in wind-solar consumption scheduling strategy[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Technology, 2023, 52 (2): 114- 117.
|
| 22 |
张涛, 刘伉, 陶然, 等. 计及热媒流率和热损耗不确定性的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (04): 146- 155.
|
|
ZHANG Tao, LIU Kang, TAO Ran, et al. Optimization scheduling of integrated energy systems considering uncertainty in heat carrier flow rate and heat loss[J]. Electric Power in China, 2023, 56 (04): 146- 155.
|
| 23 |
赵振宇, 包格日乐图, 李炘薪. 基于信息间隙决策理论的含碳捕集-电转气综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (4): 651- 665.
|
|
ZHAO Zhenyu, BAO Geriletu, LI Xinxin. Optimization and scheduling of integrated energy systems with carbon capture and storage-power to gas based on information gap decision theory[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (4): 651- 665.
|
| 24 |
彭宇文, 李瑞, 周永旺, 等. 基于IGDT和PSO-SA的综合能源系统鲁棒优化调度方法[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (9): 60- 71.
|
|
PENG Yuwen, LI Rui, ZHOU Yongwang, et al. Robust optimal scheduling method for integrated energy system based on IGDT and PSO-SA[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (9): 60- 71.
|
| 25 |
李东东, 张凯, 姚寅, 等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的电动汽车聚合商日前需求响应调度策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (24): 101- 111.
|
|
LI Dongdong, ZHANG Kai, YAO Yin, et al. Day-ahead demand response scheduling strategy of an electric vehicle aggregator based on information gap decision theory[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (24): 101- 111.
|
| 26 |
潘华, 姚正, 黄玲玲, 等. 考虑分布式电源及需求响应不确定性的园区综合能源系统经济调度[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (2): 94- 105.
|
|
PAN Hua, YAO Zheng, HUANG Lingling, et al. Economic dispatch of park integrated energy system considering the uncertainty of distribution generation and demand response[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (2): 94- 105.
|
| 27 |
罗宗龙, 刘世林. 基于信息间隙决策理论鲁棒模型的户用微电网优化运行[J/OL]. 发电技术, 1–12[2024-05-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1405.tk.20240516.1816.019.html.
|
|
LUO Zonglong, LIU Shilin. Optimized operation of a residential microgrid based on information gap decision theory robust model[J/OL]. Power Generation Technology, 1–12[2024-05-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1405.tk.20240516.1816.019.html.
|
| 28 |
叶鹤林, 刘松, 胡剑, 等. 基于IGDT的含光热电站电力系统多源联合调度策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (23): 35- 43.
|
|
YE Helin, LIU Song, HU Jian, et al. Multi-source joint dispatching strategy for a power system with concentrating solar power plants based on IGDT[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (23): 35- 43.
|
| 29 |
杨蕊, 李刚, 卢佳. 考虑分时段合约的梯级水电站中期分段鲁棒优化调度方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (04): 1481- 1492.
|
|
YANG Rui, LI Gang, LU Jia. Mid-term segmented robust optimization scheduling method for cascade hydropower stations considering time-of-use contracts[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2023, 43 (04): 1481- 1492.
|