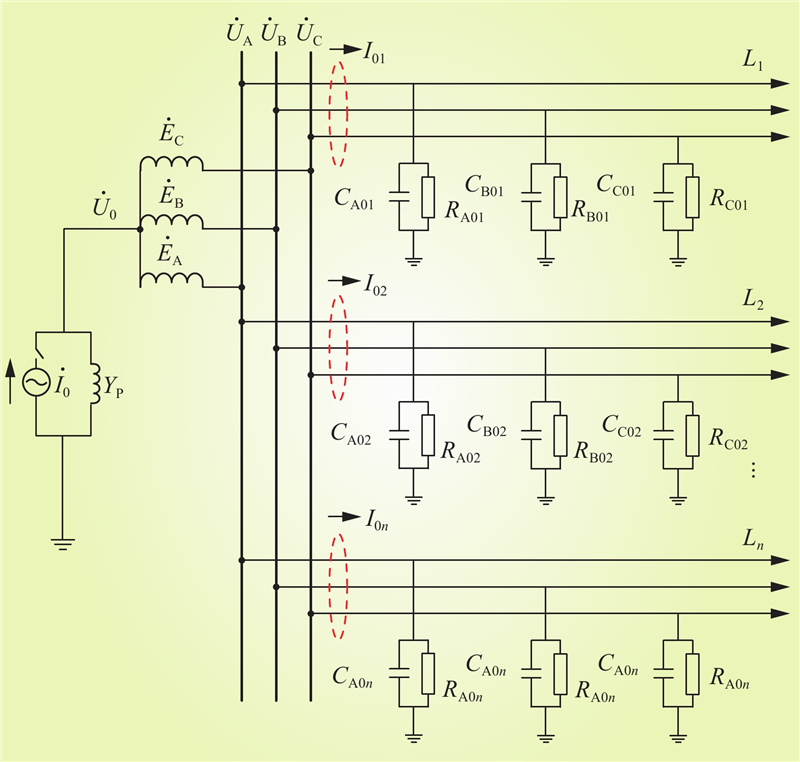
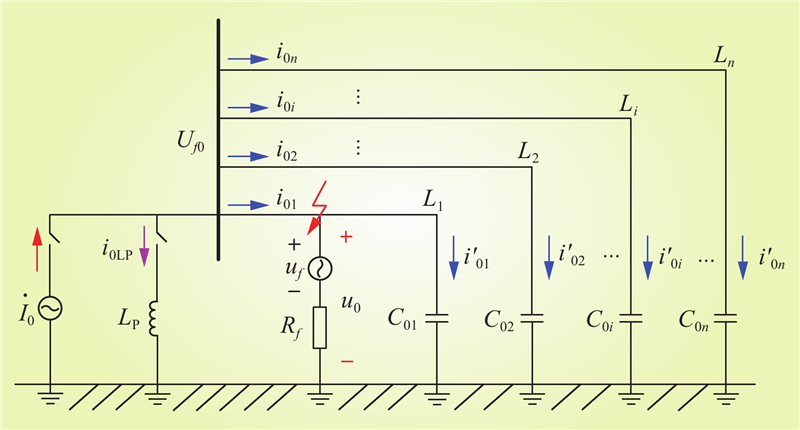
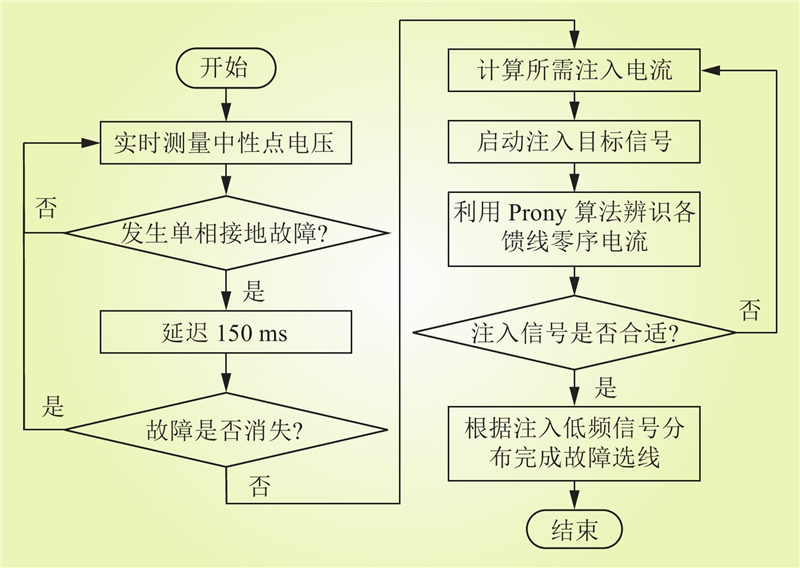
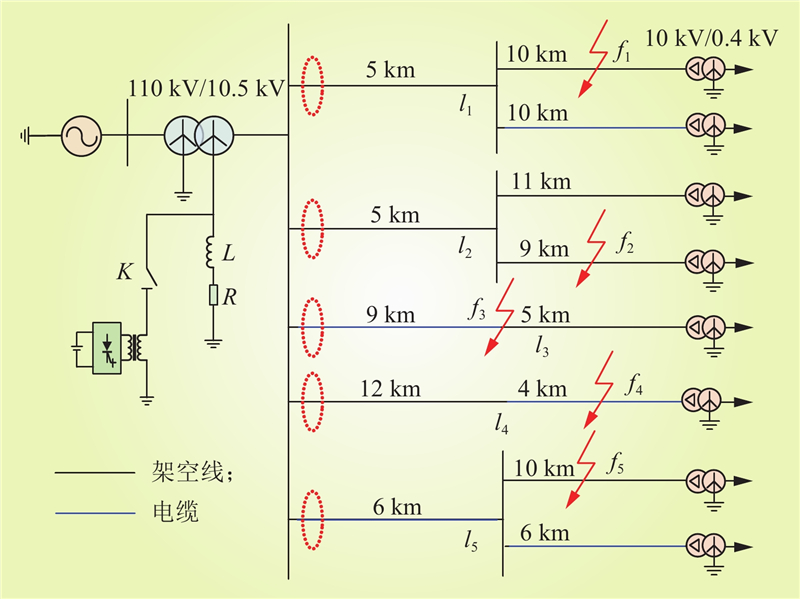
| 1 |
张帆, 薛永端, 徐丙垠. 基于信号注入的谐振接地系统故障点残流测算方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (13): 132- 138.
|
|
ZHANG Fan, XUE Yongduan, XU Bingyin. A method for calculating residual current in a resonant grounding system based on signal injection[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (13): 132- 138.
|
| 2 |
郑涛, 王赟鹏, 马家璇, 等. 适用于UPFC接入线路的主动注入式故障测距方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (6): 138- 145.
|
|
ZHENG Tao, WANG Yunpeng, MA Jiaxuan, et al. Fault locating method based on active injection for transmission lines equipped with UPFC[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (6): 138- 145.
|
| 3 |
WANG X W, GAO J, WEI X X, et al. Faulty feeder detection under high impedance faults for resonant grounding distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2023, 14 (3): 1880- 1895.
|
| 4 |
董俊, 李一凡, 束洪春, 等. 配电网馈出线路单相永久性接地故障性质辨识方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35 (21): 4576- 4585.
|
|
DONG Jun, LI Yifan, SHU Hongchun, et al. Study on identification method of single phase permanent ground fault in distribution network feedout line[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35 (21): 4576- 4585.
|
| 5 |
曹赋禄, 赵晋斌, 潘超, 等. 基于DFFT的低压直流线路主动式接地故障定位方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 184- 191.
|
|
CAO Fulu, ZHAO Jinbin, PAN Chao, et al. An active ground fault location method for low-voltage DC lines based on DFFT[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 184- 191.
|
| 6 |
黄亚峰, 王浩天, 朱登宝, 等. 基于零序电流特性的中性点灵活接地系统的故障选线方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (3): 16- 22, 71.
|
|
HUANG Yafeng, WANG Haotian, ZHU Dengbao, et al. Fault line selection method for neutral flexible grounding system based on zero sequence current characteristics[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (3): 16- 22, 71.
|
| 7 |
王尊贤, 武守远, 栾晓明. 基于虚拟能量变化率的谐振接地系统高阻接地故障选线方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (3): 137- 146.
|
|
WANG Zunxian, WU Shouyuan, LUAN Xiaoming. Fault line selection method for high-impedance grounding fault of resonant grounded system based on change rate of virtual energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (3): 137- 146.
|
| 8 |
刘宝稳, 曾祥君, 张慧芬, 等. 注入电流馈线分布特征及其在接地故障检测中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (7): 2731- 2740.
|
|
LIU Baowen, ZENG Xiangjun, ZHANG Huifen, et al. Distribution model of injection current in feeder and its application in single phase to ground fault detection[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (7): 2731- 2740.
|
| 9 |
王晨清, 陈实, 齐贝贝, 等. 基于波形相关性的直流配电网主动式接地故障选线[J]. 电力工程技术, 2023, 42 (3): 1- 10.
|
|
WANG Chenqing, CHEN Shi, QI Beibei, et al. An active grounding fault line selection method for DC distribution network based on waveform correlation[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2023, 42 (3): 1- 10.
|
| 10 |
郭谋发, 陈静洁, 张伟骏, 等. 基于单相级联H桥变流器的配电网故障消弧与选线新方法[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39 (9): 2677- 2684.
|
|
GUO Moufa, CHEN Jingjie, ZHANG Weijun, et al. A novel approach for fault arc extinguishing and feeder selection in distribution networks based on single-phase cascade H-bridge converter[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39 (9): 2677- 2684.
|
| 11 |
何瑞江, 胡志坚, 王天一. 计及分布式电源注入谐波的谐振接地系统故障选线方法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (2): 670- 680.
|
|
HE Ruijiang, HU Zhijian, WANG Tianyi. A fault line selection method for resonant grounding system considering injected harmonics of distributed generation[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (2): 670- 680.
|
| 12 |
潘贞存, 张慧芬, 张帆, 等. 信号注入式接地选线定位保护的分析与改进[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2007, 31 (4): 71- 75.
|
|
PAN Zhencun, ZHANG Huifen, ZHANG Fan, et al. Analysis and modification of signal injection based fault line selection protection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2007, 31 (4): 71- 75.
|
| 13 |
LIU B W, MA H Z, XU H H, et al. Single-phase-to-ground fault detection with distributed parameters analysis in non-direct grounded systems[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2019, 5 (1): 139- 147.
|
| 14 |
叶雨晴, 马啸, 林湘宁, 等. 基于SOP的主动式谐振接地配电网单相接地故障区段定位方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (5): 1453- 1465.
|
|
YE Yuqing, MA Xiao, LIN Xiangning, et al. Active fault locating method based on SOP for single phase grounding faults in the resonant grounding distribution network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (5): 1453- 1465.
|
| 15 |
白浩, 黄升平, 潘姝慧, 等. 配电网中性点电压主动调控的接地故障零序电流多判据选线方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (4): 105- 113.
|
|
BAI Hao, HUANG Shengping, PAN Shuhui, et al. Zero sequence current multi-criteria line selection method based on active regulation of neutral voltage in distribution networks[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (4): 105- 113.
|
| 16 |
杨喜行, 黄纯, 申亚涛, 等. 基于损失功率匹配的配电线路故障定位方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 113- 120.
|
|
YANG Xixing, HUANG Chun, SHEN Yatao, et al. Fault location method for distribution lines based on loss power matching[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 113- 120.
|
| 17 |
刘红文, 曾祥君, 柴晨超, 等. 配电网柔性接地装置注入非工频小信号的接地故障检测与区段定位方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (6): 44- 53.
|
|
LIU Hongwen, ZENG Xiangjun, CHAI Chenchao, et al. Grounding fault detection and section location method of injecting non power frequency small signal into flexible grounding device of distribution network[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (6): 44- 53.
|
| 18 |
刘映彤, 黄纯, 袁静泊, 等. 谐振接地系统两点同相接地故障暂态特征及选线[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 62- 70.
|
|
LIU Yingtong, HUANG Chun, YUAN Jingbo, et al. Transient characteristics and line selection of two-point grounding faults on same phase in resonant grounding system[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 62- 70.
|
| 19 |
盛亚如, 丛伟, 卜祥海, 等. 基于中性点电流与零序电流投影量差动的小电阻接地系统高阻接地故障判断方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (3): 17- 22, 29.
|
|
SHENG Yaru, CONG Wei, BU Xianghai, et al. Detection method of high impedance grounding fault based on differential current of zero-sequence current projection and neutral point current in low-resistance grounding system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (3): 17- 22, 29.
|
| 20 |
TAYJASANANT T, WANG W C, LI C, et al. Interharmonic-flicker curves[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2005, 20 (2): 1017- 1024.
|
| 21 |
邵文权, 程畅, 卫晓辉, 等. 利用暂态电流Hausdorff距离的谐振配电网故障选线方案[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (8): 33- 42.
|
|
SHAO Wenquan, CHENG Chang, WEI Xiaohui, et al. Fault line selection scheme using the Hausdorff distance of transient current in resonant distribution networks[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (8): 33- 42.
|
| 22 |
何小龙, 高红均, 高艺文, 等. 基于GA优化BP神经网络的有源配电网高阻接地故障选线方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (4): 54- 61.
|
|
HE Xiaolong, GAO Hongjun, GAO Yiwen, et al. High resistance grounding fault line selection method for active distribution network based on GA optimized BP neural network[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (4): 54- 61.
|
| 23 |
束洪春. 电力工程信号处理应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
|
| 24 |
郭亮, 屈新宇, 王晓卫, 等. 基于改进Hough变换的消弧线圈接地配电网故障选线新方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 132- 142.
|
|
GUO Liang, QU Xinyu, WANG Xiaowei, et al. A novel fault feeder selection method for resonant grounding distribution networks based on improved Hough transform[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 132- 142.
|
| 25 |
杨舟, 杨仁炘, 施刚, 等. 一种用于多端直流输电系统交流故障穿越的新型控制策略[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43 (2): 268- 277.
|
|
YANG Zhou, YANG Renxin, SHI Gang, et al. A novel control strategy for AC fault ride through in multi-terminal DC system[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43 (2): 268- 277.
|