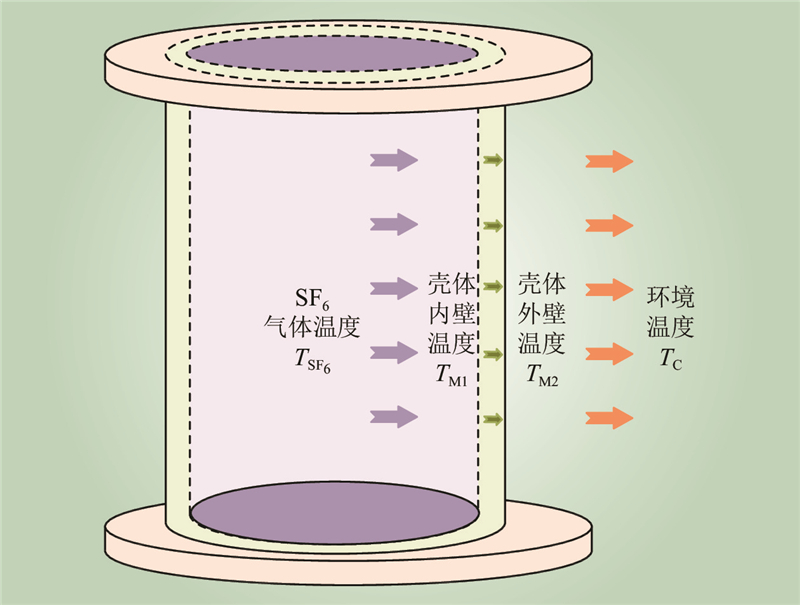
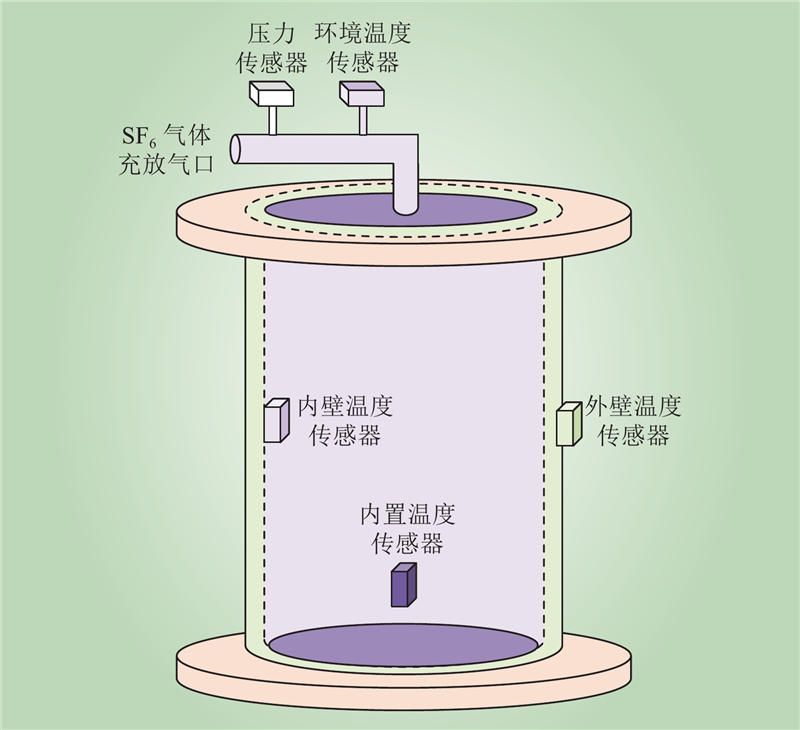
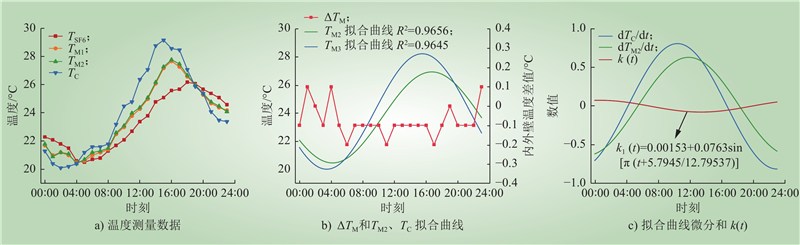
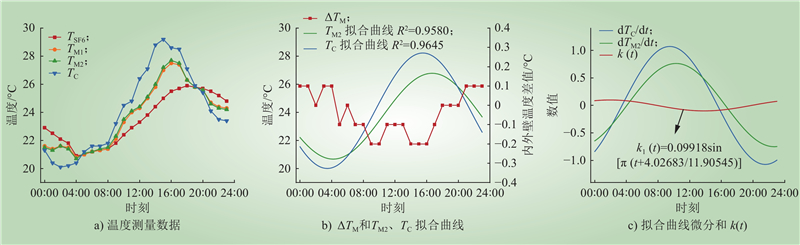
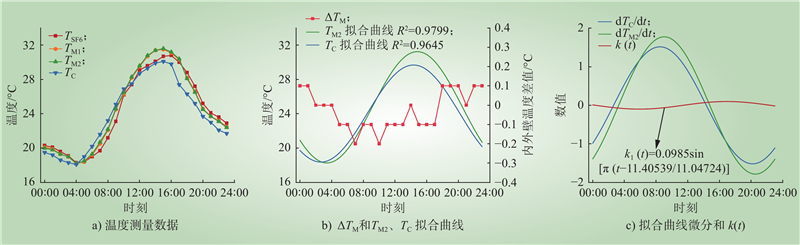
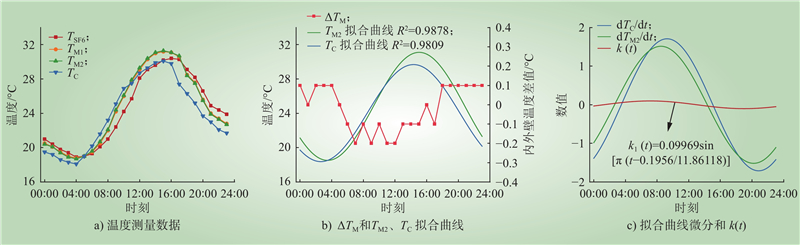
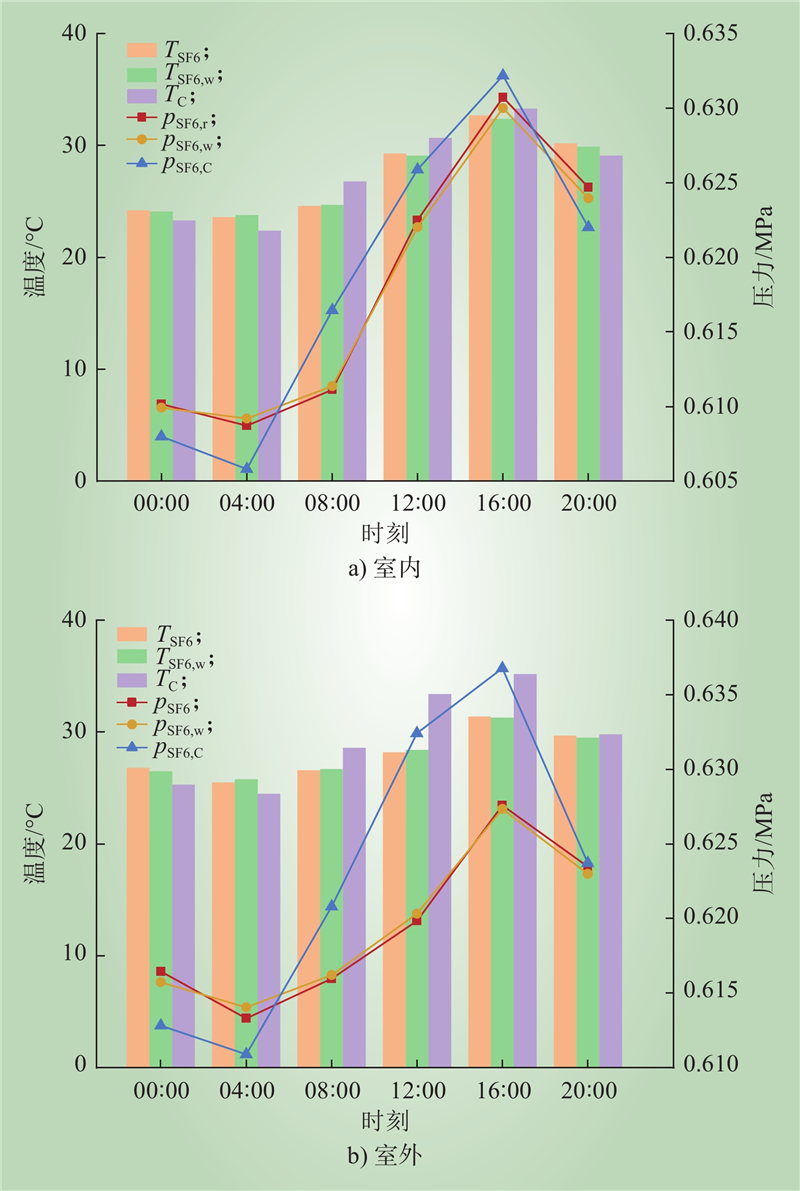
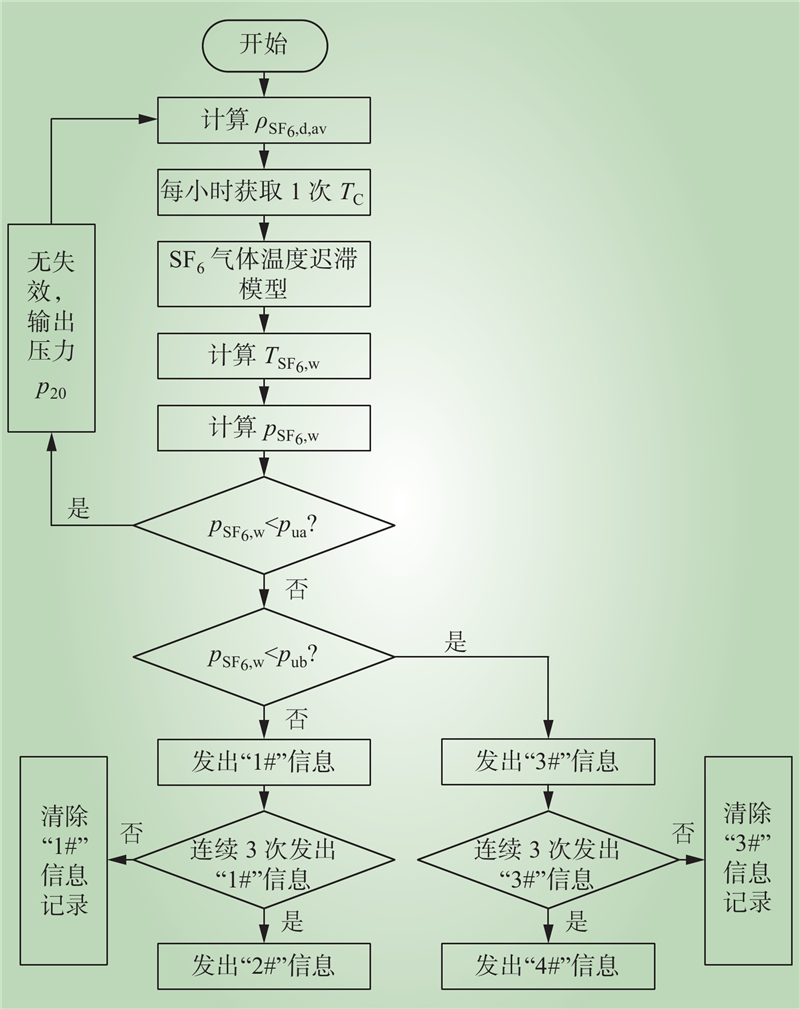
| 1 |
张晓星, 肖淞, 张博雅, 等. PFAS及含氟气体管控下环保绝缘气体研究与电力装备应用展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (1): 362- 377.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoxing, XIAO Song, ZHANG Boya, et al. Challenges and prospects for the research of environmentally friendly insulating gases and applications of power equipment under control policies of PFAS and fluorine gas[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (1): 362- 377.
|
| 2 |
王昊, 张长虹, 杨旭, 等. 420kV及以上高压断路器电寿命试验中SF6气体分解产物及其影响研究[J]. 高压电器, 2023, 59 (10): 88- 95.
|
|
WANG Hao, ZHANG Changhong, YANG Xu, et al. Study on the effect of SF6 gas decomposition products in electrical endurance test of 420 kV and above circuit breaker[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2023, 59 (10): 88- 95.
|
| 3 |
田汇冬, 靳守锋, 谢韬, 等. 高压套管表带触指SF6气氛中高温腐蚀特性研究[J/OL]. 高压电器: 1–12 [2023-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1127.TM.20231016.1712.002.html.
|
|
TIAN Huidong, JIN Shoufeng, XIE Tao, et al. Research on High Temperature Corrosion Characteristics of the Strap Contacts in SF6 Atmosphere Used in HV Bushin-g[J/OL]. High Voltage Apparatus: 1–12 [2023-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1127.TM.20231016.1712.002.html.
|
| 4 |
李飞高, 李瑄. 具有压力自动控制功能的SF6气体密度检验装置[J]. 制造业自动化, 2022, 44 (1): 170- 173.
|
|
LI Feigao, LI Xuan. SF6 gas density inspection device with automatic pressure control function[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2022, 44 (1): 170- 173.
|
| 5 |
龙军, 罗立波, 苏佳华, 等. 一种免拆卸校验的SF6气体密度继电器的研制[J]. 高压电器, 2019, 55 (7): 242- 247.
|
| 6 |
安春燕, 陆阳, 翟迪, 等. 电力智能传感器及传感网安全防护技术[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 67- 76.
|
|
AN Chunyan, LU Yang, ZHAI Di, et al. Security protection of electrical intelligent sensors and sensor networks[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 67- 76.
|
| 7 |
刘杰, 毛海波, 姜涛, 等. SF6密度继电器监测GIS气室压力的误差分析[J]. 浙江电力, 2022, 41 (2): 73- 77.
|
|
LIU Jie, MAO Haibo, JIANG Tao, et al. Error analysis of SF6 density relay in pressure monitoring of GIS chamber[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2022, 41 (2): 73- 77.
|
| 8 |
蒋树屏, 李静, 张丹丹, 等. 钢壳混凝土沉管隧道管节结构热量传递规律试验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2023, 60 (1): 168- 178.
|
|
JIANG Shuping, LI Jing, ZHANG Dandan, et al. Experimental study on the law of heat transfer of tube structure of the steel-concrete-steel immersed tube tunnel[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2023, 60 (1): 168- 178.
|
| 9 |
孙尚瑜, 许树学, 曹瑞林, 等. 家用空气源热泵蓄热式热管散热器的自然对流传热特性[J/OL]. 制冷学报: 1–8 [2023-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail /11.2182.TB.20231017.1225.002.html.
|
|
SUN Shangyu, XU Shuxue, CAO Ruilin, et al. Natural Convection Heat Transfer Characteristics of Domestic Air Source Heat Pump Regenerative Heat Pipe Radiator[J/OL]. Journal of Refrigeration: 1–8 [2023-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2182.TB.20231 017.1225.002.html.
|
| 10 |
秦晓宇, 吕寻浩, 陈玉, 等. 高寒地区GIS的适应性研究[J]. 高压电器, 2021, 57 (6): 72- 78, 85.
|
|
QIN Xiaoyu, LV Xunhao, CHEN Yu, et al. Study on adaptability of GIS in extreme cold region[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2021, 57 (6): 72- 78, 85.
|
| 11 |
薛庆宽. 高寒地区SF6断路器防液化技术研究与控制系统实现[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018.
|
|
XUE Qingkuan. Research on anti liquefaction technology and control system realization for SF6 circuit breaker in alpine region[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2018.
|
| 12 |
沈腾达, 周文俊, 王宝山, 等. SF6替代气体的分子构效关系研究进展[J]. 绝缘材料, 2022, 55 (6): 1- 5.
|
|
SHEN Tengda, ZHOU Wenjun, WANG Baoshan, et al. Research progress of molecular structure-activity relationship of SF6 substitute gas[J]. Insulating Materials, 2022, 55 (6): 1- 5.
|
| 13 |
马世恒, 葛敬冉, 刘凯, 等. 玻璃纤维/环氧树脂预浸料固化全过程的比热容和热导率研究[J/OL]. 复合材料科学与工程: 1–6[2023-08-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1683.TU.20230803.1537.008.html.
|
|
MA Shiheng, GE Jingran, LIU Kai, et al. Study on specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity of glass fiber/epoxy resin prepreg during the whole curing process[J/OL]. Composites Science and Engineering: 1–6[2023-08-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1683.TU.20230803.1537.008.html.
|
| 14 |
郑伟龙. 12 kV开关柜温度场分析及优化设计[D]. 厦门: 厦门理工学院, 2021.
|
|
ZHENG Weilong. Temperature field analysis and optimization design of 12 kV switchgear[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University of Technology, 2021.
|
| 15 |
彭波. 12 kV环保型气体绝缘开关柜传热机理研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门理工学院, 2019.
|
|
PENG Bo. Research on heat transfer mechanism of 12 kV environmentally friendly gas insulated switchgear[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University of Technology, 2019.
|
| 16 |
居一峰, 蒋卿, 杨鹤猛, 等. 异常发热复合绝缘子温升的影响因素研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48 (11): 86- 91.
|
|
JU Yifeng, JIANG Qing, YANG Hemeng, et al. Study on influence factors of temperature rise on composite insulator with abnormal heating[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48 (11): 86- 91.
|
| 17 |
斯小琴, 陈大伟, 岳生伟. 一维热传导方程数值解的计算机仿真与研究[J]. 青岛理工大学学报, 2023, 44 (5): 169- 174.
|
|
SI Xiaoqin, CHEN Dawei, YUE Shengwei. Computer simulation and research on numerical solution of one-dimensional heat conduction equation[J]. Journal of Qingdao University of Technology, 2023, 44 (5): 169- 174.
|
| 18 |
李航洋, 阳同光. 计及动态非均匀热特性的储能软包锂电池充放电热路模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (19): 104- 113.
|
|
LI Hangyang, YANG Tongguang. A charging/discharging thermal circuit model for energy storage pouch lithium batteries considering dynamic and non-uniform characteristics[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (19): 104- 113.
|
| 19 |
王为清, 杨立, 李彦强, 等. 计及容器壁温度变化的容器充气特性数值模拟[J]. 液压与气动, 2015, (1): 57- 61.
|
|
WANG Weiqing, YANG Li, LI Yanqiang, et al. Numerical simulation of gas characteristics during tank charge considering temperature variation of vessel wall[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2015, (1): 57- 61.
|
| 20 |
骆常璐, 杨姣龙, 李松磊, 等. 基于等效热路和有限元分析的GIS温升研究[J]. 高压电器, 2021, 57 (5): 67- 76.
|
|
LUO Changlu, YANG Jiaolong, LI Songlei, et al. Study on temperature rise of GIS based on equivalent thermal circuit and finite element analysis[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2021, 57 (5): 67- 76.
|
| 21 |
肖成志, 张亚涛, 于洪兴, 等. 季冻区环境温度变化对加筋土挡墙内部温度场的影响研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2023, 31 (6): 2104- 2114.
|
|
XIAO Chengzhi, ZHANG Yatao, YU Hongxing, et al. Effect of ambient temperature changing in seasonally frozen zone on temperature field of inner reinforced-soil retaining wall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31 (6): 2104- 2114.
|
| 22 |
李琳睿, 孙晓霞, 王一凡, 等. 壁面热辐射对车内温度场影响的分析[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2024, 44 (1): 60- 68.
|
|
LI Linrui, SUN Xiaoxia, WANG Yifan, et al. Effect of wall thermal radiation on temperature field of a vehicle[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2024, 44 (1): 60- 68.
|
| 23 |
薛继鹏. 大电流开关柜触头热管散热关键技术研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016.
|
| 24 |
肖淞, 石生尧, 林婧桐, 等. “碳达峰、碳中和” 目标下高压电气设备中强温室绝缘气体SF6控制策略分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (1): 339- 357.
|
|
XIAO Song, SHI Shengyao, LIN Jingtong, et al. Analysis on the control strategy of the strong greenhouse insulating gas SF6 in high-voltage electrical equipment under the goal of "emission peak and carbon neutrality"[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (1): 339- 357.
|
| 25 |
中国国家标准化管理委员会. 六氟化硫电气设备中气体管理和检测导则: GB/T 8905—2012[S]. 北京: 中国电力企业联合会, 2012.
|
| 26 |
张朕豪. 分布式GIS配电室气体安全监测系统设计与实现[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2023.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenhao. Design and implementation of distributed GIS distribution room gas safety monitoring system[D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2023.
|
| 27 |
李丰君, 王磊, 赵健, 等. 基于天气融合和LSTM网络的分布式光伏短期功率预测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 149- 154.
|
|
LI Fengjun, WANG Lei, ZHAO Jian, et al. Research on distributed photovoltaic short-term power prediction method based on weather fusion and LSTM-net[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 149- 154.
|
| 28 |
李丹, 张远航, 李黄强, 等. 基于精准气象数据的地区电网短期负荷智能预测系统设计[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 128- 133.
|
|
LI Dan, ZHANG Yuanhang, LI Huangqiang, et al. Design of a short-term load intelligent forecasting system for regional power grid based on accurate weather data[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 128- 133.
|
| 29 |
王勃, 冯双磊, 刘晓琳, 等. 计及转折性天气过程识别与检验的短期风电功率预测[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (12): 52- 62.
|
|
WANG Bo, FENG Shuanglei, LIU Xiaolin, et al. Short-term wind power prediction considering identification and testing of transitional weather processes[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (12): 52- 62.
|