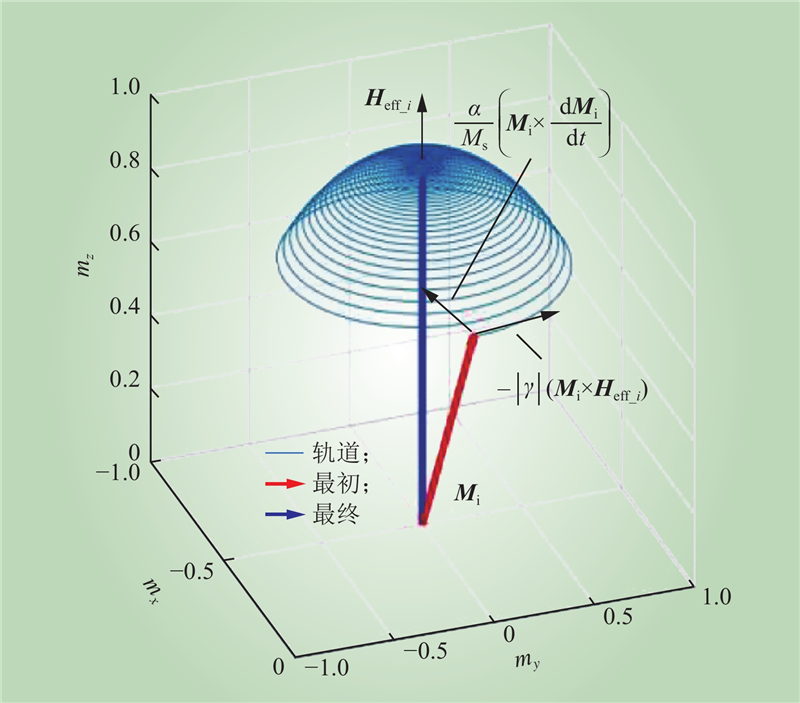
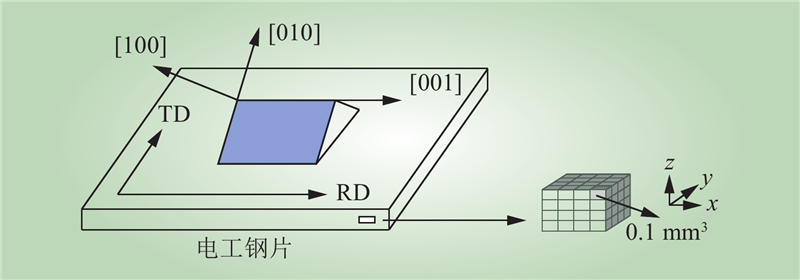
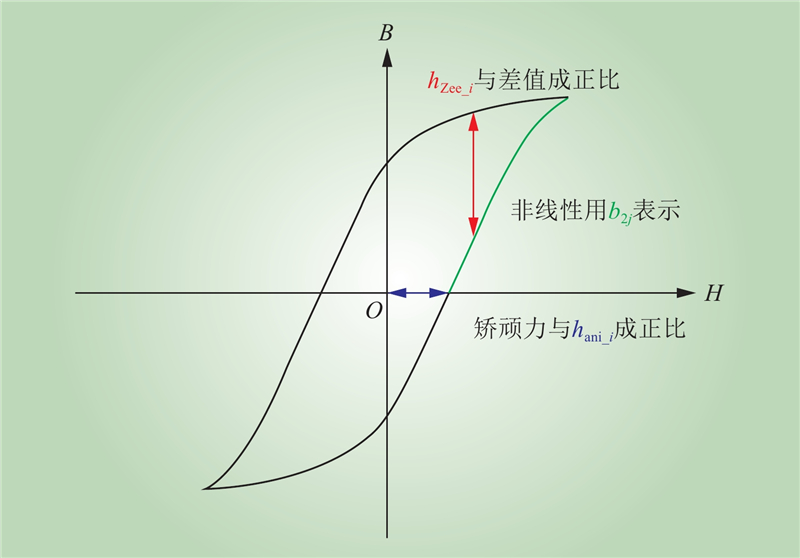
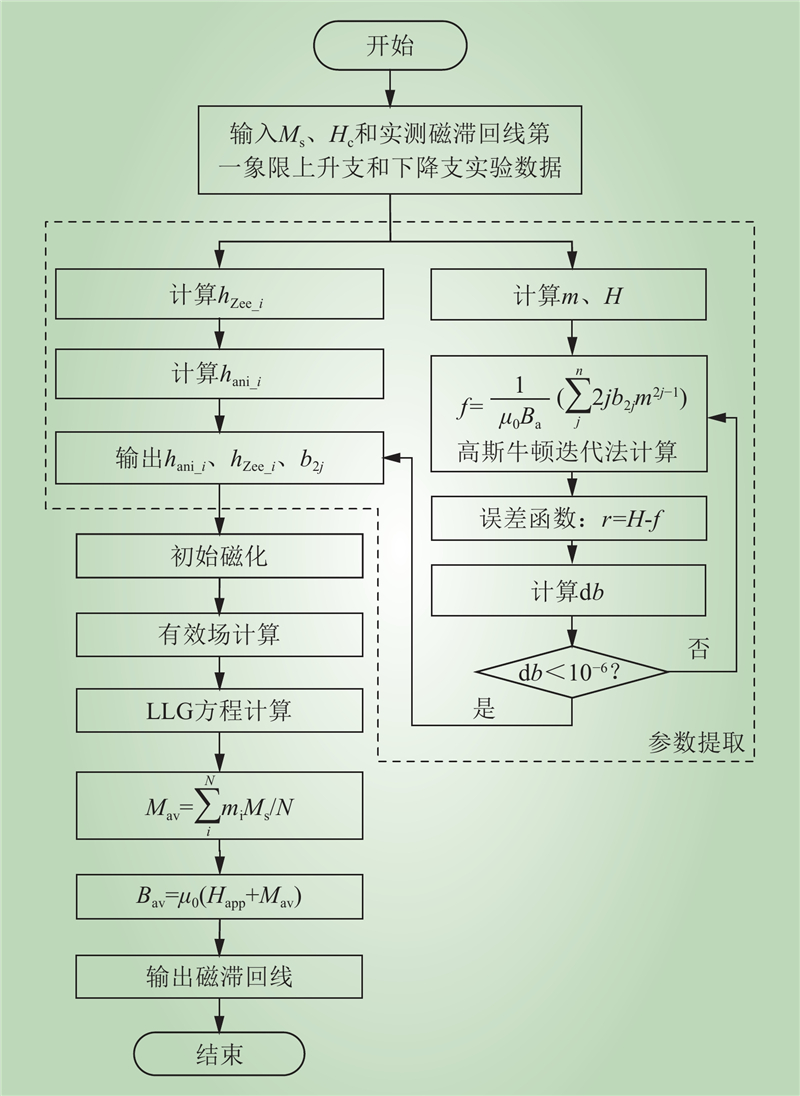
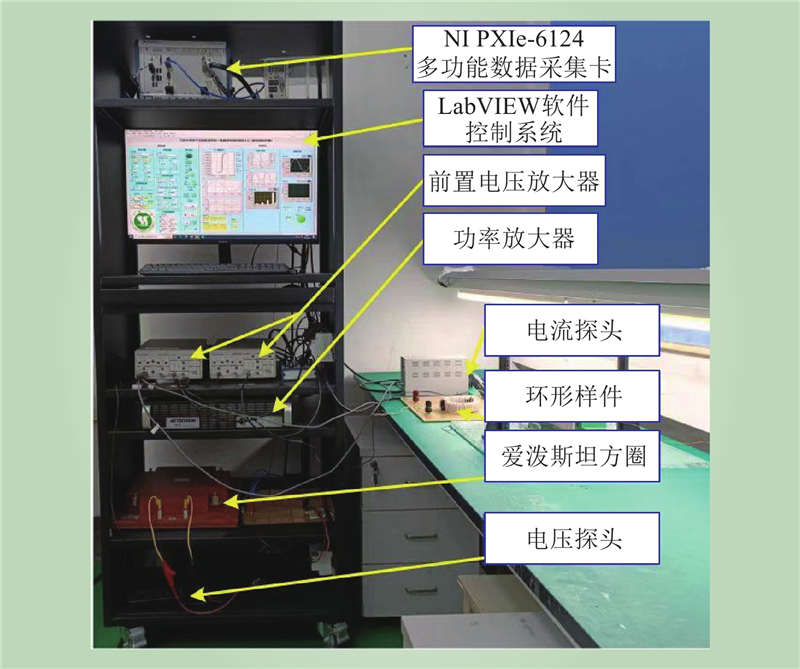
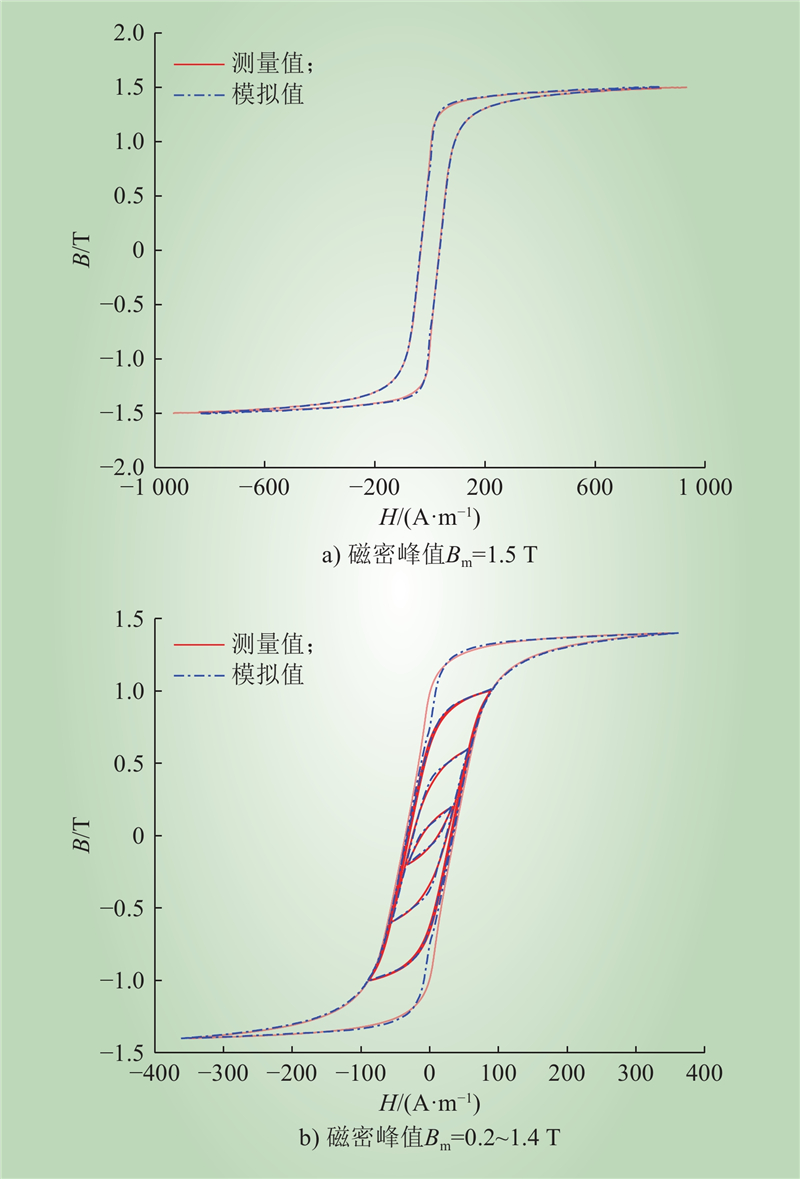
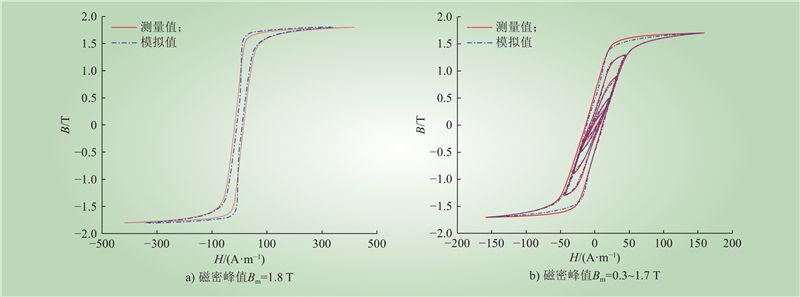
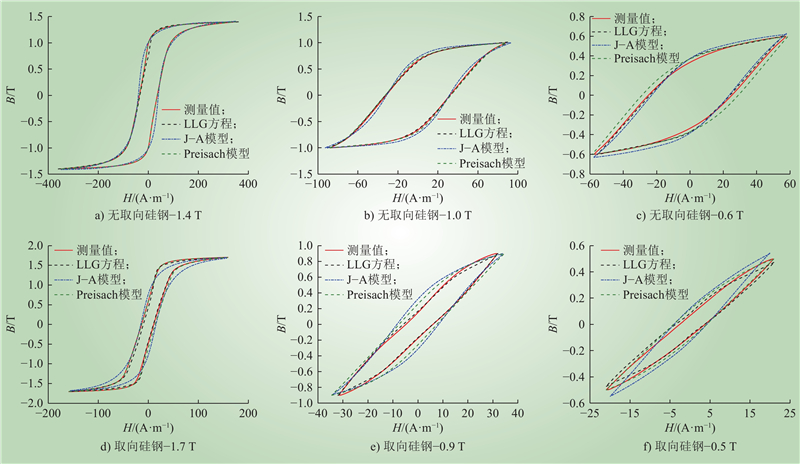
| 1 |
赵小军, 张佳伟, 王浩名, 等. 电-磁-机耦合视域下考虑气隙影响的变压器铁心振动特性精细化模拟方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39 (14): 4257- 4269.
|
|
ZHAO Xiaojun, ZHANG Jiawei, WANG Haoming, et al. A refined simulation method for the vibration characteristics of transformer core considering the influence of air gap under the perspective of electro-magnetic-mechanical coupling[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39 (14): 4257- 4269.
|
| 2 |
李伊玲, 李琳, 刘任. 机械应力作用下电工钢片静态磁滞特性模拟方法研究[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (10): 10- 18.
|
|
LI Yiling, LI Lin, LIU Ren. Modeling methods of static hysteresis characteristics of electrical steel sheets under stress[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (10): 10- 18.
|
| 3 |
王振, 张艳丽, 龚园, 等. 机械应力下无取向电工钢片磁致伸缩特性研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38 (21): 5682- 5690.
|
|
WANG Zhen, ZHANG Yanli, GONG Yuan, et al. Study on magnetostrictive properties of non-oriented electrical steel sheet under mechanical stress[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38 (21): 5682- 5690.
|
| 4 |
罗智荣, 黄丰, 郭淳, 等. 基于多物理场仿真的油浸式变压器振动特性分析及影响因素研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (11): 48- 55.
|
|
LUO Zhirong, HUANG Feng, GUO Chun, et al. Vibration characteristics analysis and influencing factors of oilimmersed transformer based on multi-physical field simulation[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (11): 48- 55.
|
| 5 |
李峰, 孟圣坤, 陆飞, 等. 基于监督学习的直流偏磁特征分析及评价方法研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (8): 111- 118.
|
|
LI Feng, MENG Shengkun, LU Fei, et al. Characteristic analysis and evaluation method of DC magnetic bias based on supervised learning[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (8): 111- 118.
|
| 6 |
赵小军, 武欣怡, 章轩源, 等. 高频多谐波激励下计及趋肤效应的软磁带材磁滞及损耗特性预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (22): 9039- 9048.
|
|
ZHAO Xiaojun, WU Xinyi, ZHANG Xuanyuan, et al. Predicting hysteresis and loss characteristics of soft magnetic tape material considering skin effect under high frequency multi-harmonic magnetization[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (22): 9039- 9048.
|
| 7 |
刘欢, 李永建, 张长庚, 等. 非正弦激励下纳米晶材料高频磁心损耗的计算方法改进与验证[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38 (5): 1217- 1227.
|
|
LIU Huan, LI Yongjian, ZHANG Changgeng, et al. Calculation and experimental verification of core loss in high frequency transformer under non-sinusoidal excitation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38 (5): 1217- 1227.
|
| 8 |
赵志刚, 毕紫莉. 正弦及谐波激励下铁磁材料损耗模型的改进和验证[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (9): 3452- 3460.
|
|
ZHAO Zhigang, BI Zili. Improvement and verification of ferromagnetic material loss model under sinusoidal and harmonic excitation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (9): 3452- 3460.
|
| 9 |
SAI RAM B, PAUL A K, KULKARNI S V. Soft magnetic materials and their applications in transformers[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2021, 537, 168210.
|
| 10 |
刘洋, 巩学海, 陈新, 等. 0.10 mm与0.23 mm取向硅钢在不同运行工况下磁特性的测量与对比分析[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (2): 181- 189.
|
|
LIU Yang, GONG Xuehai, CHEN Xin, et al. Measurement and comparison of magnetic properties of 0.10 mm and 0.23 mm oriented silicon steel under different operating conditions[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (2): 181- 189.
|
| 11 |
贲彤, 安妮, 陈龙, 等. 基于改进多尺度动态J-A模型的无取向硅钢磁致伸缩特性模拟[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (11): 4514- 4526.
|
|
BEN Tong, AN Ni, CHEN Long, et al. Simulation of magnetostrictive characteristics of non-oriented silicon steel based on improved multi-scale dynamic J-A model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (11): 4514- 4526.
|
| 12 |
李宜伦, 张异殊, 宋光. 基于改进鲸鱼算法的电流互感器J-A模型磁滞参数识别[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (2): 190- 199.
|
|
LI Yilun, ZHANG Yishu, SONG Guang. Hysteresis parameter identification of J-A model current transformer based on improved whale algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (2): 190- 199.
|
| 13 |
刘任, 杜莹雪, 李琳, 等. 解析正Preisach磁滞模型的推导与修正[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (5): 2070- 2079.
|
|
LIU Ren, DU Yingxue, LI Lin, et al. Derivation and modification of analytical forward preisach hysteresis model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (5): 2070- 2079.
|
| 14 |
胡蔡飞, 范学良, 童力, 等. 基于Jiles-Atherton逆模型的磁阀式可控电抗器铁心饱和度分析[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (12): 38- 44.
|
|
HU Caifei, FAN Xueliang, TONG Li, et al. Core saturation analysis of magnetic-valve controlled reactor based on Jiles-Atherton inverse model[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (12): 38- 44.
|
| 15 |
HAYASHI N, INOUE T, NAKATANI Y, et al. Direct solution of Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equation for domain walls in thin Permalloy films[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1988, 24 (6): 3111- 3113.
|
| 16 |
DI FRATTA G, JÜNGEL A, PRAETORIUS D, et al. Spin-diffusion model for micromagnetics in the limit of long times[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 2023, 343, 467- 494.
|
| 17 |
BERTOTTI G. Connection between microstructure and magnetic properties of soft magnetic materials[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2008, 320 (20): 2436- 2442.
|
| 18 |
ANGIZI S, HE Z Z, CHEN A, et al. Hybrid spin-CMOS polymorphic logic gate with application in in-memory computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2020, 56 (2): 3400215.
|
| 19 |
袁佳卉, 杨晓阔, 张斌, 等. 混合时钟驱动的自旋神经元器件激活特性和计算性能[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70 (20): 317- 326.
|
|
YUAN Jiahui, YANG Xiaokuo, ZHANG Bin, et al. Activation function and computing performance of spin neuron driven by magnetic field and strain[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70 (20): 317- 326.
|
| 20 |
VAN DE WIELE B, DUPRÉ L, OLYSLAGER F. Influence of space discretization size in 3D micromagnetic modeling[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2008, 403 (2/3): 372- 375.
|
| 21 |
STEPHENSON E, MARDER A. The effects of grain size on the core loss and permeability of motor lamination steel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1986, 22 (2): 101- 106.
|
| 22 |
CHENG L, WAGNER G J. A representative volume element network (RVE-net) for accelerating RVE analysis, microscale material identification, and defect characterization[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 390, 114507.
|
| 23 |
KURZKE M, MELCHER C, MOSER R. Vortex motion for the landau–Lifshitz–gilbert equation with spin-transfer torque[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 2011, 43 (3): 1099- 1121.
|
| 24 |
LAKSHMANAN M. The fascinating world of the landau–Lifshitz–gilbert equation: an overview[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2011, 369 (1939): 1280- 1300.
|
| 25 |
PAN H J, ZHANG Z H, XIE J X. The effects of recrystallization texture and grain size on magnetic properties of 6.5wt% Si electrical steel[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 401, 625- 632.
|
| 26 |
LEBECKI K M, DONAHUE M J, GUTOWSKI M W. Periodic boundary conditions for demagnetization interactions in micromagnetic simulations[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2008, 41 (17): 175005.
|
| 27 |
刘任, 顾朝阳, 孙江东, 等. Jiles-Atherton磁滞模型的改进与非正弦激励下软磁材料复杂磁滞准确模拟[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (5): 2016- 2027.
|
|
LIU Ren, GU Chaoyang, SUN Jiangdong, et al. Modified Jiles-Atherton hysteresis model and accurate simulation of complex hysteresis characteristics of soft magnetic materials under non-sinusoidal excitation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (5): 2016- 2027.
|
| 28 |
刘任, 杜莹雪, 李琳, 等. 解析逆Preisach磁滞模型[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38 (10): 2567- 2576.
|
|
LIU Ren, DU Yingxue, LI Lin, et al. Analytical inverse Preisach hysteresis model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38 (10): 2567- 2576.
|