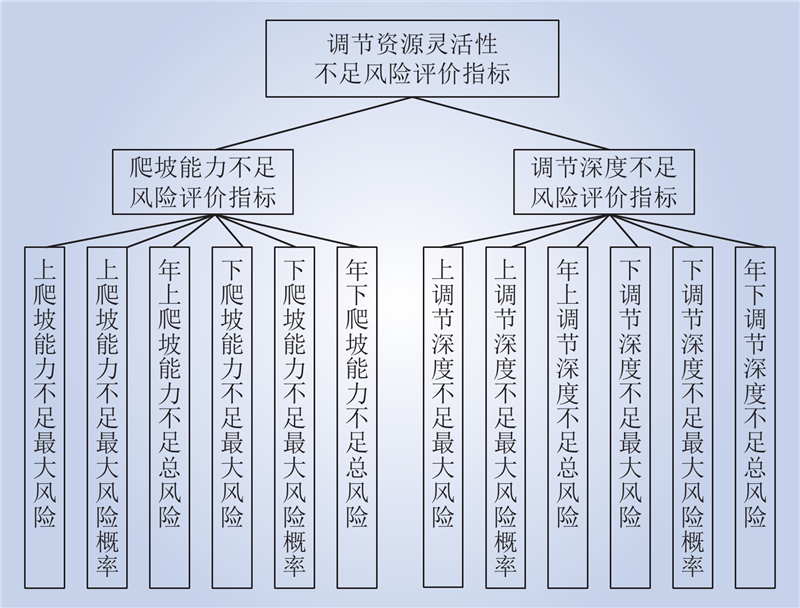
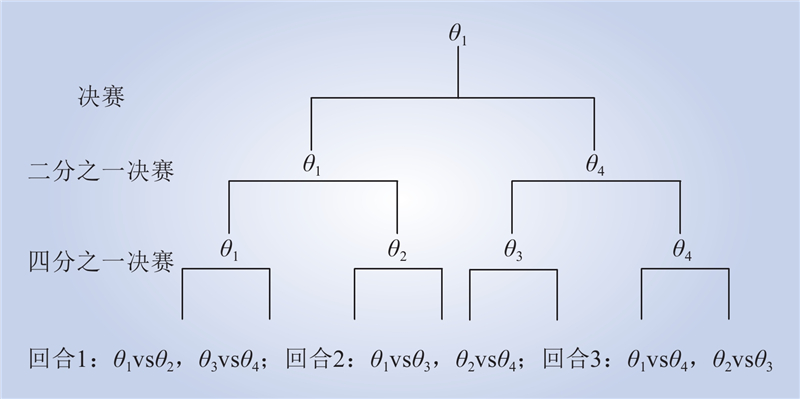
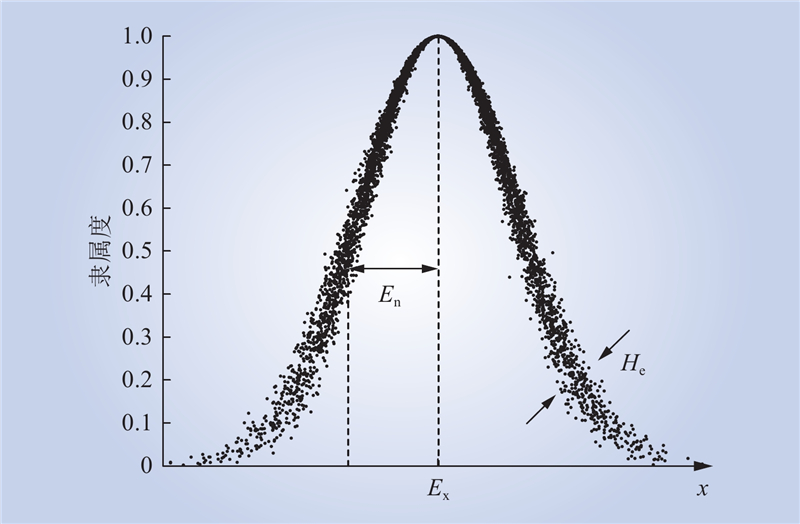
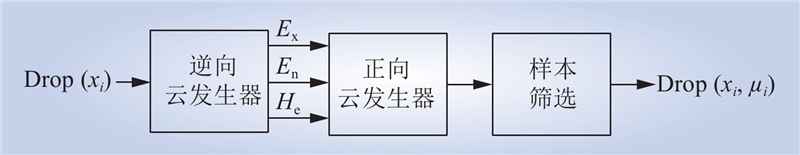
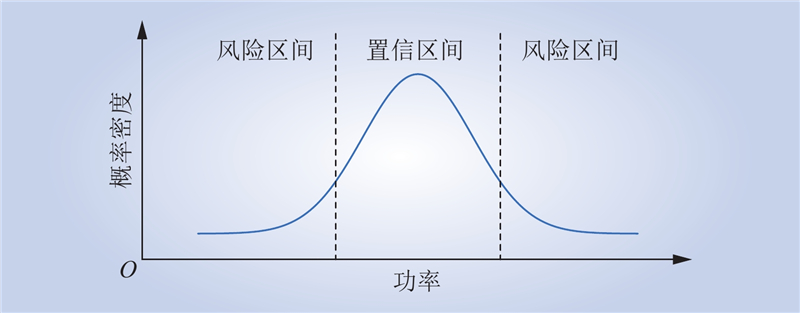
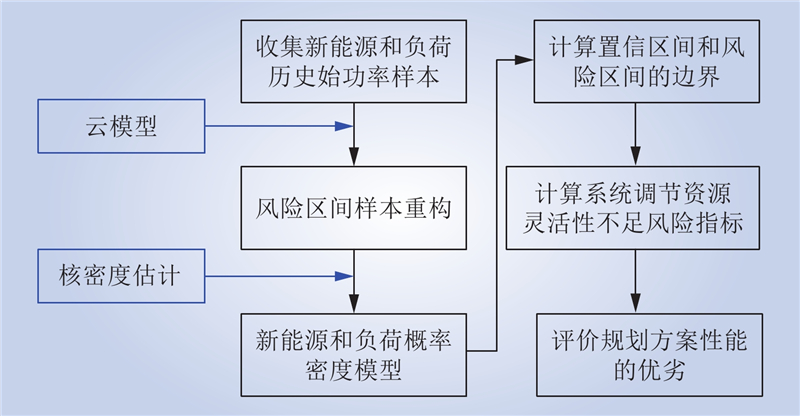
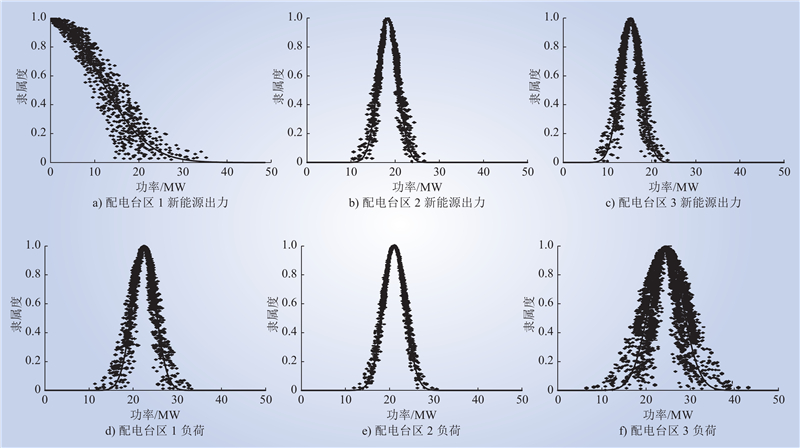
| 1 |
周孝信, 陈树勇, 鲁宗相, 等. 能源转型中我国新一代电力系统的技术特征[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (7): 1893- 1904, 2205.
|
|
ZHOU Xiaoxin, CHEN Shuyong, LU Zongxiang, et al. Technology features of the new generation power system in China[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (7): 1893- 1904, 2205.
|
| 2 |
CRUZ M R M, FITIWI D Z, SANTOS S F, et al. A comprehensive survey of flexibility options for supporting the low-carbon energy future[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 97, 338- 353.
|
| 3 |
罗毅, 李昱龙. 基于熵权法和灰色关联分析法的输电网规划方案综合决策[J]. 电网技术, 2013, 37 (1): 77- 81.
|
|
LUO Yi, LI Yulong. Comprehensive decision-making of transmission network planning based on entropy weight and grey relational analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37 (1): 77- 81.
|
| 4 |
张建平, 胡建绩. 面向智能电网的多适应性规划体系设计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2011, 35 (10): 1- 7.
|
|
ZHANG Jianping, HU Jianji. Design of smart grid oriented adaptive planning system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2011, 35 (10): 1- 7.
|
| 5 |
马欢, 王柏公, 蔡亮, 等. 冷端耦合相变储热罐的间接空冷机组热力特性及热经济性评价[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (24): 9616- 9629.
|
|
MA Huan, WANG Baigong, CAI Liang, et al. Thermal characteristic and thermo-economic evaluation on the indirect air-cooled power generating unit with a cold-end system integrating a phase-change heat storage tank[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (24): 9616- 9629.
|
| 6 |
马玉锴, 田亮. 基于证据理论与云模型的火电机组节能减排绩效综合评价[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49 (3): 96- 103, 126.
|
|
MA Yukai, TIAN Liang. Energy saving and emission reduction evaluation of thermal power units based on evidence theory and cloud model[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 49 (3): 96- 103, 126.
|
| 7 |
李响, 牛赛. 双碳目标下源–网–荷多层评价体系研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (S1): 178- 184.
|
|
LI Xiang, NIU Sai. Study on multi-layer evaluation system of source-grid-load under carbon-neutral goal[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (S1): 178- 184.
|
| 8 |
白小元, 吴有兵, 林勇, 等. 含间歇性电源的能源基地源网协调发展评价[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2023, 39 (3): 109- 115.
|
|
BAI Xiaoyuan, WU Youbing, LIN Yong, et al. Evaluation of source network coordination development for energy base containing intermittent power[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2023, 39 (3): 109- 115.
|
| 9 |
赵娟, 王雷, 吴磊, 等. 基于年费用的电源结构评价[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2019, 35 (12): 7- 14.
|
|
ZHAO Juan, WANG Lei, WU Lei, et al. Power structure evaluation based on annual cost[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2019, 35 (12): 7- 14.
|
| 10 |
吕游, 吴斌, 秦瑞钧, 等. 燃煤机组灵活运行性能评价及成本分析[J]. 热力发电, 2023, 52 (12): 20- 28.
|
|
LYU You, WU Bin, QIN Ruijun, et al. Flexible operation performance evaluation and cost analysis of coal-fired units[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2023, 52 (12): 20- 28.
|
| 11 |
王志杰, 陈文, 朱晓星, 等. 基于数据驱动的火电机组灵活性综合评价方法及应用[J]. 现代电力, 2024, 41 (4): 667- 672.
|
|
WANG Zhijie, CHEN Wen, ZHU Xiaoxing, et al. Comprehensive Evaluation Method for Thermal Power Unit Flexibility Based on Data-driven and its Application[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2024, 41 (4): 667- 672.
|
| 12 |
肖定垚, 王承民, 曾平良, 等. 考虑可再生能源电源功率不确定性的电源灵活性评价[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2015, 35 (7): 120- 125, 139.
|
|
XIAO Dingyao, WANG Chengmin, ZENG Pingliang, et al. Power source flexibility evaluation considering renewable energy generation uncertainty[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2015, 35 (7): 120- 125, 139.
|
| 13 |
TANG H L, WU J K, CHEN L M, et al. A control optimization model for CVaR risk of distribution systems with PVs/DSs/EVs using Q-learning powered adaptive differential evolution algorithm[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 132, 107209.
|
| 14 |
JIA J C, YIN G L, SUN L L, et al. Schedule strategy considering the overload violation risk to the security region in distribution networks[J]. Energies, 2022, 15 (23): 8781.
|
| 15 |
JIA J C, YIN G L, SUN L L, et al. Uncertainty risk assessment of overloading violation based on security region and risk scheduling of active distribution networks[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2024, 155, 109498.
|
| 16 |
ROSEWATER D, BALDICK R, SANTOSO S. Risk-averse model predictive control design for battery energy storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (3): 2014- 2022.
|
| 17 |
JU L W, ZHAO R, TAN Q L, et al. A multi-objective robust scheduling model and solution algorithm for a novel virtual power plant connected with power-to-gas and gas storage tank considering uncertainty and demand response[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250, 1336- 1355.
|
| 18 |
杨楠, 黄禹, 叶迪, 等. 基于自适应多变量非参数核密度估计的多风电场出力相关性建模[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (13): 3805- 3812, 4021.
|
|
YANG Nan, HUANG Yu, YE Di, et al. Modeling of output correlation of multiple wind farms based on adaptive multivariable nonparametric kernel density estimation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (13): 3805- 3812, 4021.
|
| 19 |
COWLING A, HALL P. On pseudodata methods for removing boundary effects in kernel density estimation[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology, 1996, 58 (3): 551- 563.
|
| 20 |
李德毅, 刘常昱. 论正态云模型的普适性[J]. 中国工程科学, 2004, 6 (8): 28- 34.
|
|
LI Deyi, LIU Changyu. Study on the universality of the normal cloud model[J]. Engineering Science, 2004, 6 (8): 28- 34.
|