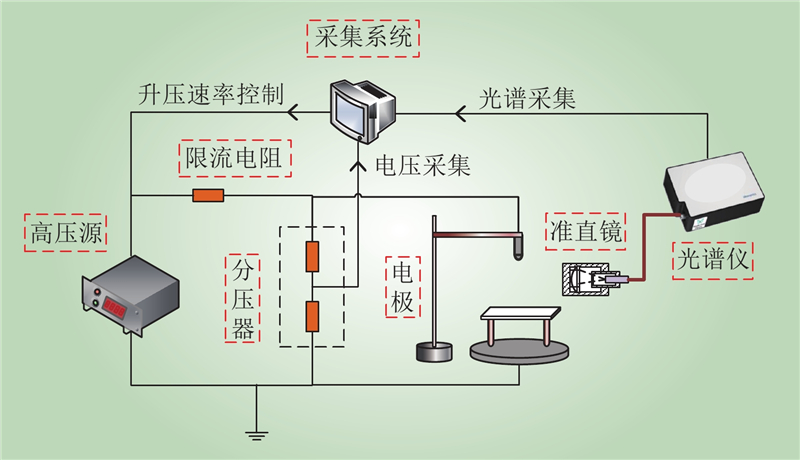
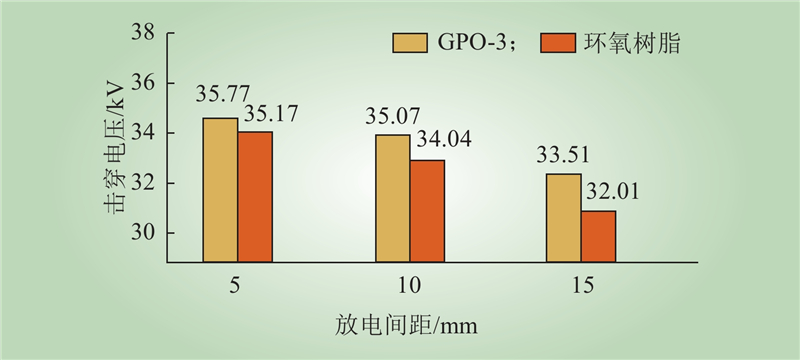
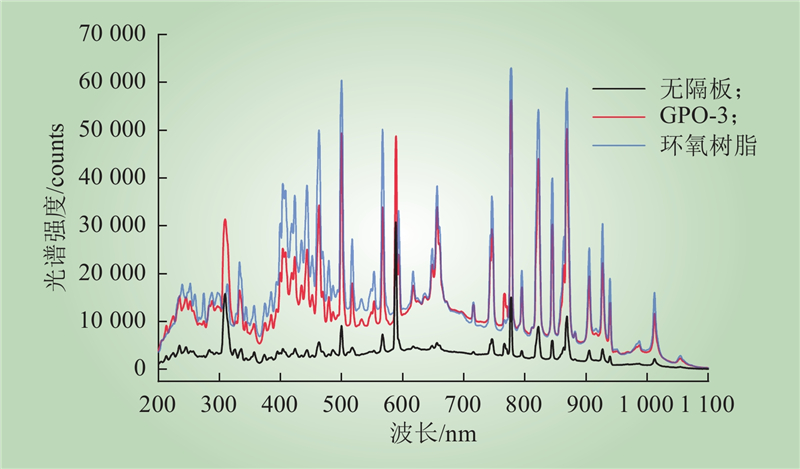
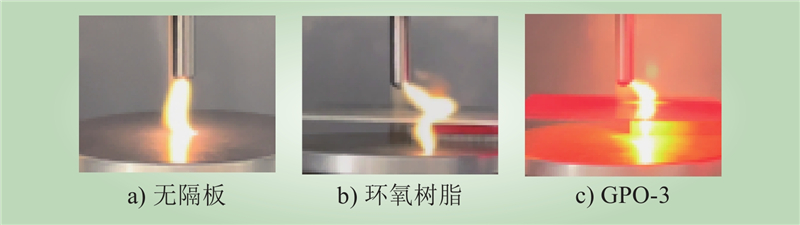
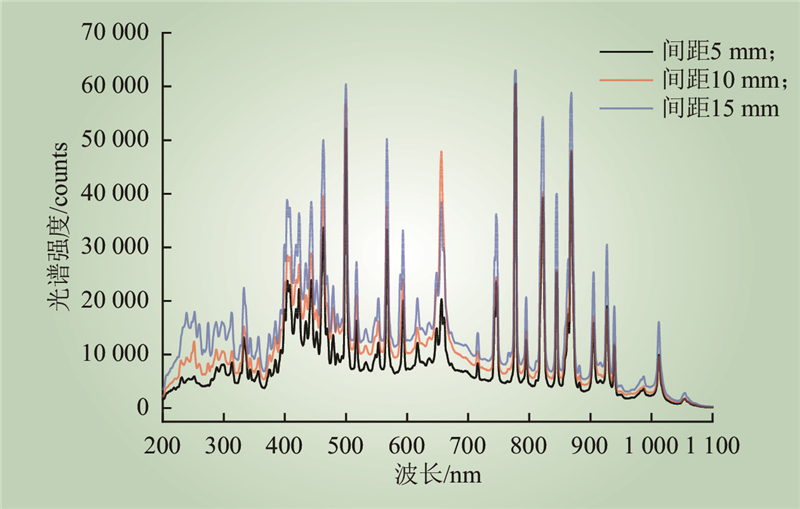
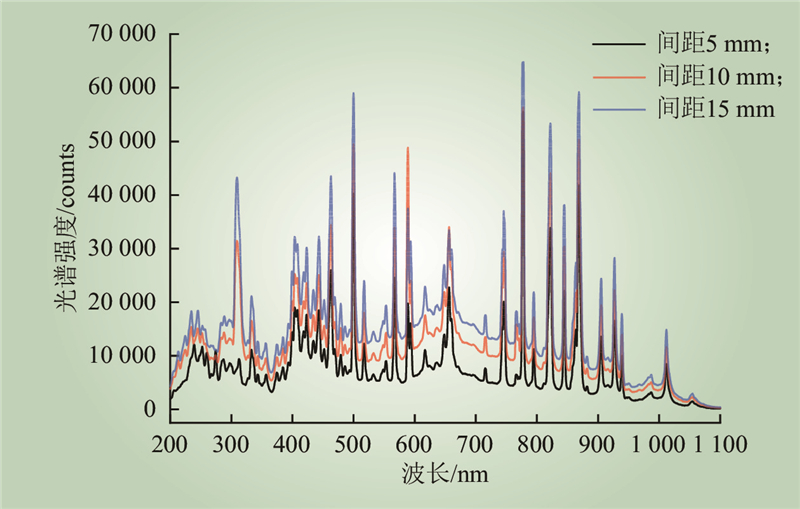
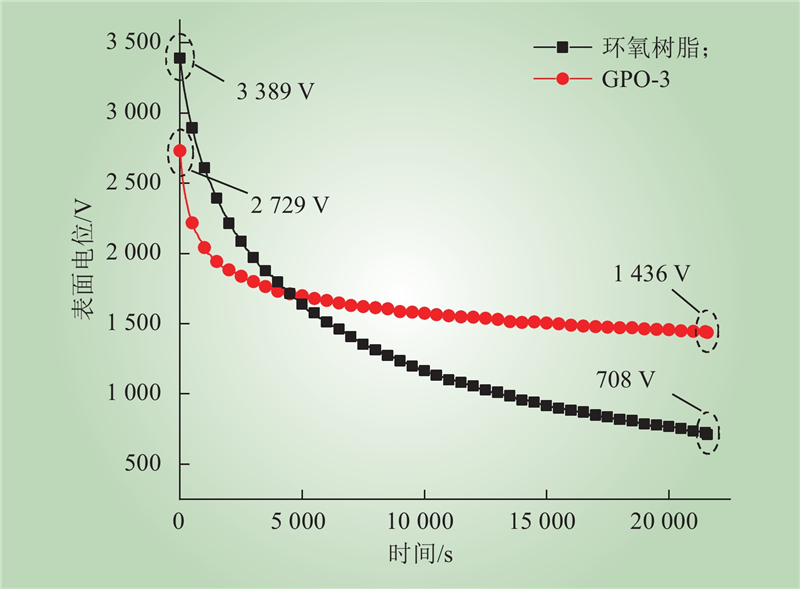
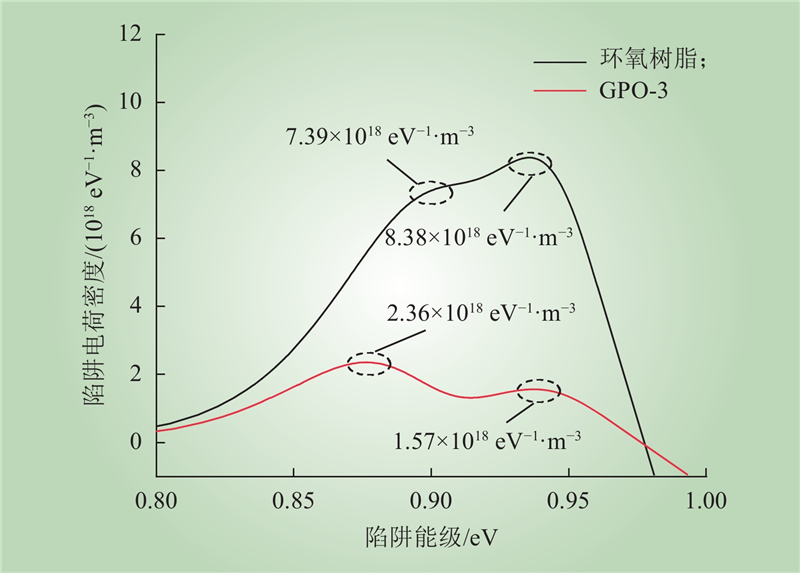
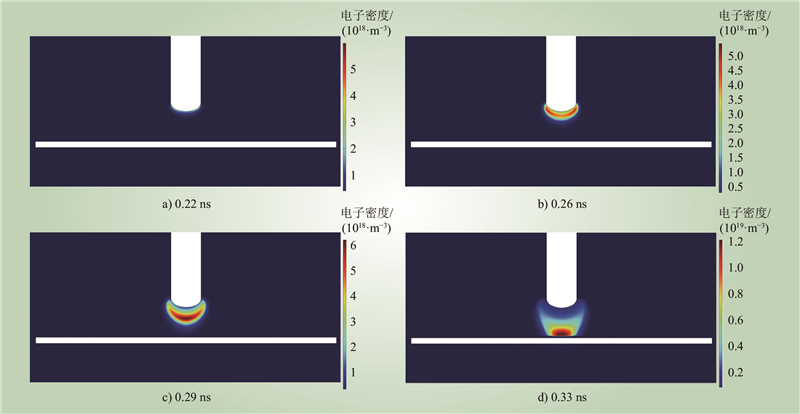
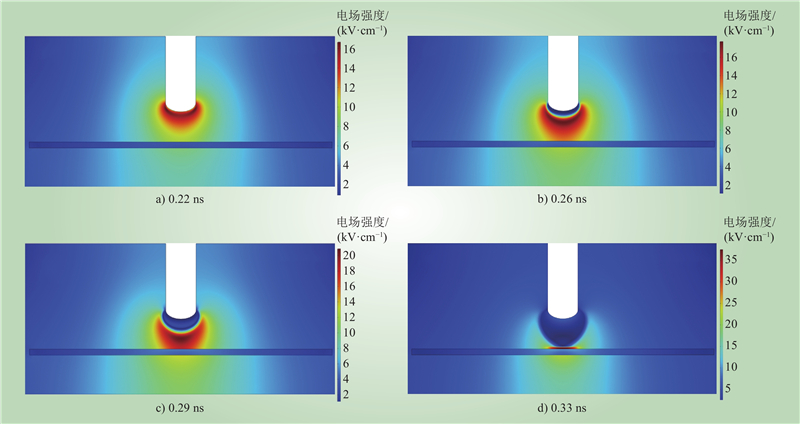
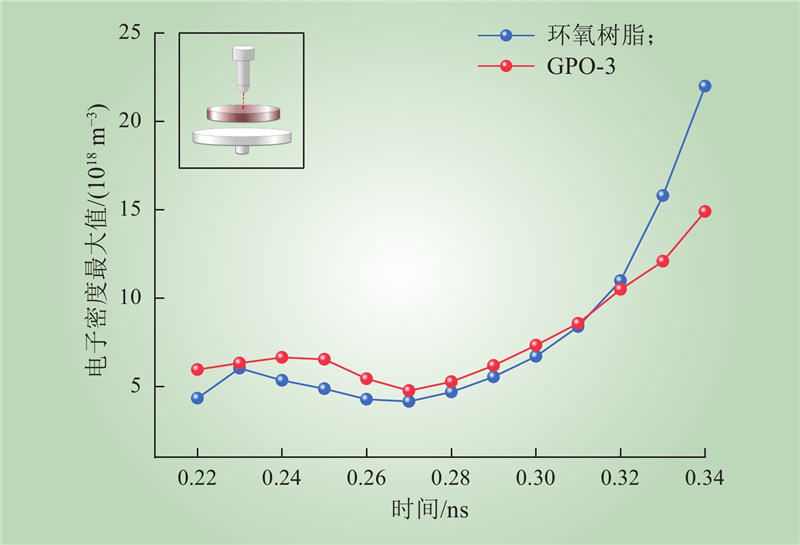
| 1 |
ZHANG C X, DONG M, REN M, et al. Partial discharge monitoring on metal-enclosed switchgear with distributed non-contact sensors[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18 (2): 551.
|
| 2 |
谢荣斌, 杨超, 申强, 等. TEV与HFCT法测量开关柜局部放电的特性对比[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (3): 37- 47.
|
|
XIE Rongbin, YANG Chao, SHEN Qiang, et al. Comparative study on the switchgear partial discharge characteristics based on transient earth voltage and pulse current detection methods[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (3): 37- 47.
|
| 3 |
昝海斌, 李国倡, 王景兵, 等. GPO-3隔板对棒-板间隙工频击穿电压的影响及表面残余电荷特性[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35 (8): 1799- 1806.
|
|
ZAN Haibin, LI Guochang, WANG Jingbing, et al. Influence of GPO-3 barrier on AC breakdown voltage of rod-plane gaps and surface residual charge characteristics[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35 (8): 1799- 1806.
|
| 4 |
郑跃胜, 陈雍, 钟小燕, 等. 隔板尺寸对棒-板空气绝缘间隙工频耐压特性的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2018, 44 (1): 195- 200.
|
|
ZHENG Yuesheng, CHEN Yong, ZHONG Xiaoyan, et al. Effects of barrier dimensions on AC withstand characteristics of air insulated rod-plane gaps[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2018, 44 (1): 195- 200.
|
| 5 |
FORUZAN E, AKMAL A A S, NIAYESH K, et al. Comparative study on various dielectric barriers and their effect on breakdown voltage[J]. High Voltage, 2018, 3 (1): 51- 59.
|
| 6 |
MERABET S, BOUDISSA R, SLIMANI S, et al. Optimisation of the dielectric strength of a non-uniform electric field electrode system under positive DC voltage by insertion of multiple barriers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2014, 21 (1): 74- 79.
|
| 7 |
LI G C, WANG J X, WEI Y H, et al. Effect of insulation barrier on AC breakdown voltage of rod-plane gaps and analysis of surface residual charge property[J]. Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30 (10): 9513- 9519.
|
| 8 |
齐冰, 王涵. 气液相变对高压纳秒脉冲作用下变压器油中流注放电的影响[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (3): 23- 30.
|
|
QI Bing, WANG Han. Effect of gas-liquid phase change on injection and discharge in transformer oil under high pressure nanosecond pulse[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (3): 23- 30.
|
| 9 |
方子豪, 陈潇一, 孙佳伦. 基于指数目标函数优化的变压器局部放电故障最佳定位点估计方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (5): 51- 56, 118.
|
|
FANG Zihao, CHEN Xiaoyi, SUN Jialun. Optimal estimation of partial discharge fault location in transformer based on exponential objective function optimization[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (5): 51- 56, 118.
|
| 10 |
刘东超, 陈志刚, 崔龙飞. 基于物联网的环网柜在线监测技术研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (20): 60- 67.
|
|
LIU Dongchao, CHEN Zhigang, CUI Longfei. Online monitoring technology of a ring network cabinet based on the Internet of Things[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (20): 60- 67.
|
| 11 |
屈斌, 张利, 王永宁, 等. 基于振动信号的GIS机械松动与局部放电诊断方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36 (2): 98- 106.
|
|
QU Bin, ZHANG Li, WANG Yongning, et al. Study of mechanical looseness and partial discharge diagnoses of GIS based on vibration signals[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2021, 36 (2): 98- 106.
|
| 12 |
鞠玲, 黄怿. 基于EFPI的数字配电网超声检测传感器[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 194- 201.
|
|
JU Ling, HUANG Yi. Ultrasonic detection sensor of digital distribution network based on EFPI[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 194- 201.
|
| 13 |
WU S Y, ZHENG S S. Detection of partial discharge in GIS and transformer under impulse voltage by fluorescent optical fiber sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21 (9): 10675- 10684.
|
| 14 |
JIA S R, JIA Y F, BU Z W, et al. Detection technology of partial discharge in transformer based on optical signal[J]. Energy Reports, 2023, 9, 98- 106.
|
| 15 |
李军浩, 韩旭涛, 刘泽辉, 等. 电气设备局部放电检测技术述评[J]. 高电压技术, 2015, 41 (8): 2583- 2601.
|
|
LI Junhao, HAN Xutao, LIU Zehui, et al. Review on partial discharge measurement technology of electrical equipment[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2015, 41 (8): 2583- 2601.
|
| 16 |
FUJII K, YAMADA M, TANAKA A, et al. Emission spectrum of partial discharge light in SF6/gas[C]//Conference Record of the 1992 IEEE International Symposium on Electrical Insulation. Baltimore, MD, USA. IEEE, Aug. 2002: 332–335.
|
| 17 |
REN M, SONG B, ZHUANG T X, et al. Optical partial discharge diagnostic in SF6 gas insulated system via multi-spectral detection[J]. ISA Transactions, 2018, 75, 247- 257.
|
| 18 |
李彦飞, 汤贝贝, 韩冬, 等. SF6放电的发射光谱特性分析与放电识别[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37 (7): 1866- 1874.
|
|
LI Yanfei, TANG Beibei, HAN Dong, et al. Spectroscopy analysis of emission spectrum characteristics and discharge recognition of SF6 gas discharge[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37 (7): 1866- 1874.
|
| 19 |
LIEBERMAN M A, LICHTENBERG A J. Principles of plasma discharges and materials processing[M]. Wiley, 2005.
|
| 20 |
LI G C, LI S T, PAN S M, et al. Dynamic charge transport characteristics in polyimide surface and surface layer under low-energy electron radiation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2016, 23 (4): 2393- 2403.
|
| 21 |
MEUNIER M, QUIRKE N, ASLANIDES A. Molecular modeling of electron traps in polymer insulators: chemical defects and impurities[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2001, 115 (6): 2876- 2881.
|
| 22 |
SIMMONS J G, TAM M C. Theory of isothermal currents and the direct determination of trap parameters in semiconductors and insulators containing arbitrary trap distributions[J]. Physical Review B, 1973, 7 (8): 3706- 3713.
|
| 23 |
MEYYAPPAN M, KRESKOVSKY J P. Glow discharge simulation through solutions to the moments of the Boltzmann transport equation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1990, 68 (4): 1506- 1512.
|
| 24 |
PANCHESHNYI S, NUDNOVA M, STARIKOVSKII A. Development of a cathode-directed streamer discharge in air at different pressures: experiment and comparison with direct numerical simulation[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2005, 71 (1): 016407.
|
| 25 |
蔡新景, 王新新, 邹晓兵, 等. 基于玻尔兹曼方程的不同密度等离子体电子弛豫相似性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (10): 3109- 3115, S31.
|
|
CAI Xinjing, WANG Xinxin, ZOU Xiaobing, et al. Research on similarity of electron relaxation in plasmas with different densities based on boltzmann equation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (10): 3109- 3115, S31.
|