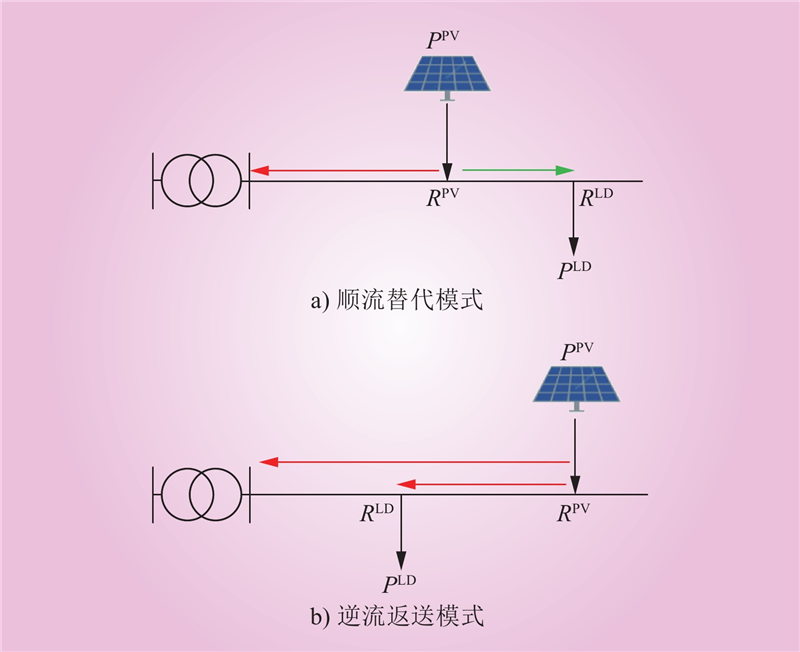
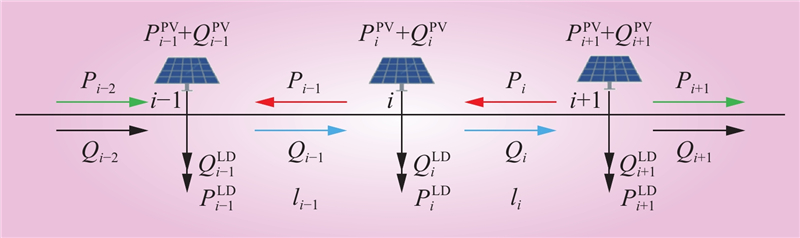
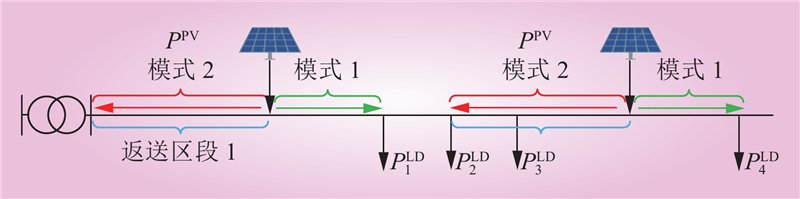
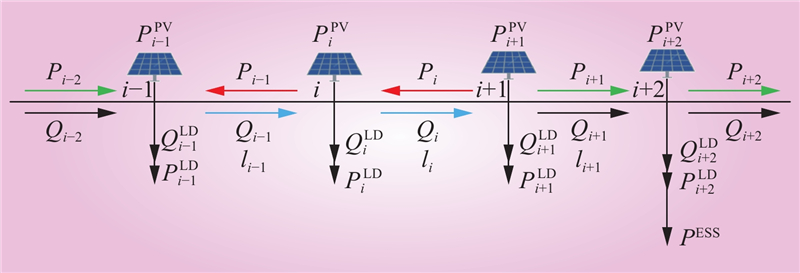
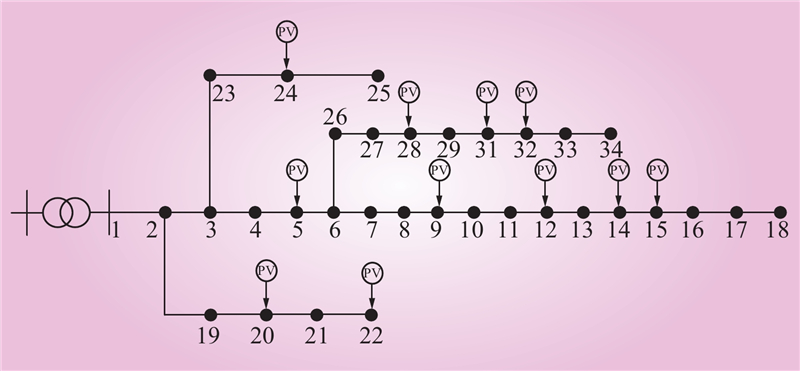
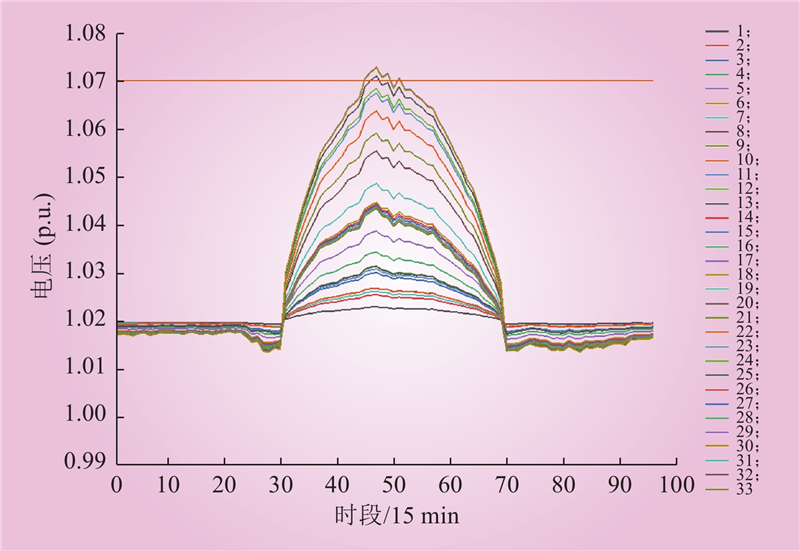
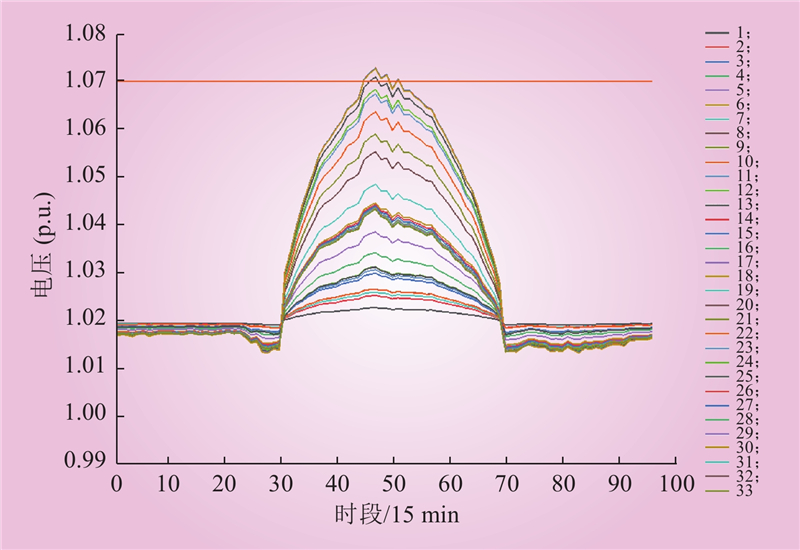
| 1 |
光伏细则出台[J]. 国家电网, 2013(12): 16.
|
| 2 |
吕贝, 邱河梅, 张宇. 太阳能光伏发电产业现状及发展[J]. 华电技术, 2010, 32 (1): 73- 76, 82.
|
|
LÜ Bei, QIU Hemei, ZHANG Yu. Situation and development of solar photovoltaic power generation industry[J]. Huadian Technology, 2010, 32 (1): 73- 76, 82.
|
| 3 |
刘蕾, 楚春礼, 鞠美庭. 中国分布式光伏发电政策演变和发展探讨[J]. 未来与发展, 2018, 42 (6): 6- 14.
|
|
LIU Lei, CHU Chunli, JU Meiting. Policy evolution and development of distributed photovoltaic power generation in China[J]. Future and Development, 2018, 42 (6): 6- 14.
|
| 4 |
李世辉, 王琪, 贾晓卜, 等. 虑热泵负荷和分布式光伏的配微网协调调度[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
|
LI Shihui, WANG Qi, JIA Xiaobo, et al. Coordinated scheduling of distribution networks and microgrids considering heat pump load and distributed photovoltaic[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
| 5 |
陈璨, 白明辉, 张婉明, 等. 分布式光伏边界渗透率快速定位及消纳方案择优[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 40- 50.
|
|
CHEN Can, BAI Minghui, ZHANG Wanming, et al. Fast positioning of marginal hosting capacity and optimal selection of accommodation scheme for distributed PVs[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 40- 50.
|
| 6 |
宣文博, 李慧, 刘忠义, 等. 一种基于虚拟电厂技术的城市可再生能源消纳能力提升方法[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42 (3): 289- 297.
|
|
XUAN Wenbo, LI Hui, LIU Zhongyi, et al. A method for improving accommodating capability of urban renewable energy based on virtual power plant technology[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2021, 42 (3): 289- 297.
|
| 7 |
曾鸣, 杨雍琦, 向红伟, 等. 兼容需求侧资源的“源-网-荷-储”协调优化调度模型[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2016, 36 (2): 102- 111.
|
|
ZENG Ming, YANG Yongqi, XIANG Hongwei, et al. Optimal dispatch model based on coordination between "generation- grid- load- energy storage" and demand-side resource[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36 (2): 102- 111.
|
| 8 |
徐韵, 颜湘武, 李若瑾, 等. 电力市场环境下含“源-网-荷-储”互动的主动配电网有功/无功联合优化[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (10): 3778- 3789.
|
|
XU Yun, YAN Xiangwu, LI Ruojin, et al. Joint optimization of active and reactive powers in active distribution network with "generation-grid-load-energy storage" interaction in power market environment[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (10): 3778- 3789.
|
| 9 |
蒋凯, 李浩秒, 李威, 等. 几类面向电网的储能电池介绍[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2013, 37 (1): 47- 53.
|
|
JIANG Kai, LI Haomiao, LI Wei, et al. On several battery technologies for power grids[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37 (1): 47- 53.
|
| 10 |
严干贵, 冯晓东, 李军徽, 等. 用于松弛调峰瓶颈的储能系统容量配置方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32 (28): 27- 35, 22.
|
|
YAN Gangui, FENG Xiaodong, LI Junhui, et al. Optimization of energy storage system capacity for relaxing peak load regulation bottlenecks[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32 (28): 27- 35, 22.
|
| 11 |
陈崇德, 郭强, 宋子秋, 等. 计及碳收益的风电场混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 22- 33.
|
|
CHEN Chongde, GUO Qiang, SONG Ziqiu, et al. Optimal configuration of hybrid energy storage capacity for wind farms considering carbon trading revenue[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 22- 33.
|
| 12 |
史林军, 杨帆, 刘英, 等. 计及社会发展的多场景用户侧储能容量优化配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (22): 59- 66.
|
|
SHI Linjun, YANG Fan, LIU Ying, et al. Multi-scenario user-side energy storage capacity optimization configuration considering social development[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (22): 59- 66.
|
| 13 |
张冲, 荣娜. 基于改进粒子群算法的新能源侧储能容量配置[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2022, 38 (10): 98- 105.
|
|
ZHANG Chong, RONG Na. Energy storage capacity allocation of renewable energy side based on improved particle swarm optimization[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2022, 38 (10): 98- 105.
|
| 14 |
温春雪, 赵天赐, 于赓, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的储能优化配置[J]. 电气技术, 2022, 23 (10): 1- 9, 58.
|
|
WEN Chunxue, ZHAO Tianci, YU Geng, et al. Optimal configuration of energy storage based on improved particle swarm optimization[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2022, 23 (10): 1- 9, 58.
|
| 15 |
汤翔鹰, 胡炎, 郑棣, 等. 考虑电网灵活性的微电网储能优化配置方法[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37 (12): 54- 60.
|
|
TANG Xiangying, HU Yan, ZHENG Di, et al. Research on optimal configuration of energy storage in microgrid considering grid flexibility[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37 (12): 54- 60.
|
| 16 |
王成磊, 唐岚, 周子超, 等. 计及灵活性供需平衡的储能优化配置[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2023, 39 (4): 1- 11.
|
|
WANG Chenglei, TANG Lan, ZHOU Zichao, et al. Energy storage optimal allocation considering flexibility supply and demand balance[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2023, 39 (4): 1- 11.
|
| 17 |
朱佩雪, 郭倩, 李灵至, 等. 考虑主动配电网脆弱性的分布式储能配置[J/OL]. 电测与仪表: 1–8[2023-10-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20221019.1512.014.html.
|
|
ZHU Peixue, GUO Qian, LI Lingzhi, et al. Distributed energy storage configuration considering the vulnerability of active distribution network[J/OL]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation: 1–8[2023-10-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20221019.1512.014.html.
|
| 18 |
梅书凡, 檀勤良, 代美. 考虑风光出力季节性波动的储能容量配置[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (4): 51- 57.
|
|
MEI Shufan, TAN Qinliang, DAI Mei. Energy storage capacity configuration considering seasonal fluctuation of wind and photovoltaic output[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (4): 51- 57.
|